Evaluation of the dosimetric impact of autodelineation uncertainties in prostate radiotherapy.
Kevin Alty,
United Kingdom
PO-1663
Abstract
Evaluation of the dosimetric impact of autodelineation uncertainties in prostate radiotherapy.
Authors: Kevin Alty1, Daniel Marshall1, Andrew Bird1, Richard Powis1, Gareth Webster1
1Worcestershire Oncology Centre, Radiotherapy, Worcester, United Kingdom
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Several commercial products automatically delineate
radiotherapy planning structures, which could improve workflow efficiency. Evaluating
these algorithms for clinical use is challenging, with the dosimetric impact of
autodelineation uncertainties arguably of most interest. An efficient dosimetric
evaluation pipeline has been developed and tested in prostate planning.
Material and Methods
11 Prostate patients had the target volumes manually
outlined by the treating clinician1. OAR structures (MS) were
delineated by Mirada DLCExpert AI autocontouring system (DLC)2 and then modified manually (DS) by a
dosimetrist. An autoplanning script was then run on both structure sets,
producing a Mirada-only plan (MP) and a plan based on the modified structures
(DP). The dose distributions for both MP and the gold standard DP plans were
compared on the DS structures (MP-DS, DP-DS). Time savings due to Mirada were
quantified against a historic benchmark.
Results
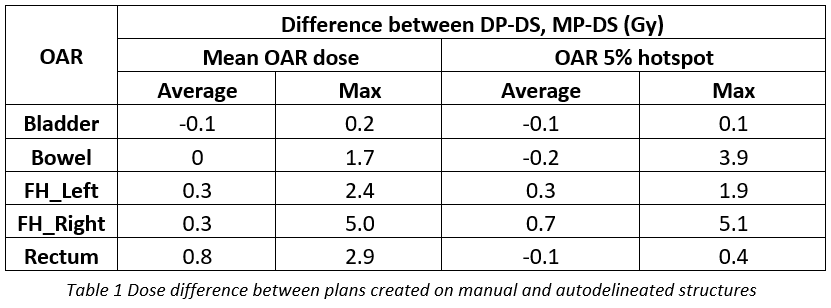
All MP-DS plans were clinically acceptable on all metrics
and following expert plan review. OAR dose differences are shown in table 1. Bladder
dose variations were small, femoral head variations were larger but well within
tolerances. Both the rectum and bowel showed larger variations, which disappeared
with small modifications to the sup extent of the structures. The average time to
modify the autodelineated contours was 6.5 minutes against a dosimetrist-only
benchmark average of 14 minutes.
Conclusion
Plans optimised using unedited autodelineated OAR structures
were found to be clinically acceptable when reported on gold standard outlines.
Reporting errors associated with autodelineated structures were small in most
cases but warrant further investigation in outlying cases. Production of DS
showed over 50% times savings against manual contour creation, with the results
of this study suggestive of further gains to be made through a reduction in the
modifications needed.
1RayStation
product version: RayStation 9B SP1, with
IronPython 2.7.
2Mirada product version:
Workflow Box 2.6 with DLCExpert AI autocontouring, Mirada Medical Ltd., Oxford,
United Kingdom