Factors affecting the implementation of technological and treatment innovations in radiotherapy
Rachelle Swart,
The Netherlands
PO-1043
Abstract
Factors affecting the implementation of technological and treatment innovations in radiotherapy
Authors: Rachelle Swart1, Liesbeth Boersma1, Rianne Fijten2, Sasha Raj3, Salina Thijssen2, Cheryl Roumen2, Maria Jacobs4
1Stichting Maastricht Radiation Oncology, Radiotherapy, Maastricht, The Netherlands; 2Stichting Maastricht Radiation Oncology, Radiotherapy , Maastricht, The Netherlands; 3Maastricht University Medical Center, Faculty of Health Medicine and Life Science, Maastricht, The Netherlands; 4Tilburg University, Tilburg School of Economics and Management, Tilburg, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Previous research has shown that radiotherapy (RT)-treatment innovations are
four times less likely to be timely implemented, in comparison to technological innovations1. This study aims to investigate which
factors are related to this difference, to find clues to improve implementation-efficiency
for treatment innovations.
Material and Methods
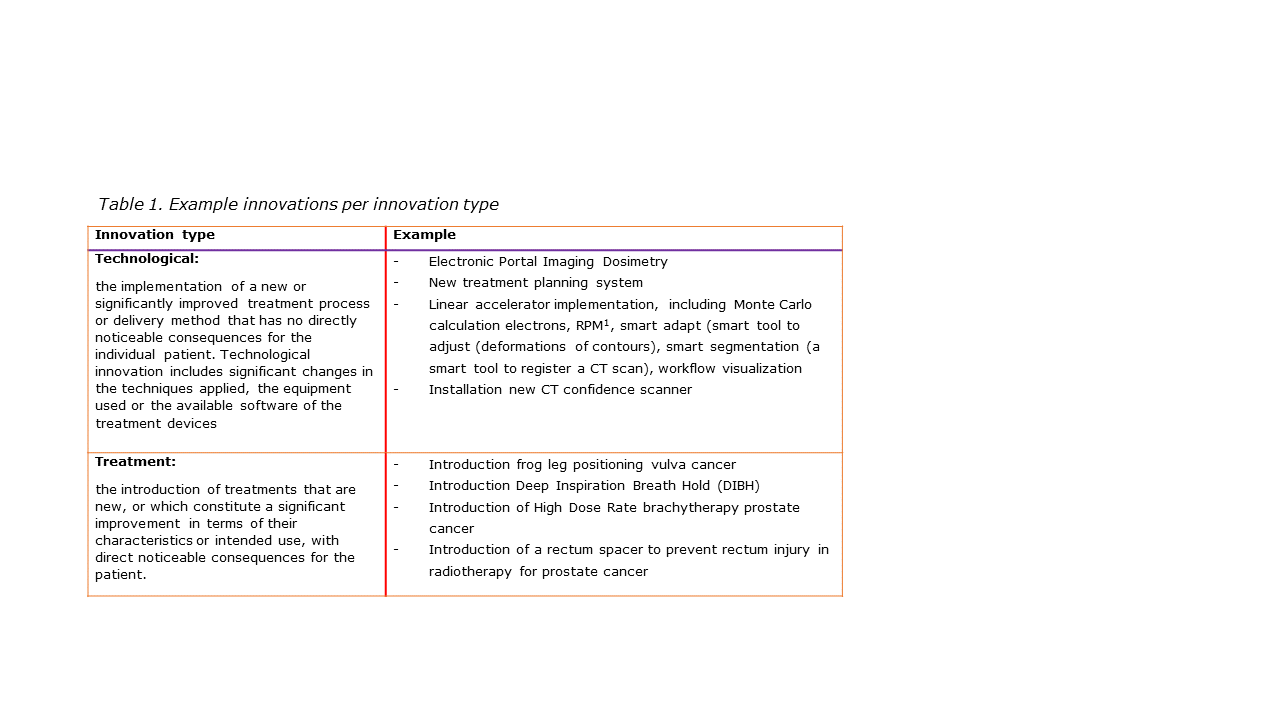
First, a scoping literature
review on success factors for treatment and technological innovations (see
Table 1 for some examples) was performed. Second, the database of the original
research1, consisting of 163 innovations (only 54% were successfully implemented), was analysed for
differentiating
success factors for treatment and technological innovations by means of descriptive statistics. Univariate
comparisons of categorical data were performed using cross tables and
Chi-square tests. Subsequently, semi-structured interviews on experienced facilitators and
barriers were conducted with eight experts involved in the implementation of
four selected innovations at a Dutch RT-centre.
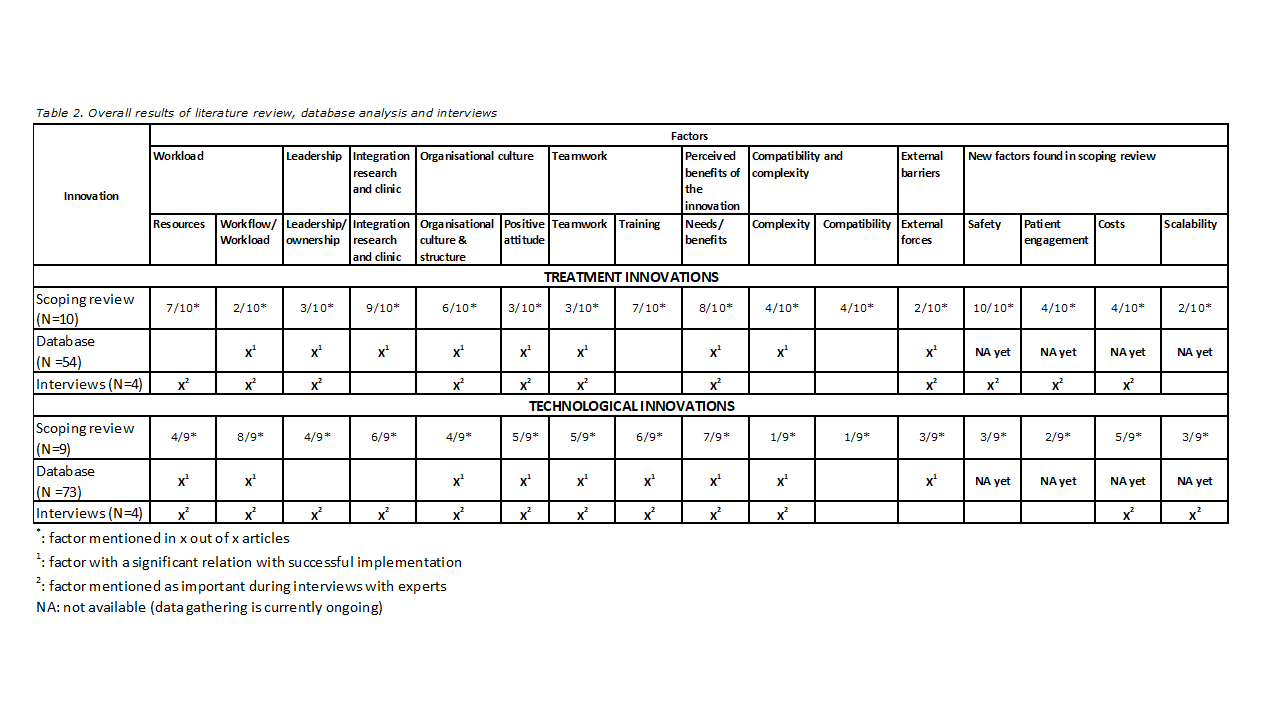
Results
The literature search yielded 276 unique
studies, of which ultimately 19 articles (9 technological, 10 treatment innovations) were included in the study. Apart from the earlier
found success factors1, four additional success factors were
identified: patient engagement, patient safety, scalability and costs.
Analyses of the database showed that
treatment and technological innovations had many factors in common, such as complexity, clear roles for
each member in every step of the implementation process and good understanding
and awareness of the goals of the project and the process of implementation.
Differentiating factors for technological
innovations were
sufficient resources and
a positive organizational climate with a friendly and respectful approach to
employees, whereas for treatment innovations feasibility & desirability, and a project leader who clearly promotes the benefits of the innovation to the project
members, are key factors.
The interviews with experts
showed that patient safety, external forces and patient engagement play a part
only in treatment innovations, whereas training and scalability were important
for technological innovations. The expected
workflow/workload as result of the innovation was mentioned in all innovations,
this was expected to lead to a higher workload for treatment innovations and to
improved efficiency and less workload in technological innovations.
Conclusion
Based on
our results (Table 2), including patient engagement and patient safety is
crucial before implementing treatment innovations, since our results indicate
that the low success rate of treatment innovation implementations, is caused by
these two determinants. The already higher success rate of technological
innovations can probably be accelerated if the new technology is scalable and introduced
by a solid training plan.
References
1. Swart
RR et al Br J Radiol 2021;94 (1117):20200613.