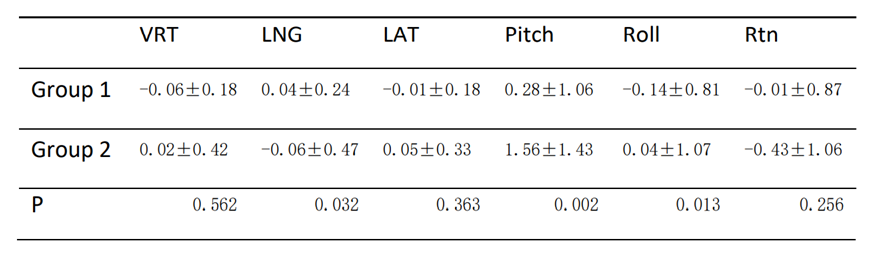
The result showed that the mean and standard deviations for Group 1 and 2 were (-0.06±0.18)cm, (0.04±
0.24)cm, (-0.01±0.18)cm, (-0.14±0.81)°, (0.28±1.06)°, (-0.01±0.87)° and (0.02±0.42)cm, (-0.06±
0.47)cm, (0.05±0.33)cm, (0.04±1.07)°, (1.56±1.43)°, (-0.43±1.06)° in vertical, lateral, longitudinal,
roll, pitch and rotation directions. Data analysis (Table 1) has shown statistically significant (p<0.05)
in longitudinal, roll and pitch directions. The maximum displacements for Group 1 and 2 were (-
0.58/0.58)cm, (-0.66/0.57)cm, (-0.56/0.69)cm, (-2.8/2.7)°, (-2.6/2.8)°, (-2.7/2.6)° and (-0.98/0.92)cm,
(-1.02/0.87)cm, (-0.86/0.91)cm, (-3.8/2.7)°, (-2.3/5.7)°, (-3.5/2.6)° in vertical, lateral, longitudinal,
roll, pitch and rotation directions. In terms of residual error rates, Group 1 had no patient with the
discrepancies that were more than 3° in all three rotational directions; while there were 9.6% and
3.9% of CBCT images were larger than 3° in pitch and roll direction in Group 2. The average
positioning time using surface-guided was (102.5±12.9)s.
Table 1: The mean and standard deviations of SGRT-based positioning (Group 1) method and skin marking-based positioning (Group 2) method.