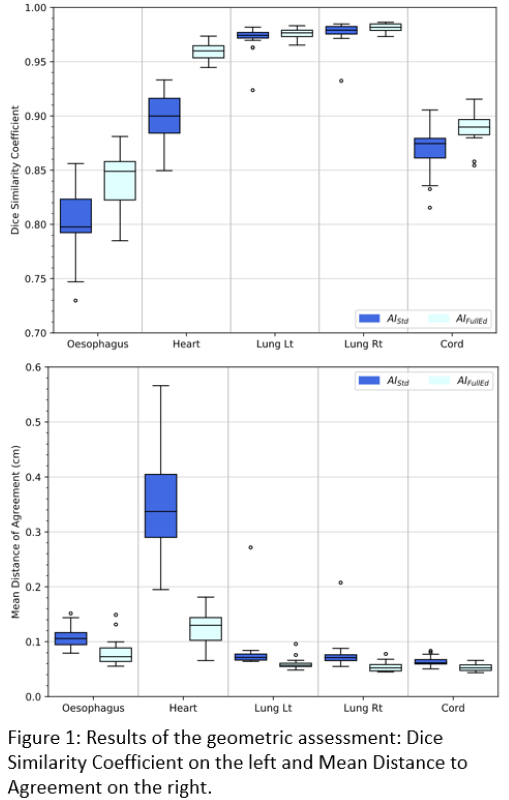
Compared to MD-Ob1, AI-FullEd reduced median delineation time by 50%, 61%, 37%, 28% and 14% for lung_lt, lung_rt, oes, cord and heart respectively. For heart, AI-FullEd increased delineation time in 8 of 20 cases. For lung_lt, lung_rt, oes and cord, AI-Std contours exhibited good geometric alignment to MD-Ob1 with median mean surface distances (MSD) <1.1mm and median DSC results of 0.97, 0.98, 0.80 and 0.88 respectively. For heart, agreement was poorer (MSD=3.4mm, DSC=0.90). AI-FullEd led to small improvements in overall agreement for lung, cord and oes, with moderate improvements for heart (Fig1).
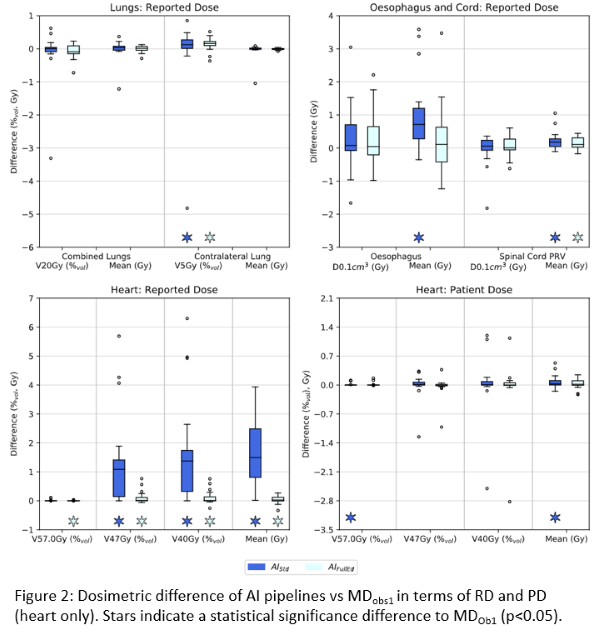
Except for heart RD, all pipelines exhibited excellent dosimetric agreement with MD-Ob1 (Fig2). For RD, median deviations were within ±0.1% (c.f. ±1.4% for heart) and ±0.7Gy (c.f. ±1.5Gy) for relative volume and dose metrics respectively. For PD, agreement was improved with respective values (inc. heart) within ±0.2% and 0.1Gy. Except for a few outliers and heart RD, the distribution of PD/RD deviations for AI-Std and AI-FullEd was considered nominally equivalent.