Loco-regional failure is associated with the stem cell marker SLC3A2, volume and HPV/p16 in HNSCC
Morten Horsholt Kristensen,
Denmark
OC-0435
Abstract
Loco-regional failure is associated with the stem cell marker SLC3A2, volume and HPV/p16 in HNSCC
Authors: Morten Horsholt Kristensen1, Brita Singers Sørensen1, Jan Alsner1, Christian Rønn Hansen2, Ruta Zukauskaite2, Eva Samsøe Hinsby3, Christian Maare4, Jørgen Johansen2, Hanne Primdahl5, Claus Andrup Christensen6, Maria Andersen7, JK Lilja-Fischer1, Trine Tramm1, Jens Overgaard1, Jesper Grau Eriksen1
1Aarhus University Hospital, Dept of Experimental Clinical Oncology, Aarhus, Denmark; 2Odense University Hospital, Dept of Oncology, Odense, Denmark; 3Zealand University Hospital, Dept of Oncology, Næstved, Denmark; 4Herlev Hospital, Dept of Oncology, Herlev, Denmark; 5Aarhus University Hospital, Dept of Oncology, Aarhus, Denmark; 6Copenhagen University Hospital, Dept of Oncology, Copenhagen, Denmark; 7Aalborg University Hospital, Dept of Oncology, Aalborg, Denmark
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Large tumor
volume and HPV/p16- status are known to be poor prognostic factors for
loco-regional failure for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) after
primary curative radiotherapy (RT). However, the response to RT is
heterogeneous and the objective was to identify the presence and possible
impact of the stem cell marker SLC3A2.
Material and Methods
Patients
(Pts) in the study represented a subgroup of the DAHANCA 19 study with
available formalin-fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) primary tumor tissue. Pts
were treated with primary RT 66-68Gy, 33-34fx, 6 fx/wk; concomitant weekly
cisplatin (40mg/m2) if UICC stage III/IV (7th ed.) and
the hypoxic radiosensitizer nimorazole. FFPE tumor tissue were collected and
dissected and sufficient amount of cancer tissue was ensured. RNA was extracted
and qPCR was applied to measure the gene expression of the cancer stem cell
marker SLC3A2. Selected reference genes were used to determine the relative
expression of SLC3A2. Volume of GTV-T and -N (GTVTot) was extracted from the original
planning-CT. p16-status was evaluated with immunohistochemistry with a cut-off
of 70 %.
SLC3A2 was
categorized according to expression and p16 status. Further subclassification
was performed according to HPV/p16-status, 50-percentile of SLC3A2 (high/low) and
GTVTot (large/small) into three predefined groups. Loco-regional failure was
used as endpoint and Cox-regression was used to establish hazard ratios (HR).
Results
Full
data-sets were available from 143 primary tumors. Primary tumor site was: oral
cavity (n=4); oropharynx (n=114; of those were 72 p16 positive);
larynx (n=25).
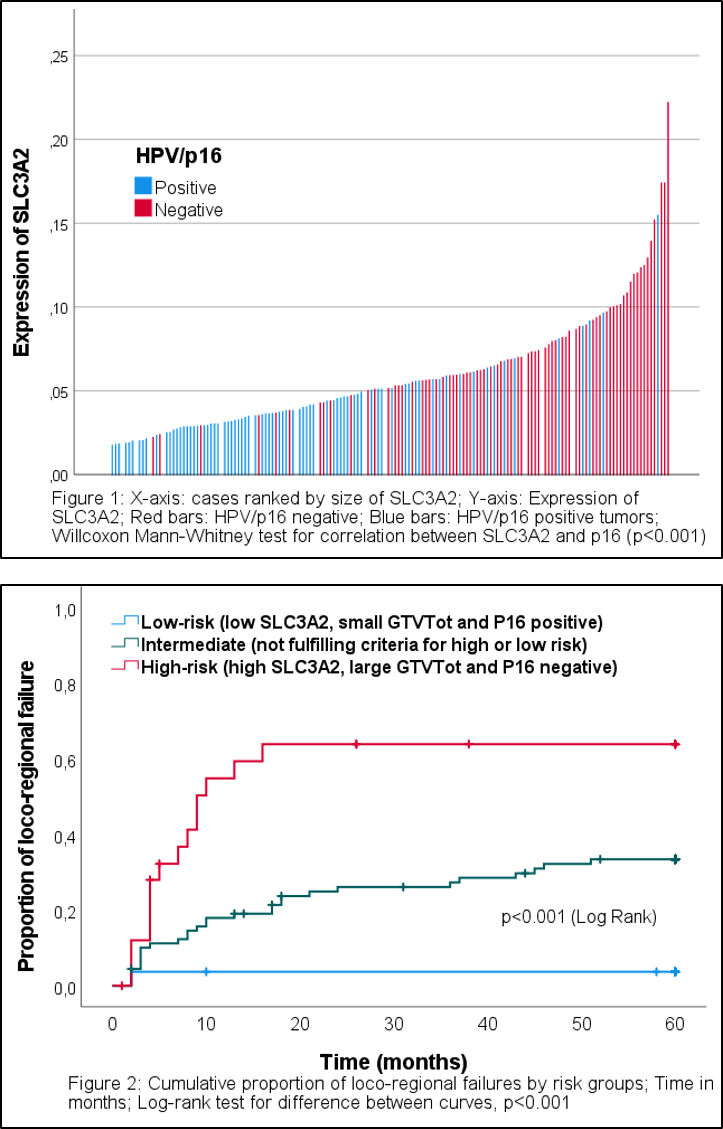
Expression
of SLC3A2 was more prominent in HPV/p16 negative tumors compared to HPV/p16
positive tumors, p<0.001 (Fig. 1).
When
dividing pts into the three predefined groups, the risk of loco-regional failure
was significantly worse for tumors with large volume, HPV/p16 negative status
and high SLC3A2 compared to tumors with low volume, HPV/p16 positivity and low
SLC3A2, p<0.001 (Fig. 2). In total, 4 % of the pts in the low risk-group (n=27) and 56 % in the high-risk group (n=26) had loco-regional failure.
In a multivariate
Cox-regression the above mentioned classification was the most important factor
(HR=0.07; 95%CI(0.007-0.6); p=0.02) among
stage, T-stage, nodal status, tumor differentiation grade and tumor
site.
Conclusion
Presence of
the stem cell marker SLC3A2 is significantly more frequent in HPV/p16 negative
HNSCC and is together with tumor volume a poor prognostic factor. SLC3A2 may be
a putative marker of radioresistance in primary RT of HNSCC.