Synthetic patient-specific whole-body CT for the calculation of peripheral dose during radiotherapy
Beatriz Sanchez Nieto,
Chile
PO-1559
Abstract
Synthetic patient-specific whole-body CT for the calculation of peripheral dose during radiotherapy
Authors: Isidora Muñoz1, Beatriz Sánchez-Nieto1, Ignacio Espinoza1
1Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Instituto de Física, Santiago, Chile
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
An accurate assessment
of peripheral dose is necessary to estimate the risk of second cancer after
radiotherapy. The calculation of dose to out-of-field organs, no matter how
distant they are from the Irradiated Volume (IV), requires the knowledge of
their shape and positions. Nevertheless, typical planning CTs (PCT) only
consider a few cm superior and inferior to the IV. And yet, taking a whole-body
CT of each patient is also not justifiable because of the extra whole-body
exposure. This work aimed to use the already available PCT to generate a
synthetic whole-body CT, which should approximately represent the unique
geometry of each treated patient.
Material and Methods
An interactive
computer program, developed in MATLAB, takes the PCT as an input and transforms
the ICRP110 adult reference computational phantom according to a rigid
registration of both images. The user visually defines a subregion of the
computational phantom that corresponds to the part of the patient included in
the PCT. Several image pre-processing steps were tested to segment the bones on
both images before the registration process. Finally, the best methods (the
ones generating the highest Sørensen-Dice coefficients) segmentation/registration
methodologies were selected and implemented in the code. The methodology was
then validated using a published database (New Mexico Decedent Image Database)
containing whole-body CT images.
Results
A software termed IS2aR (Interactive
Software for Image Segmentation and Registration) was created. It allows
for registration of the patient’s PCT with the ICRP110 phantom. Figure 1 presents a screenshot of the program graphical
interface. The results in a chest IV are shown in figure 2.
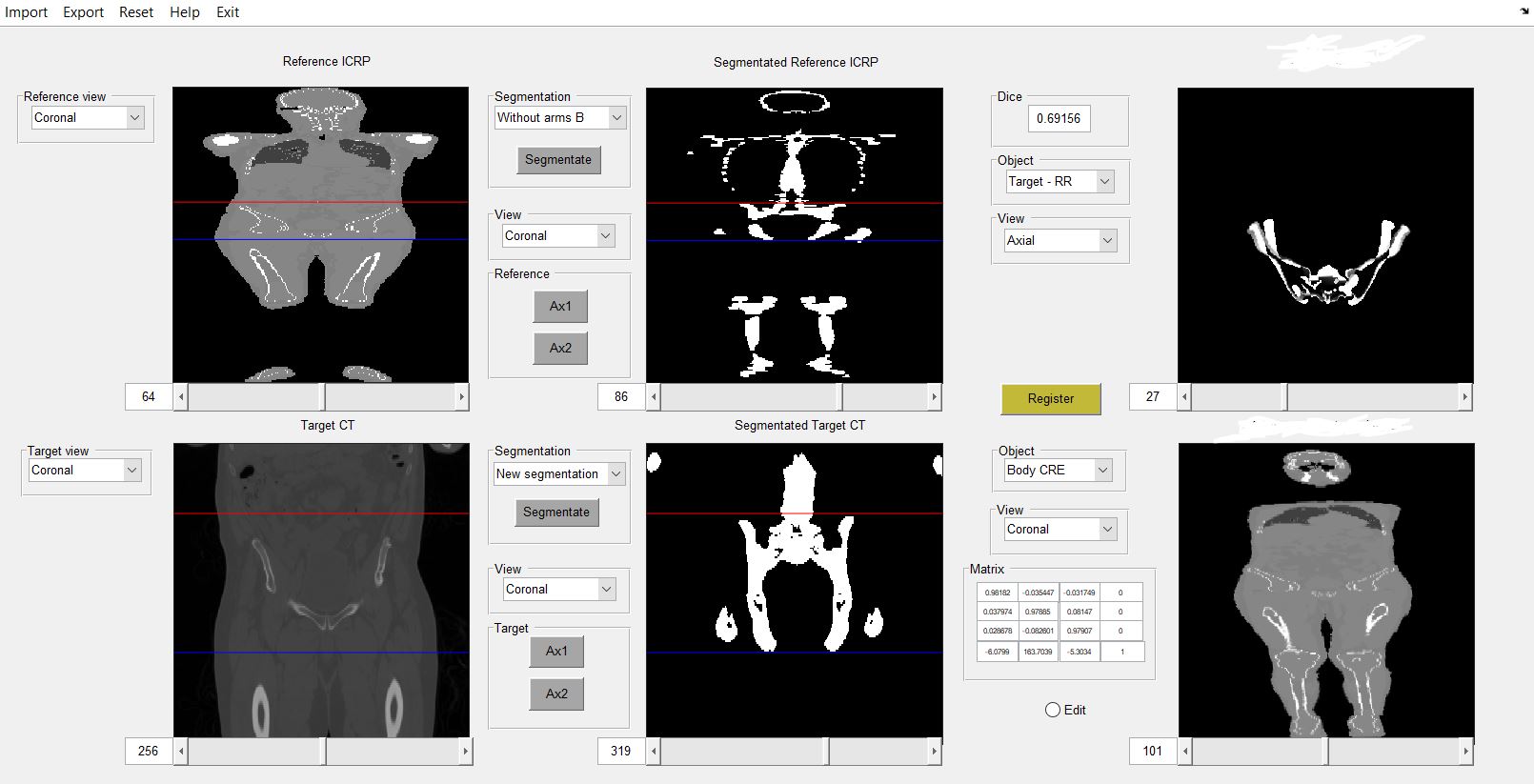
Figure 1 shows the interface for a pelvis case: patient's
CT and ICRP110 (left column), their respective bone segmentations (center
column), and the synthetic whole-body CT obtained by
registering the subregions, together with their Sørensen-Dice index and transformation matrix
(right column).
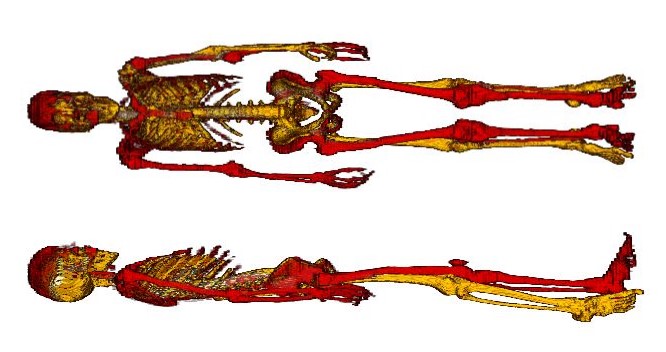
Figure 2 shows the validation in a coronal and
sagittal view of the program, with the overlay of the whole-body CT (yellow) and
the synthetic whole-body CT (red) generated by abdomen registration.
Conclusion
A user-friendly
computational tool to generate synthetic patient-specific whole-body CTs was
developed. It may be used, for example, for the accurate determination of
peripheral dose during radiotherapy using our Periphocal 3D software (see abstract E22-0473). This is an important step towards personalized treatment planning
that takes into consideration the probability of second cancer induction.
Acknowledgements:
Fondecyt
N1181133
The Free Access
Decedent Database funded by the National Institute of Justice grant
number 2016-DN-BX-0144.