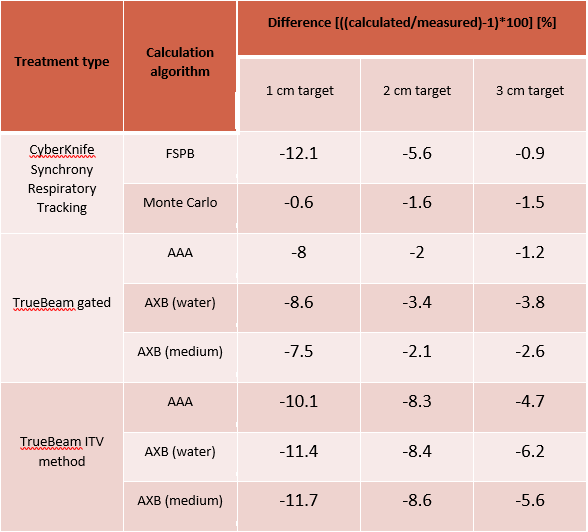
In the case of CyberKnife treatments, the differences
between the calculated and measured doses for 1 cm, 2 cm and 3 cm targets were
-12.1%. -5.6% and -0.9% with FSPB and -0.6%, -1.6%, -1.5% with Monte Carlo,
respectively. In the case of gated TrueBeam treatments the differences for 1
cm, 2 cm and 3 cm targets were -8%, -2%, -1.2% with AAA, -8.6%, -3.4%, -3.8% with
AXB dose to water, and -7.5%, -2.1%, -2.6% with AXB dose to medium,
respectively. In the case of ITV method treatments on the TrueBeam, the
differences for 1 cm, 2 cm and 3 cm targets were -10.1%, -8.3%, -4.7% with AAA,
-11.4%, -8.4%, -6.2% with AXB dose to water, and -11.7%, -8.6%, -5.6% with AXB dose
to medium, respectively. For gated treatments better results could be achieved
if the ionization chamber was present in the insert on the gated planning CT. With ITV method too many artefacts were generated
due to the presence of high density parts of the ionization chamber. To
increase the accuracy of calculations for small targets in the future, we plan
to use a homogeneous insert to replace the ionization chamber during planning
CT scans.