Planning feasibility study of three and single fraction Pancreas MR-Linac SBRT - Phase 1 trial setup
Kwun-Ye Chu,
United Kingdom
PO-1677
Abstract
Planning feasibility study of three and single fraction Pancreas MR-Linac SBRT - Phase 1 trial setup
Authors: Kwun-Ye Chu1,2, Suliana Teoh1, Tim Maughan1, Maxwell Robinson2, Joseph Drabble3, Tom Whyntie4, Somnath Mukherjee4,2
1MRC Oxford Institute for Radiation Oncology, University of Oxford, Oncology, Oxford, United Kingdom; 2Oxford University Hospitals NHS FT, Radiotherapy, Oxford, United Kingdom; 3GenesisCare Oxford, Radiotherapy, Oxford, United Kingdom; 4MRC Oxford Institute for Radiation Oncology, Oncology, Oxford, United Kingdom
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
To
assess whether three and single fraction Pancreas SBRT can be delivered within
defined PTV coverage targets and organs-at-risk (OAR) constraints on an
MR-Linac.
Material and Methods
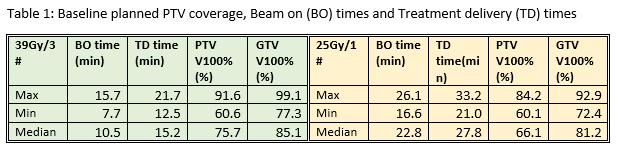
8 pancreas SABR patients were planned with 39Gy/3# (BED10=90)
and 25Gy/1# (BED10=88) with a minimum dose coverage objective of PTV V100%≥60%
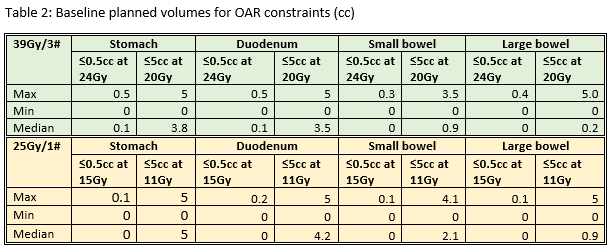
(CTV=GTV+2mm, PTV=CTV+3mm). OAR constraints were established from national
guidelines and published research (see tables). All plans were done on the ViewRay
MRIdian®
platform (ViewRay®, USA, 2021) using a TRUFI MRI with an accompanying
planning CT for electron density information. ~24 IMRT beams were arranged in a
pseudo-arc formation avoiding entrance through patients’ arms and couch sides. Beam
on time and treatment delivery (beam on time plus time for gantry/MLC
mechanical motion) time were noted. The impact of a daily non-adaptive workflow was assessed by rigid registration of the plans on the treatment
fraction MRIs. Assessment was done following an IGRT match and with GTV, PTV and
OARs re-contoured to determine the predicted dose if plans were delivered without
adaptation on each treatment day.
Results
All plans generated were able to meet the minimum dose coverage
objective and OAR constraints (see tables). The median PTV V100 coverage for
39Gy/3# and 25Gy/1# was 75.7% (60.6-91.6%) and 66.1 (60.1-84.2%) respectively.
The median treatment delivery times were 15.2min (12.5-21.7min) and 27.8min (21.0-33.2min)
for 39Gy/3# and 25Gy/1# respectively.
The predicted doses generated from the treatment fraction
MRIs showed potential for PTV under-coverage compared to the planned dose with OARs
doses exceeding tolerance, therefore daily adaptive recontouring and planning
was essential.
Conclusion
The study results support proceeding with a Phase 1 trial of
three and single fraction Pancreas SBRT as all dose coverage and OAR
constraints can be met, as well as all treatments can be delivered in a
reasonable timeframe. Given that the pancreas is adjacent to radiosensitive OARs
and that there is potential for exceeding dose constraints if the treatment is
delivered as originally planned, this supports the use of adaptive planning
prior to each treatment fraction to ensure that the treatment is delivered
safely. There is on-going work to show the dosimetric impact of a daily online adaptive workflow.