Automatic plan optimization in Italy: where we are and where we are going.
PO-1672
Abstract
Automatic plan optimization in Italy: where we are and where we are going.
Authors: Stefania Pallotta1,2, Livia Marrazzo3, Calusi Silvia4, Roberta Castriconi5, Claudio Fiorino5, Gianfranco Loi6, Christian Fiandra7
1University of Florence, Biomedical, Experimental and Clinical Sciences “Mario Serio”, Florence, Italy; 2AOU Careggi, Medical Physics , Florence, Italy; 3AOU Careggi , Medical Physics, Florence, Italy; 4University of Florence, Biomedical, Experimental and Clinical Sciences “Mario Serio”, Florence, Italy; 5San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Medical Physics, Milan, Italy; 6AOU Maggiore della Carità, Medical Physics, Novara, Italy; 7University of Turin, Department of Oncology, Turin, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
To improve the efficiency and quality of radiotherapy
plan optimization, automated planning (AP) systems were developed. Several
publications [1] report on time savings, increased efficiency, and standardization
of plans but the actual deployment of these systems is still unknown. This work aims to evaluate the diffusion of AP
in Italy and to analyze the perception of the medical physics community
involved in radiotherapy regarding the use of these new tools.
Material and Methods
Between February and April
2021 an online survey, using Google Forms, was created, and sent by e-mail to a
single medical physicist for each Italian radiotherapy centre. 175 physicists
were contacted. The survey consisted of
28 questions and was divided into three sections aimed at collecting
information on the participating centres, opinions on the use of AP and
experience in using AP. For some questions, more than one answer was allowed.
Results
125 of the centres
(71%) answered the survey. Among these, 48.8% have a TPS with some automatic
option but in only 32.8% of the centres, these systems are in clinical use.
Among the responding centres, the most used systems are Pinnacle (16.0%),
Raystation (8.8%) and Eclipse (4%) All
Raystation users make use of a genetic optimizer implemented through advanced
phyton scripting. At
the top of Fig. 1 is shown the percentage diffusion of different TPSs a), of
TPSs with AP b) and of TPSs with AP in clinical use c). At the bottom of Fig.1,
is shown the % of centres using AP in
varying percentages (less than 5%, between 5% and 10%, 10% and 20%,
20% and 50% and more than 50%) to plan the total amount of IMRT/VMAT
plans.
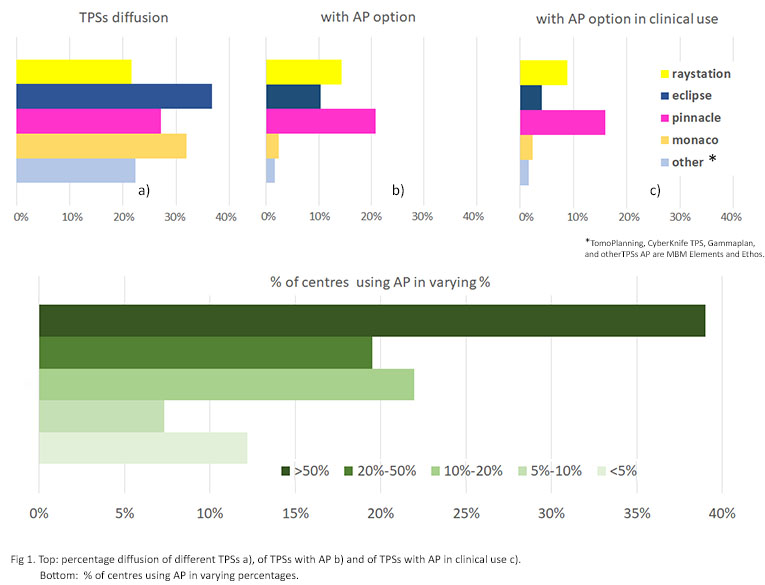
The total number of
centres using an automated approach in clinical practice will increase shortly
since 10.2% are in the validation phase. In addition, we have identified a
growing interest among those who do not currently own such systems. The most
frequently cited reason for the unavailability of automated options (32.8%) is
the lack of economic resources; 21.9% of responders stated that automated
system acquisition has a low priority with respect to other needs. The majority of
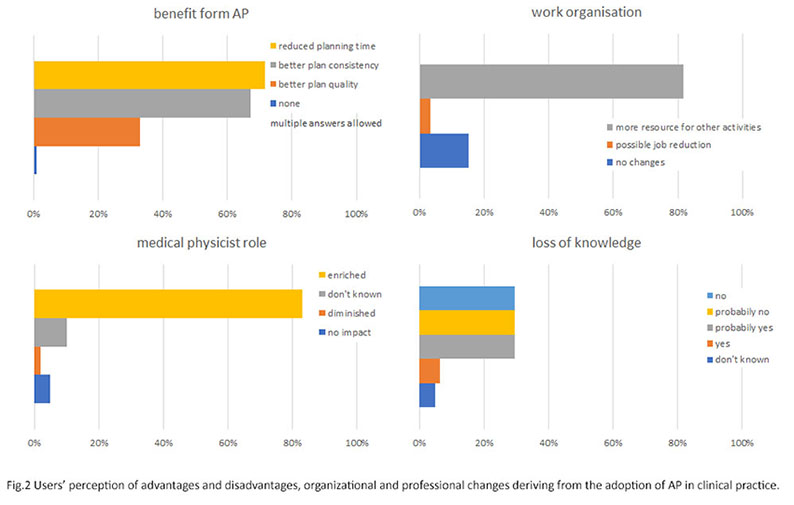
participants consider the use of automated techniques to be beneficial, while
only 1% do not see any advantage; 81% of respondents see the possibility of
enriching their professional role as a potential benefit, while 3% see
potential threats Fig.2.
Conclusion
The high percentage of responding centres
(71.4 %) demonstrates that automated planning is perceived as a relevant topic
for the community of Italian medical physicists. 48,8% of the responding
centres have an automatic planning solution although clinically used in only
32.8% of the cases. The vast majority of Italian medical physicists consider
automated planning techniques advantageous and approach them with a
predominantly positive attitude.
[1] Hussein M, et al. Br J Radiol
2018;91.