Evaluation of synthetic-CT generated from prostate MRI (0.35T) with a 2D+ Pix2Pix method
Jean-Claude Nunes,
France
PO-1611
Abstract
Evaluation of synthetic-CT generated from prostate MRI (0.35T) with a 2D+ Pix2Pix method
Authors: Jean-Claude Nunes1,1, Smaïn Fettem1, Safaa Tahri1, Lhassa Macke1, Hilda Chourak2, Anaïs Barateau1, Caroline Lafond1, Renaud de Crevoisier1, Igor Bessieres3, Louis Marage3, Oscar Acosta1
1Université de Rennes 1, LTSI (Laboratoire du Traitement du Signal et de l'Image), INSERM UMR 1099, CLCC Eugène Marquis , Rennes, France; 2Université de Rennes 1, LTSI (Laboratoire du Traitement du Signal et de l'Image), INSERM UMR 1099, CLCC Eugène Marquis, Rennes, France; 3Centre Georges-François Leclerc (CGFL), Departement of Medical Physics, Dijon, France
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
In the
context of MR-only radiotherapy workflow, several deep learning methods (DLMs)
have been developed for synthetic-CT (sCT) generation from MR images. The Pix2Pix
DLM (a conditional generative adversarial network [cGAN]) can be applied on the
3 MRI views (transverse, sagittal and coronal) and not only on the axial view.
The aim of this study was to compare the sCTs resulting from the 2D+ Pix2Pix model
(in the 3 views) and the 2D Pix2Pix model (axial view) for prostate MRI-only
radiotherapy.
Material and Methods
Prostate CT and MR images were acquired in treatment position for 39
patients. MR acquisitions, using T2/T1-weighted TrueFISP sequences, were
performed with an MRI-linac device (MRIdian, Viewray, 0.35T). 2D+ method
consists of generating 3 sCTs (according to each view) per patient, and
combined in one sCT by using the median voxel value. sCTs generated by the 2D Pix2Pix
model (axial view) were compared to sCTs generated with the 2D+ Pix2Pix model. For
both of these methods, the perceptual loss function, a ResNet 9 blocks
generator, a PatchGAN discriminator, and Adam optimizer were used. The evaluation
was performed on a 5-fold cross validation using 30 patient images for training
and 9. Finally, both sCT were compared to the original CT from a voxel-wise
comparison with the mean absolute error (MAE) in Hounsfield units (HU), mean
absolute percentage error (MAPE)
in % , and peak signal to
noise ratio (PSNR) in dB. The Wilcoxon test was used to compare the results
obtained with the 2D+ model to those obtained with the 2D model. Significant
differences were considered for
p-value<0.05.
Results
Table 1
presents the results of MAE, MAPE and PSNR for the two methods. For the body
and the bones, significantly lower MAE and MAPE results were found with the 2D+
Pix2Pix model, compared to the 2D Pix2Pix model. For the body and the bones, significantly higher PSNR
results were found with the 2D+ Pix2Pix model,
compared to the 2D Pix2Pix model.
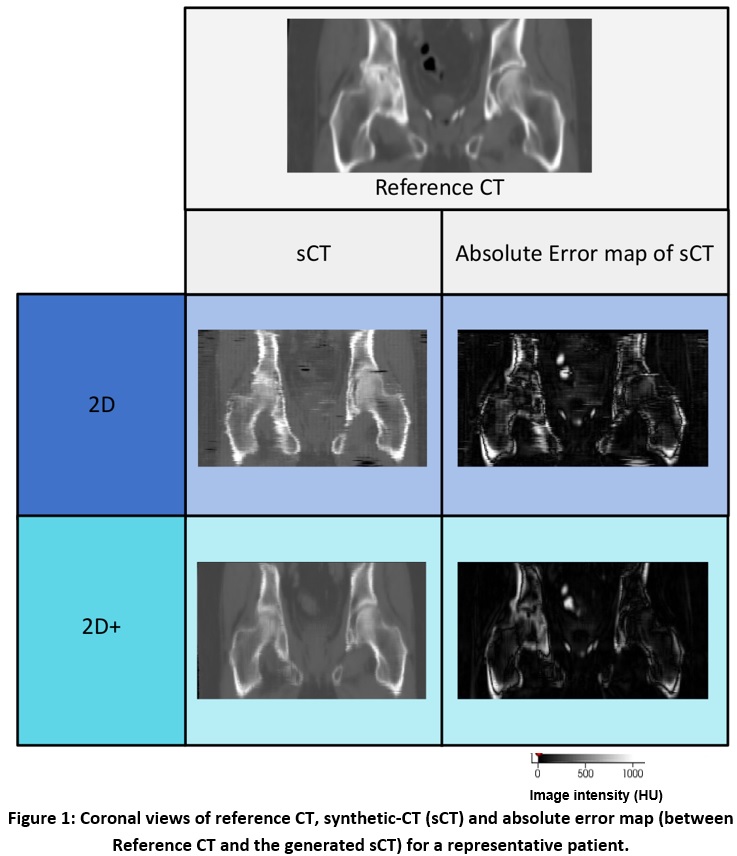
sCTs generated from 2D+ Pix2Pix model were less impacted by inter-slices
artefacts (Figure 1) than sCTs generated by 2D Pix2Pix model.
|
|
MAE (HU)
|
MAPE (%)
|
PSNR (dB)
|
|
|
Body
|
Bones
|
Body
|
Bones
|
Body
|
Bones
|
|
|
|
2D Pix2Pix
|
34.6 ± 7.1
|
136.8 ± 20.7
|
1.2 ± 0.3
|
0.5 ± 0.1
|
29.8 ± 1.6
|
18.7 ± 1.2
|
|
|
|
2D+ Pix2Pix
|
29.2 ± 5.0*
|
121.0 ± 20.4*
|
1.1 ± 0.2*
|
0.4 ± 0.1*
|
31.0 ± 1.6*
|
19.1 ± 1.4*
|
|
|
Table 1: MAE, ME and PSNR (mean
± standard deviation) results in the body
and the bones for 39 patients
*Significant differences were considered at
p-value<0.05.
Conclusion
In
order to generate sCT from prostate MRI, the 2D+ Pix2Pix model allows to
generate sCT with less image uncertainties than the 2D Pix2Pix model. The next
step will be a dosimetric evaluation of sCTs generated by the 2D+ Pix2Pix model.