16/135 tox events were
scored.
Baseline levels of PDGF, TGFβ1, & TNFα were significantly
associated with aGI: we developed an LR-based poly-cytokine risk score for aGI (CytoScore, p=0.01, AUC=0.67)
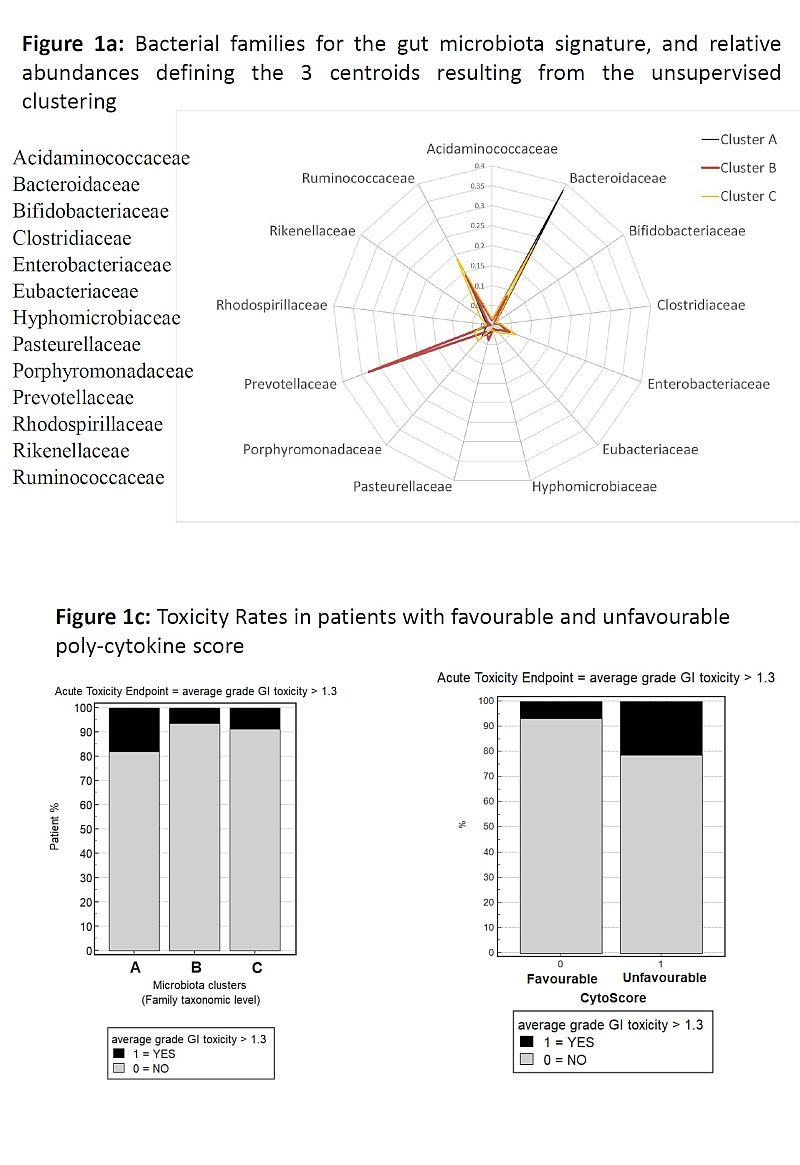
MB clustered in 3 groups at the Family taxonomic
level, with 13 families included in the centroid signature (Fig1a). Pts in
cluster A had a significantly higher probability of aGI tox (unfavourable MB) compared
to pts in clusters B and C (favourable MB): tox rates were 17.9 vs 7.6%, OR=2.6
(p=0.05, Fig1b).
MB clustering was confirmed in the validation
cohort: tox rates 13 vs 8% in unfavourable vs favourable MB (without any change
in centroids for clustering).
We classified
pts at low-risk (LR) of tox if they had “favourable MB AND Cytoscore”, at
intermediate-risk (IR) if “favourable MB OR Cytoscore”, at high-risk (HR) if
“unfavourable MB AND Cytoscore”. Observed toxicity rates in LR/IR/HR were 3/10/35%
(p=0.003).
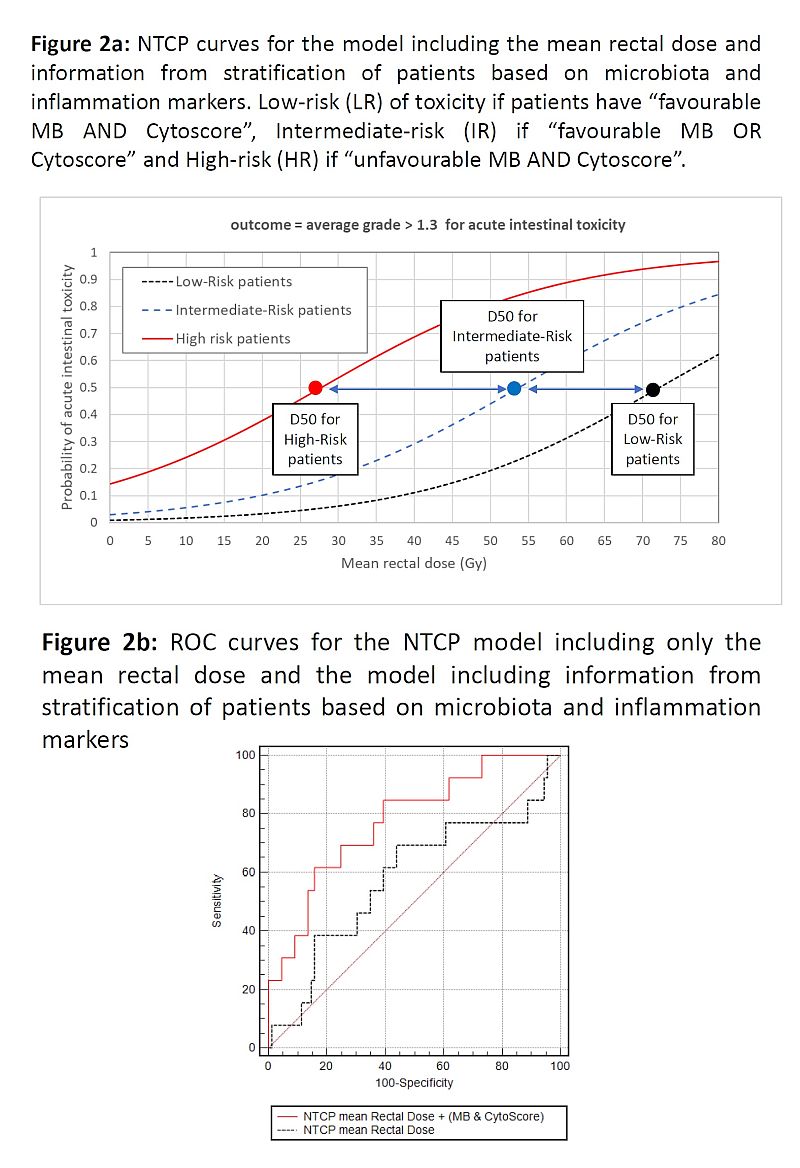
NTCP model including only mean rectal dose had AUC=0.53.
When we introduced pts stratification from MB &
CytoScore: D50=72Gy, k=2.9, DMF for IR pts=0.74, DMF for HR pts=0.38, AUC=0.78 (details in fig2)