Detection rate of 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT from a prospective study: PSICHE trial (NCT05022914)
PO-1363
Abstract
Detection rate of 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT from a prospective study: PSICHE trial (NCT05022914)
Authors: Giulio Francolini1, Vanessa Di Cataldo2, Beatrice Detti1, Andrea Allegra3, Luca Burchini3, Lucia Pia Ciccone3, Cecilia Cerbai3, Chiara Mattioli3, Giulio Frosini3, Barbara Guerrieri3, Michele Aquilano3, Viola Salvestrini3, Arturo Chiti4, Martina Sollini4, Gabriele Simontacchi1, Isacco Desideri3, Lorenzo Livi5
1Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi, Radiation Oncology Unit Oncology Department, Florence, Italy; 2Istituto Fiorentino di Cura e Assistenza (IFCA), Radiation Oncology CyberKnife Center, Florence, Italy; 3University of Florence, Department of Biomedical, Experimental and Clinical Sciences "Mario Serio", Florence, Italy; 4Department of Biomedical Sciences - Humanitas University, Department of Nuclear Medicine - IRCCS Humanitas Research Hospital, Milan, Italy; 5University of Florence, Department of Biomedical, Experimental and Clinical Sciences "Mario Serio", Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi, Radiation Oncology Unit Oncology Department, Florence, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Salvage radiotherapy (SRT) is the main approach for early biochemical relapse (BR) after radical prostatectomy (RP). However, 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT implementation in this setting prompted significant changes in current management of patients, leading to the development of imaging-guided approaches. In our department, a prospective study aimed to explore the outcomes after 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT restaging and pre-defined treatment is currently running. Here we present early results of the first cohort enrolled, focusing on 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT detection rate and following approach.
Material and Methods
PSICHE (NCT05022914) is a prospective observational multicenter study including patients treated with RP +/- postoperative prostate bed radiotherapy, affected by BR (defined as PSA >0.2 ng/ml) with a PSA at recurrence <1 ng/ml. Patients are staged with centralized 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT and treated with a pre-defined approach based on 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT findings. Briefly, patients with negative 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT or positive findings within prostate bed are treated with prostate bed RT (or observation if postoperative RT already administered), pelvic nodal recurrence (defined as nodal disease <2 cm under aortic bifurcation) and oligometastatic disease (defined as defined as ≤3 non visceral metastatic lesions, according to Association of Radiotherapy and Clinical Oncology definition) are treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) to all positive sites of disease. Non oligometastatic disease (>3 lesions or visceral metastases) is treated with androgen deprivation therapy +/- other systemic therapies available for metastatic hormone sensitive prostate cancer, at physician discretion. All doses and fractionations allowed are pre-specified. Complete protocol details are available on clinicaltrials.gov .
Results
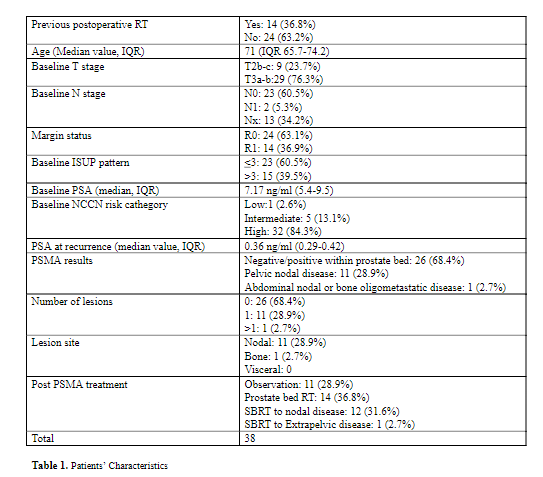
Enrollment started on 19/03/2021. Up to date, 38 patients have been enrolled (Table 1). Median PSA triggering PSMA re-staging was 0.36 ng/ml. Overall, PSMA results were negative/positive in prostate bed in 26 patients (68.4%), while pelvic nodal or extrapelvic metastatic disease was detected in 11 (28.9%) and 1 (2.7%) patients, respectively. After re-staging, 14 patients (36.8%) had prostate bed RT, 12 (31.6%) underwent SBRT on pelvic nodal relapse and 1 patient (2.7%) was treated with SBRT to extrapelvic disease. 11 patients with negative staging previously received prostate bed RT, and underwent observation only after re-staging. No significant impact of PSA at recurrence or time to relapse (defined as time between surgery and BR) was detected on PSMA PET/CT detection rate (p=0.1 and p=0.43, respectively). ISUP ≤ or > 3 and D’amico risk category (low/intermediate vs high) had no influence or PSMA detection rate (p=0.36 and p=0.52, respectively).
Conclusion
Early results from PSICHE trial showed that macroscopic disease is detected in a significant percentage of patients affected by early BR. PSMA staging is necessary in this setting to avoid undertreatment and allow tailored treatment.