Patient specific QA for the HyperArc technique using radiochromic films
PO-1579
Abstract
Patient specific QA for the HyperArc technique using radiochromic films
Authors: Maja Rumak1,2, Marta Kruszyna-Mochalska1,2, Kinga Graczyk2, Agnieszka Skrobała3,2, Weronika Kijeska2, Hubert Szweda4, Julian Malicki1,2
1University of Medical Sciences, Electroradiology Department, Poznan, Poland; 2Greater Poland Cancer Centre, Medical Physics Department, Poznan, Poland; 3University of Medical Sciences, Electroradiology Department, Poznań, Poland; 4Greater Poland Cancer Centre , Medical Physics Department, Poznan, Poland
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
HyperArc is
a relatively new VMAT non-coplanar technique that is used for stereotactic
radiotherapy in brain metastasis treatment. Due to the challenges associated
with high doses per fraction equal 21Gy and small-field dosimetry, it is
extremely important to select an adequate radiation detector to perform
dosimetric verification of treatment plan. The main aim was to consider film
dosimetry (EBT-XD) as a verification method for and patient specific QA for HyperArc treatment
plans using film dosimetry.
Material and Methods
A group of
15 patients with one, two or three intracranial lesions were selected.
Gafchromic EBT-XD (Ashland, USA) dosimetry films were used to perform patient
specific QA for multimetastasis lesions with a single isocenter for the
HyperArc (HA) stereotactic irradiation technique (Varian Medical Systems, USA).
In order to properly prepare, detectors were calibrated (dose range 0-40 Gy) and
characterized in 6 MV FFF beam. Radiochromic films were placed in a PMMA
phantom, in coronal plane, in the middle of each lession. As the reference
detector, the Semiflex ionization chamber (PTW, Freiburg), was selected. The
films were scanned on the Epson perfection v850 PRO flatbed scanner (Seiko
Epson Corporation, Japan) with 72 dpi, single scan, in red-green-blue (rbg)
mode with no color or sharpness correction and consistent orientation and
analyzed using gamma evaluation criteria (2%/2mm, local normalization, threshold
30%, gamma passing rates – GPR – tolerance limits> 90%, action limits>85%)
in the VeriSoft program (PTW, Freiburg).
Results
Gafchromic EBT-XD films do not show significant
dose rate dependence for 6 FFF MV beam and the obtained calibration curve for
the red channel was used for the analysis. The patient specific QA results were
shown in the Figure 1. Using dosimetry films, the most favorable results (GPR)
were obtained for patients with one intracranial lesion (mean 98,84%, standard deviation 1,15%), three
lesions (mean 98,04%, standard deviation 2,12%) and two lesions (mean 94,95%,
standard deviation 4,99%) for the 2%/2mm acceptance criteria.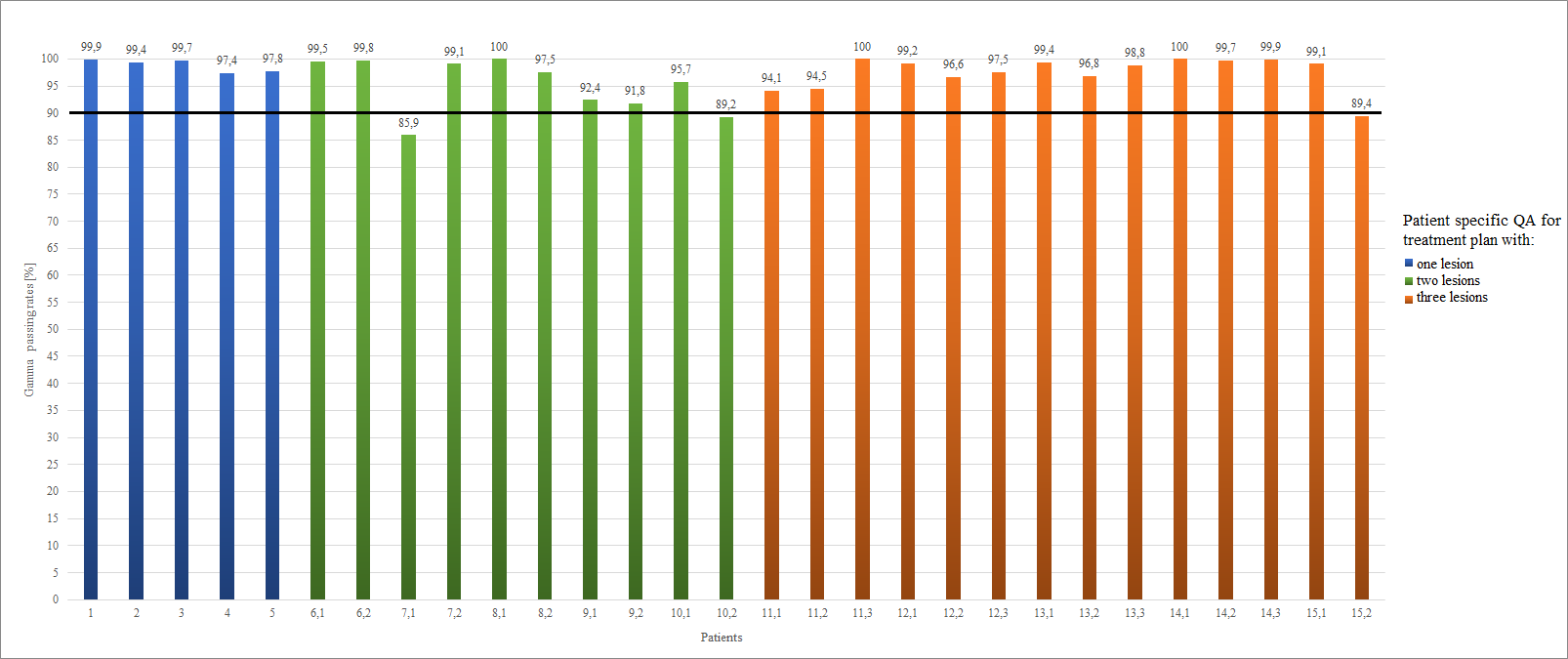
Figure 1.
Summary of result (GPS) for gamma evaluation method for patient specific QA for
the HyperArc technique using radiochromic films. The black line shows the
tolerance limit > 90%.
Conclusion
As a result of performed verification of the
feasibility of stereotactic treatment plans, acceptable results were obtained
for selected dosimetric method according to the adopted analysis criteria. After
proper characterization and calibration Gafchromic EBT-XD films, are a suitable
tool for HyperArc verification method.