Ten consecutive patients treated with definitive RT including SIB of PILN and with daily cone beam CT (CBCT) for all fractions (fx) were included. RT was delivered by VMAT. Dose to the elective target was 51.2/32 fx with a SIB of 64 Gy/32 fx to the primary tumor and PILN.
PILN were contoured on both planning CT and MRI (GTV-N). The images were rigidly registered. For each PILN, the GTV-N contoured on MRI and CT were combined to form ITV-N. Each PILN was also contoured on every second or third CBCT for a total of 11 CBCTs evaluated in all patients.
For OAR the following contours were considered: subcutaneous tissue (SC), inguinal vessels, skin rim, bowel and body contour.
Three plans were created for every patient:
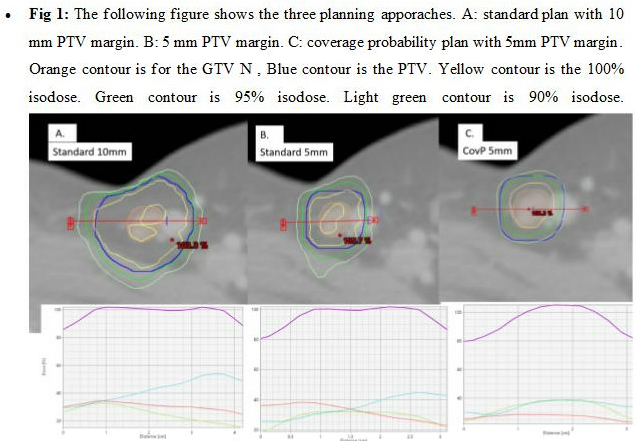
A– Standard CT based planning; PTV-N using GTV-NCT with a 10mm isotropic margin. GTV-NCT was delineated on the planning CT. The coverage criteria were PTV-N D98% ≥ 95% of prescribed dose (PD).
B– CT and MRI based planning with smaller margins: PTV-N using a 5mm isotropic margin added to ITV-N. The coverage criteria was the same as in plan A.
C– CovP: PTV-N was the same as in plan B. Coverage criteria were: ITV-N D98% ≥ 100% PD and PTV-N D98% ≥ 90% of PD.(Fig1).
Rigid registration was performed between CBCTs and the planning CT, and all the CBCTs delineations were propagated to the planning CT. For every PILN (contoured on the planning CT and each contoured CBCT: D98%, D50%, D2% were extracted for the GTV N on the CBCT and the PTV for the three plans. The total delivered dose was estimated by accumulating dose across all CBCT. Doses to OAR were evaluated on the planning CT for the three different planning approaches.