Prognostic value of HPV in a cohort of patients affected by adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix
PO-1352
Abstract
Prognostic value of HPV in a cohort of patients affected by adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix
Authors: Giulia Malfatti1, Concetta Laliscia1, Natalina Coccia2, Roberto Mattioni1, Taiusha Fuentes1, Riccardo Morganti3, Fabiola Paiar1
1Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Pisana, Unità Operativa Radioterapia, Pisa, Italy; 2Azienda Universitaria Pisana, Unità Operativa Radioterapia, PIsa, Italy; 3University of Pisa, Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Section of Statistics, Pisa, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The aim of this study is to evaluate the impact of human papilloma virus
(HPV) status in the clinical outcome of patients affected by adenocarcinoma of
the uterine cervix treated with surgery followed by concurrent chemo-radiotherapy
(CCRT) +/- brachyteraphy (BT).
Material and Methods
We retrospectively evaluated 39 patients (median age
52 years, range 33-75 years) with FIGO (IB2-III) stage cervical adenocarcinoma,
who were treated in our Institution, from January 2012 to December 2020; 29
patients (74%) were HPV (mostly HPV 16 or HPV 18) associated adenocarcinoma
subtype (HPVA) and 10 patients (26%) were HPV not associated (NHPVA). Twenty-one
patients (54%) received combined neoadjuvant chemotherapy of
taxane and platinum, with or without anthracycline. All
the women underwent surgery (type II-III radical hysterectomy with bilateral
pelvic lymphadenectomy) followed by adjuvant pelvic
RT (45-50.4Gy in 25-28 daily fractions) and 23 women (59%) received concomitant
chemotherapy (weekly cisplatinum 40mg/m2). Sequential vaginal high-dose rate
(HDR)-BT boost, up to a dose of 10Gy in 2 fractions of 5Gy, was delivered in 20
patients (51%). Pelvic RT was performed with a 6-15 MV beam using four-field
conformal technique or Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT). Vaginal HDR-BT was
delivered using a 192Ir source, HDR afterloader,
with a vaginal applicator set.
Results
Two-years and five years overall survival (OS) were 92% and 73%, and two-years
and five years progression free survival (PFS) were 72% and 59%. At log rank
test analysis, HPVA patients had a significant lower risk of death (p=0.004), as
well as in the same cohort there was a trend for a lower risk of progression
(p=0.098).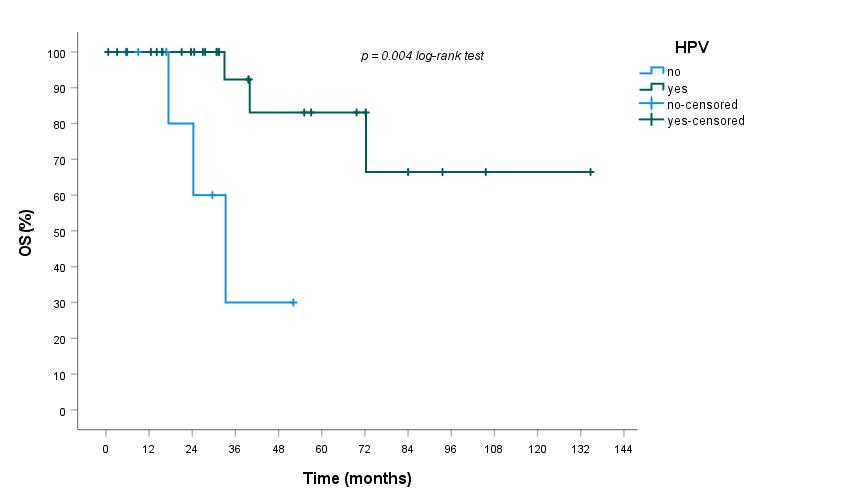
Conclusion
Adenocarcinomas of the uterine cervix consist of a large heterogenous
group of tumours, with about 35% correlated to HPV infection. The
prognosis of these malignancies is worse than for other histologies. As shown in other
organs, in our study HPV status significantly affects prognosis. In conclusion, HPV status in cervical cancer may be a useful prognostic
biomarker before treatment.