Intrafraction prostate motion during CBCT-guided online adaptive radiotherapy
Lisanne Zwart,
The Netherlands
PO-1691
Abstract
Intrafraction prostate motion during CBCT-guided online adaptive radiotherapy
Authors: Lisanne Zwart1, Jens Jasper1,2, Elianne Vrieze1,2, Liselotte ten Asbroek1, Francisca Ong1, Siete Koch1, Erik van Dieren1
1Medisch Spectrum Twente, Radiotherapy, Enschede, The Netherlands; 2Hanzehogeschool Groningen, MIRT, Groningen, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Since
July 2020, CBCT-guided online adaptive radiotherapy (oART) is the standard
treatment for prostate cancer patients in our department. The applied CTV-PTV
margin has been the same as for image-guided radiotherapy. However, with
CBCT-guided oART the remaining uncertainty comes primarily from intrafraction
motion. The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate the
intrafraction prostate motion with respect to the currently used CTV-PTV
margin.
Material and Methods
Between
November 2020 and March 2021, 28 prostate cancer patients were clinically treated
using Ethos therapy (Varian Medical Systems, Palo Alto, CA, US) with a dose of 60
Gy in 20 fractions to the prostate and 54 or 60 Gy in 20 fractions to the
seminal vesicles for more advanced stages. For all patients, a 9- or 12-field
IMRT plan was created, applying a CTV-PTV margin of 7 mm in lateral (x) and
anterior-posterior (y) direction and 8 mm in superior-inferior (z) direction. For
all patients a CBCT was acquired at the start (CBCT1) and prior to treatment
delivery for position verification (CBCT2). On a weekly basis, a third CBCT was
acquired after treatment delivery (CBCT3). In this study, a virtual couch shift
was retrospectively applied based on the prostate motion determined from CBCT2
using the gold fiducials within the prostate. The remaining prostate motion
between CBCT2 and CBCT3 was determined based on a gold fiducial match and was
assumed to be the intrafraction prostate motion during oART delivery. Moreover,
the time between CBCT2 and CBCT3 was recorded.
Results
In
total, 124 fractions were evaluated. The mean time ± standard deviation between CBCT2 and CBCT3 was
4.2±0.6
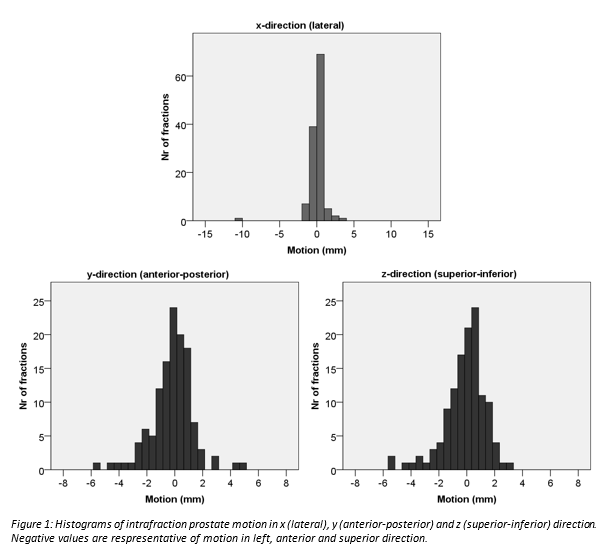
minutes (range: 3.2-7.1 minutes). Median intrafraction prostate motion ± standard deviation was 0.0±1.2 mm, 0.0±1.5 mm and 0.1±1.5 mm in x-, y- and z-direction, respectively.
Histograms of the intrafraction prostate motion in the different directions are
shown in Figure 1. The intrafraction prostate motion was within the currently
used CTV-PTV margin in 99.2%, 100% and 100% of fractions in x-, y- and
z-direction, respectively. The 95th percentile of the intrafraction
prostate motion was 1.7 mm in x-direction, 3.1 mm in y-direction and 3.2 mm in
z-direction.
Conclusion
The
measured intrafraction prostate motion during CBCT-guided oART delivery was
within the currently used CTV-PTV margin of 7 to 8 mm in ≥99% of fractions. When taking the 95th
percentile of the intrafraction prostate motion, the required population margin
is 2 mm in x-direction and 4 mm in y- and z-direction, suggesting that smaller
CTV-PTV margins can be safely implemented in clinical practice. Further
research is necessary to determine the intrafraction motion of the seminal
vesicles.