IMRT of the prostate following focal treatment: Analysis of Toxicity.
Alfonso Valcárcel Díaz,
Spain
PO-1426
Abstract
IMRT of the prostate following focal treatment: Analysis of Toxicity.
Authors: Alfonso Valcárcel Díaz1
1Puerta de Hierro University Hospital, Radiation Oncology, Madrid, Spain
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Cryotherapy (CRYO), irreversible electroporation
(IRE), or high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), are different treatment options for early-stage
adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Failures following this procedure are not
infrequently and little data exists regarding salvage radiotherapy. We
summarize our experience.
Material and Methods
All consecutive ten cases of salvage radiotherapy following
cryoablation, IRE or HIFU failure for cancer prostate from 2011 to 2021 were
analyzed.Patients were treated with IMRT and received a mean dose of 72.2
Gy (range, 70-76 Gy) to the prostate and seminal vesicles alone. PSA failure
was defined by Phoenix consensus definition. Acute and late GI and GU toxicity were graded according to the
CTCAE v5 scale.
Results
Patients characteristics are shown in table 1. Mean pre-focal
treatment PSA was 9.03 ng/ml (4.7-17). Mean PSA prior to irradiation was 10.61
ng/ml (2.2-26.4). Median interval to RT was 25.95 months. Median follow up was 30.63 months. Biochemical control was
achieved in 8 of the 10 patients and one developed nodal relapse. All of them
are alive at last follow up. Median time to highest GU and GI toxicity was 4,36 and 11.5 months
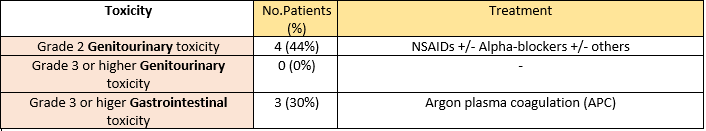
respectively. The acute and highest late toxicity is summarized in table2.
Three patients experienced late grade 3 rectal bleeding needing Argon laser
treatment (previous
diabetes and hypertension in two of them). Only one patient who did not have erectile dysfunction previously,
developed it after radiation therapy.
Table 1: Patients characteristics.
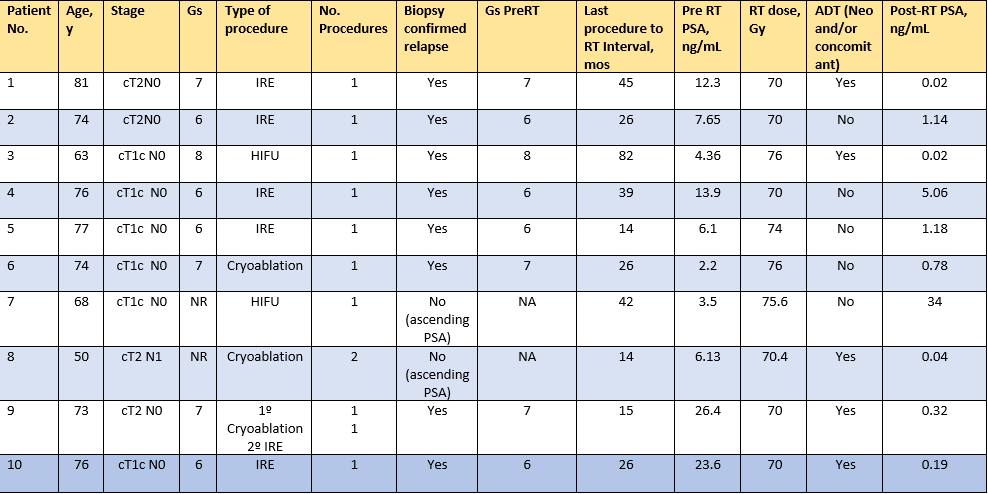
Table 2: Acute and highest late toxicity.
Conclusion
In our experience a high dose IMRT
irradiation following CRYO, IRE or HIFU is well tolerated with moderate acute and late toxicity.