FAST protocol in breast radiotherapy: anthropometric parameters, dosimetric results and toxicity.
Rita Marina Niespolo,
Italy
PO-1212
Abstract
FAST protocol in breast radiotherapy: anthropometric parameters, dosimetric results and toxicity.
Authors: Rita Marina Niespolo1, Sara Terrevazzi2, Sara Trivellato3, Chiara Chissotti2, Maria Chiara Innati4, Paolo Caricato5, Valeria Faccenda6, Gianluca Montanari5, Denis Panizza5, Valerio Pisoni1, Stefano Arcangeli1
1 H.S. Gerardo, Radiation Oncology, Monza, Italy; 2H.S. Gerardo, Radiation Oncology, Monza, Italy; 3H.S. Gerardo, Physics Department, Monza, Italy; 4 H.S. Gerardo , Radiation Oncology, Monza, Italy; 5 H.S. Gerardo, Physics Department, Monza, Italy; 6 H.S. Gerardo, Physics Department, Monza, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Hypofractionated radiotherapy is not widespread,
although recent studies have proven its non-inferiority after primary surgery
for early-stage breast cancer (BC). This study analysed the preliminary data
and factors influencing acute skin toxicity in BC patients, treated according
to the radiotherapy FAST protocol.
Material and Methods
Early-BC patients were treated with 28.5 Gy in 5
fractions once a week (FAST protocol) using the 3D-CRT field-in-field (FIF)
technique at a single Institution. Clinical target volumes (CTVs), dosimetric
parameters, and tumour characteristics were recorded and analysed. The
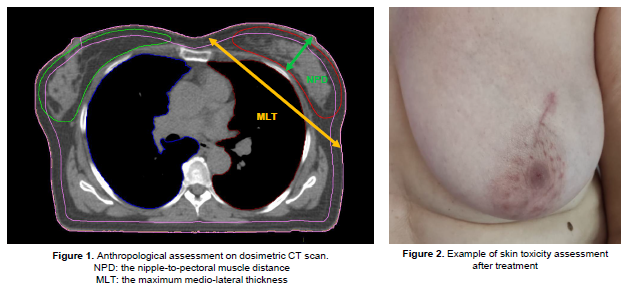
parameters measured to assess the breast size are the cup size, the
nipple-to-pectoral muscle distance (NPD), and the maximum medio-lateral
thickness (MLT), along tangential fields. Adverse skin reactions were assessed
according to CTCAE v. 5.0 at the end of treatment and after one month.
Results
Between December 2020 and October 2021, 34
early-BC patients (median age 66 years, 51–84) were enrolled, of whom 6
underwent forced deep-inspiration breath-hold. 57% of patients had fair skin
(skin phototype I/II according to the Fitzpatrick scale). The median CTV volume
was 393 cm3 (60.3-855.7) with a median NPD of 4.7 cm (1.7-8)
and a median MLT of 21.9 cm (14.3-32.3). The 5,8%, 34,2%, 40%, and 20% of
patients wore an A, B, C, and D bra cup-size, respectively. CTVs registered a
median V95% of 99.6% (96.6-100.0) and a median V105% of 0.1% (0.0-4.7). The
median 105% isodose was 2.33 cm3 (0.0-48.0) of whom 0.6 cm3 (0.0-5.2) in the first centimetre below the skin
surface. Lung and heart dose constraints were never exceeded. Only 4 patients,
out of 34, showed a grade 1 (G1) erythema and no instance of grade 2 (G2) skin
toxicity was documented.
Conclusion
Our findings confirmed the safety of the FAST
regimen also in BC patients with fair skin and large breast volume. The use of
FIF technique helped in mitigating the acute skin reactions, minimizing the
target dose inhomogeneity and hot spots usually associated to a higher risk of
acute adverse events and suboptimal final cosmetic outcomes. A longer follow-up
and a larger patients’ population are required to confirm these results