SBRT Patient Specific QA: Adaptive dose accumulation from deformable CBCT image registration
Steffen Borup Vestergaard,
Denmark
PO-1490
Abstract
SBRT Patient Specific QA: Adaptive dose accumulation from deformable CBCT image registration
Authors: Steffen Borup Vestergaard1, Martin Skovmos Nielsen2,3, Rasmus Kjeldsen1
1Aalborg University Hospital, Clinical Surgery and Cancer Treatment, Aalborg, Denmark; 2Aalborg University Hospital, Clinical Surgery and Cancer Treatment, Aalbrog, Denmark; 3Aalborg University, Clinical Medicine, Aalborg, Denmark
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Daily image guided radiotherapy does not necessarily
handle anatomical changes concerning organs at risk (OAR). Thus, dose to the OAR
may be a limiting factor for stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) as the
dose may exceed tolerance levels. The aim is to justify a patient specific dose
plan Quality Assurance (QA) for individual treatment sessions.
Material and Methods
Patient material consist of 24 patients
referred for lung SBRT (3 x 22.5 Gy). A CBCT acquired prior at each treatment
fraction, are matched trough a workflow starting with a bone match follow by a
soft tissue (tumor) match (Online-match). As an offline strategy a solitary
bony match is performed, leading to strategies with one starting from a bone
match and the other from the tumor match. the three CBCTs are deformable
registered to the planning CT (Velocity 4.1, Varian Medical Systems) and a ‘plan-of-the-day’
is calculated on the generated artificial-CT (aCT). The calculated dose
distribution is deformed back to the original CT, then subtracted from the
planed dose distribution. The dose difference for the OARs are examined. Due to
OAR dose constrains defined by maximum values, only the 200 voxels (0.4 cm³) in
an OAR (OAR200) receiving the larges additional doses are included.
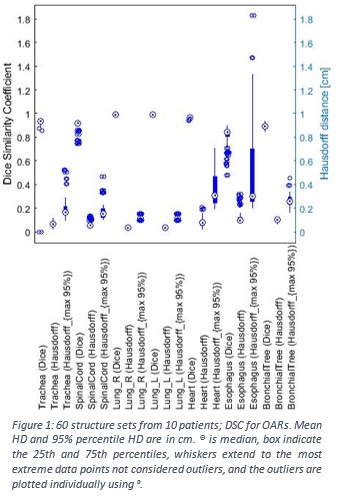
A total of 60 structure sets (10 patients,
three CBCT and two deformations) are examined for correlation between the
deform-registered and radiographer contoured OAR on each aCT. Dice-Similarity
coefficient (DSC) and Hausdorff distance (HD) are calculated, in order to ensure the quality of the deformable
registrations.
Results
The association between the deform-registered and radiographer contoured
structures (fig. 1) shows mean DSC ranging [0.92; 0.98] and the mean HD ranging
[0.06; 0.10] cm. The 95% percentile HD ranging from [0.12; 0.38] cm, with
deviations primarily from the esophagus and heart due to broad distributions.
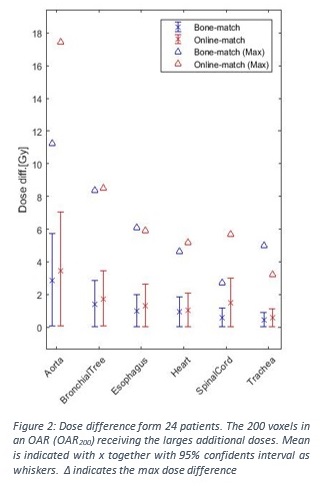
The added mean dose to OAR200 (fig. 2) ranging from 0.5
Gy for the trachea and up to 5 Gy for the aorta. The maximum dose difference
for a single OARs is 18 Gy for the aorta. When comparing OAR200
dose difference for the two match strategies it is see that on
average OAR200 receive more [0.1-1.1 Gy] with
Online-match then with Bone-match.
Conclusion
Patient specific dose plan QA shows in general
good agreement within the deform-registered structures and radiographer
contoured structures. The rather large HD for some regions of structures may be
explained by variation in inter radiographer variations. However, large dose
difference in some OAR (aorta and bronchial tree), indicates that inter
fractional patient specific QA may be required to avoid exceeding dose
constrains.