Robotic stereotactic body radiotherapy for prostate cancer : an initial monoistitutional experience.
Ariadna Sanchez Galvan,
Italy
PO-1372
Abstract
Robotic stereotactic body radiotherapy for prostate cancer : an initial monoistitutional experience.
Authors: Ariadna Sanchez Galvan1, Andrei Fodor1, Claudio Fiorino2, Paola Mangilli2, Chiara Lucrezia Deantoni1, Cesare Cozzarini1, Roberta Tummineri1, Simone Baroni1, Stefano Lorenzo Villa1, Giuseppina Mandurino1, Pietro Pacifico1, Stefano Arcangeli3, Nadia Gisella Di Muzio4,5
1IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Radiotherapy, Milan, Italy; 2IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Medical Physics, Milan, Italy; 3University of Milano-Bicocca, Radiotherapy, Monza, Italy; 4 IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Radiotherapy, Milan, Italy; 5Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, Radiotherapy, Milan, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Ultrahyprofractionation (UHF, SBRT) is a treatment option for patients with prostate cancer (PCa), with clinical and health-related quality-of-life (QOL) outcomes comparable to standard fractionation. The goal of this analysis is to evaluate outcomes and toxicity after an initial experience with robotic SBRT (CyberKnife, Accuray, Sunnyvale, CA, USA).
Material and Methods
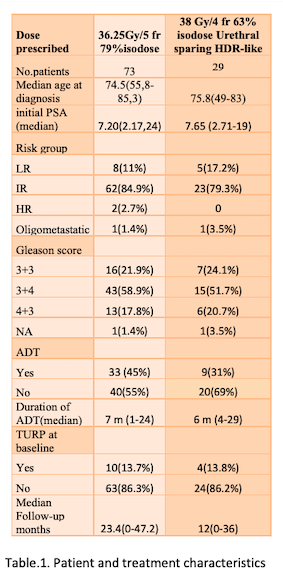
Between 10/2017-05/2021 102 patients with PCa were treated using a robotic SBRT. For pts characteristics see table 1. Fiducial markers were implanted into the prostate in all pts. In 52% of pts a steroid therapy and/or alpha-lytics was prescribed to prevent side effects. EORTC Quality of Life Questionnaire - Prostate Cancer Module (EORTC QLQ-PR25) and International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) toxicity data were recorded in pts who agreed to respond. Toxicity was scored in accordance with CTCAE v 5.0. Biochemical failure was assessed using the nadir + 2 ng/ml definition.
Results
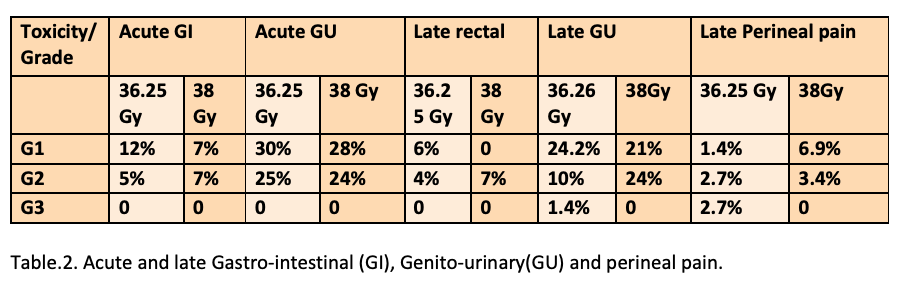
Median follow-up was 22 (3-47) months. For acute and late toxicities see table 2. One (1.4%) late G3 GU toxicity occurred in a patient treated with 36.25 Gy (transurethral incision). Median post-SBRT PSA level was 0.370 (0,001-98.92) ng/ml. At the last follow up 3 pts died due to a non-cancer related cause, 4 pts had a biochemical failure with PSMA/Choline-PET positive progression: 3 treated to 36.25 Gy and 1 treated to 38 Gy. Two-year bRFS rates were 94.8% and 88,9% for pts treated with 36.25Gy and 38Gy, respectively (p= 0.6). OS rate was 96.7% at 2 years. DFS was 94.8% and 88.9%, respectively (p=0.6).
Conclusion
Urethral sparing technique allowed dose escalation (from EQD2 91 Gy to EQD2 ≥ 120 Gy with α/β 1.5) without increasing G3 toxicity and with not inferior bRFS despite less ADT prescription. Longer follow-up is needed to confirm these results.