An investigation of gamma parameters for VMAT plans treating multiple metastases
PO-1560
Abstract
An investigation of gamma parameters for VMAT plans treating multiple metastases
Authors: Lotte Stubkjaer Fog1, Frank Gagliardi2
1The Alfred Hospital, Radiation oncology, Melbourne, Australia; 2The Alfred Hospital, Radiation Oncology, Melbourne, Australia
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The simultaneous irradiation of multiple
metastases represent a particular challenge since the radiation fields may be
large but the positional resolution required is high. In this work, we
investigate patient-specific quality
assurance measurements (PSQAMs ) for
such plans with several different measurement systems, and investigate pass
rates and failure modes for several different criteria.
Material and Methods
Ten patients treated with volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for multiple metastases
(MMs) or hippocampus sparing whole brain radiotherapy (HSWBRT) with VMAT at our
clinic were included. Each plan was calculated using Eclipse™ (Varian, Palo Alto), Acuros v 13.6 with a calculation grid
size of 1.25 mm. PSQAM were carried out
using Octavius/
Verisoft v 7. (O/V, PTW) and Portal Dosimetry (PD, Varian). Additionally, for
one particularly complex case, film measurements were carried out (EBT3 film, Epsom
V850 Pro scanner) in an antropomorphic phantom. Gamma analysis was carried out
using dose difference/distance to agreement of 3%3mm, 3%2mm, 3%1mm and 5%1mm.
The failure modes were recorded.
Results
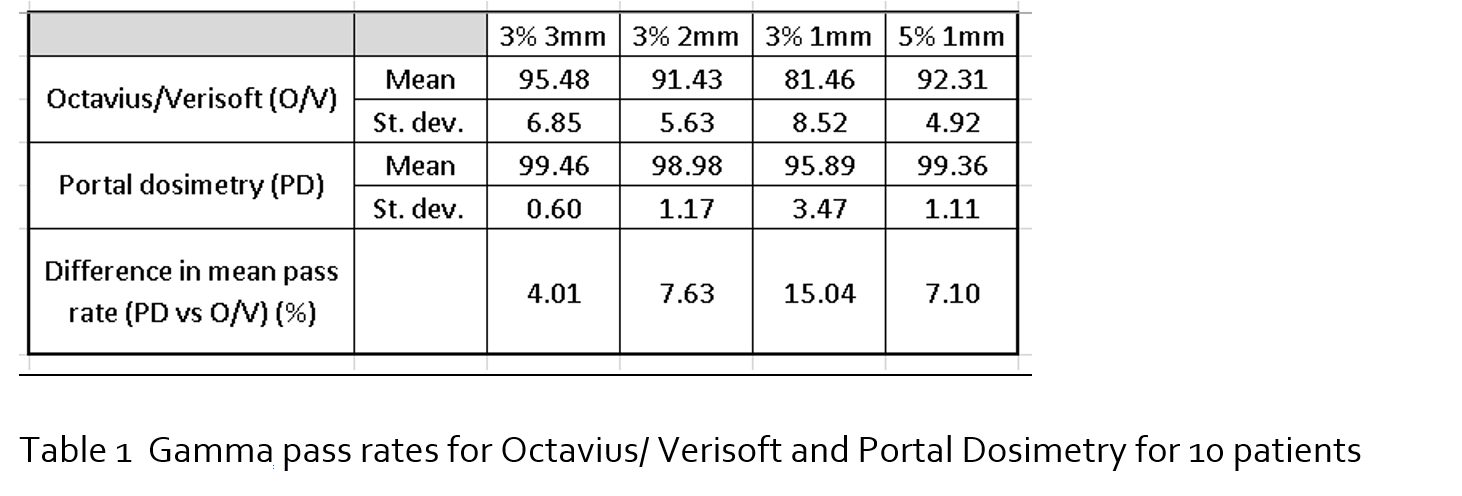
The pass rates were 4-15% greater for PD than for O/V,
with the difference being greatest for the analyses with finer spatial resolution,
and the standard deviation was greater (table 1).
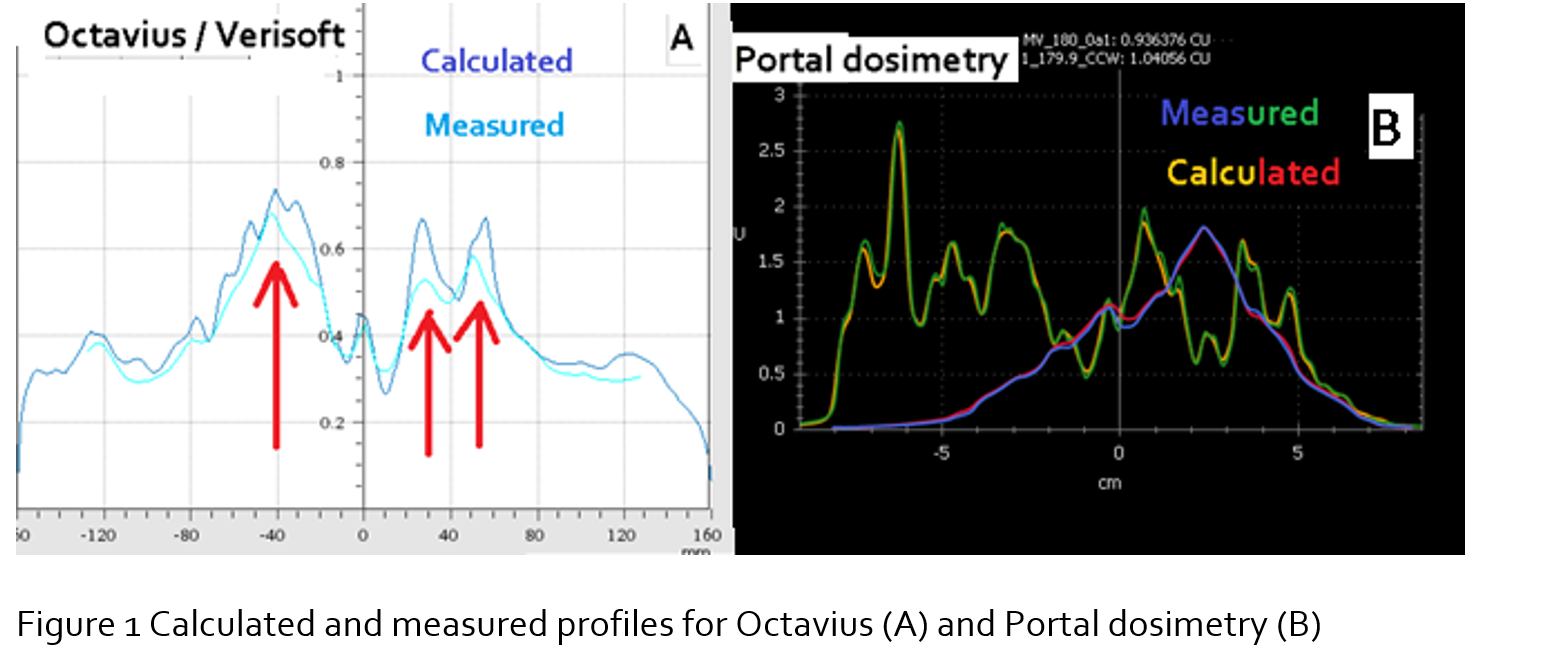
The measured and calculated profiles agreed very well in
general with portal dosimetry (fig 1B) while for Octavius, the measured
profiles in general were less modulated than the calculated (1A, red arrows).
The doses measured with film were smaller than the
calculated doses by up to 15%, and this difference varied throughout the
phantom.
Conclusion
The patient specific quality assurance systems indicate quite
different trends, with the Octavius measurements showing lower pass rates and less
modulation than the calculated dose distributions. Further work with high
resolution detectors is required to fully explore the accuracy of the delivered
doses for patients with multiple metastases.