Hippocampus delineation by a neural network and CT-brain projections.
Anders Traberg Hansen ,
Denmark
PO-1650
Abstract
Hippocampus delineation by a neural network and CT-brain projections.
Authors: Anders Traberg Hansen1
1Århus University Hospital, Department of Oncology, Medical Physics, Aarhus , Denmark
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The aim is to demonstrate the ability of a neural network based on the
TensorFlow software to perform automatic delineation of the hippocampus based
only on lateral and frontal projections of the brain contour obtained from a
CT-scan.
Material and Methods
The computer used was a 64 bits Intel Core i5 desktop computer with
Python 3.8.3 and TensorFlow version 2.2.0 installed. The neural structure used
consisted of three stages. First three dense layers with a total of 3940
neurons. Then a reshaping of the data, and finally a transposed convolutional
layer that generated the output image. The data basis was the delineated brain
from CT-scans and the left hippocampus from MR-scans of 16 brain patients.
Several Python programs were designed to do the following three types of data
processing.
Training data
From the data basis the training data was created as a multitude of image
triplets consisting of two input images and one output image. These triplets were
made by rotating and longitudinally translating the 3D contours of the brain
and left hippocampus in a multitude of ways. And register frontal (x-z) and
lateral (y-z) projections of the brain and the corresponding transversal (x-y,
z=0) contours of the left hippocampus. The brain projections were pooled to 100
× 100
pixels, smoothed and contrast enhanced. The hippocampus contour was filled it
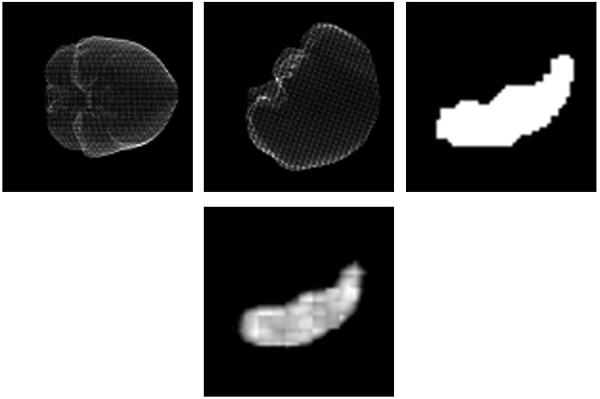
had a size of 56 × 56 pixels. (see figure 1, top row). The final number of training image
triplets were 83871.
Training
The neural network was trained (fitted) to the relation between the input
brain projections and the output hippocampus contour. The network was fitted
for 2000 iterations which took 80 seconds each, close to two days in total.
Prediction
The trained neural network can predict a 2D hippocampus contour from two input
projections (see figure 1, bottom). For an unknown patient several predictions
can be joined to create a 3D hippocampus contour. This contour can be written
in DICOM to be exported to the Eclipse treatment planning system.
Results
Five brain patients unknown to the neural network were used for
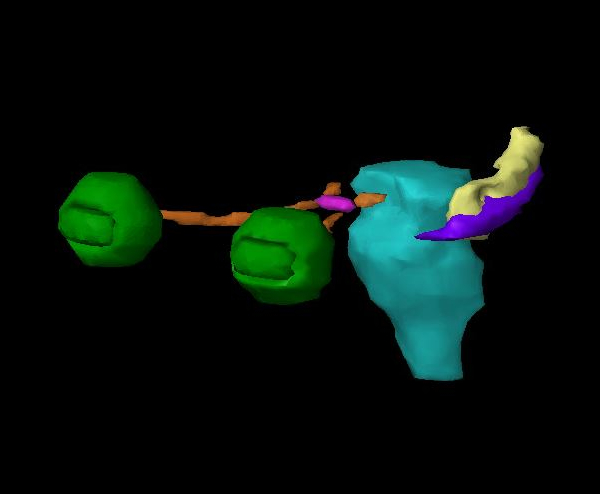
evaluation. The predictions of the left hippocampus were imported to the
Eclipse treatment planning system (figure 2). The dice coefficients between the
humanly delineated hippocampus (purple) and the machine delineated hippocampus (yellow) were found
to be in the range from 0.15 to 0.41. This could be clinically relevant where
only an approximate location of the hippocampus is needed.
Conclusion
It is found that a simple neural network based on the TensorFlow software
package is able to predict the position and shape of the hippocampus fairly
well based only on the brain contour from a CT-scan. This find is useful in
itself because a MR-scan can be omitted, but also promising for future
developments of more sophisticated neural networks for automatic delineation.