a pet/ct radiomics model for predicting distant metastasis in lung cancer patients treated with SBRT
Zhen Zhang,
The Netherlands
PD-0972
Abstract
a pet/ct radiomics model for predicting distant metastasis in lung cancer patients treated with SBRT
Authors: Zhen Zhang1, Lu Yu2, Zhixiang Wang3, Andre Dekker3, Leonard Wee3, Alberto Traverso3, Zhiyong Yuan2
1Maastricht University Medical Centre+, Department of Radiation Oncology , Maastricht, The Netherlands; 2Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Department of Radiation Oncology, Tianjin, China; 3Maastricht University Medical Centre+, Department of Radiation Oncology, Maastricht, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) is a guideline-recommended treatment for patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who are medically unfit or unwilling to undergo surgery. Some patients may experience distant failure after SBRT. The goal of this work is to develop and validate a radiomics model for predicting distant failure in early-stage NSCLC patients treated with SBRT.
Material and Methods
Patients who received SBRT at five institutions were enrolled. A total of 103 CT-based radiomics features and 103 PET-based radiomics features of each lung lesion were extracted based on the pretreatment PET/CT images. After feature selection in the training set (from Tianjin), CT-based and PET-based radiomics signatures were calculated by linear combinations. Models based on CT and PET signatures, respectively, were built and validated in external datasets (from Zhejiang, Zhengzhou, Shandong and Shanghai). An integrated model was developed, which included both CT and PET radiomic signatures. The performance of the proposed model was evaluated in terms of discrimination, calibration, and clinical utility.
Results
A total of 228 patients were enrolled. The median follow-up time was 31.4 (2.0-111.4) months. The model based on CT radiomics signatures had an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.819 in the training set (n=139) and 0.786 in the external dataset (n=89). The PET radiomics model had an AUC of 0.763 in the training set and 0.804 in the external dataset. The model combining CT and PET radiomics had an AUC of 0.835 in the training set and 0.819 in the external dataset. This combined model showed moderate calibration and a positive net benefit.
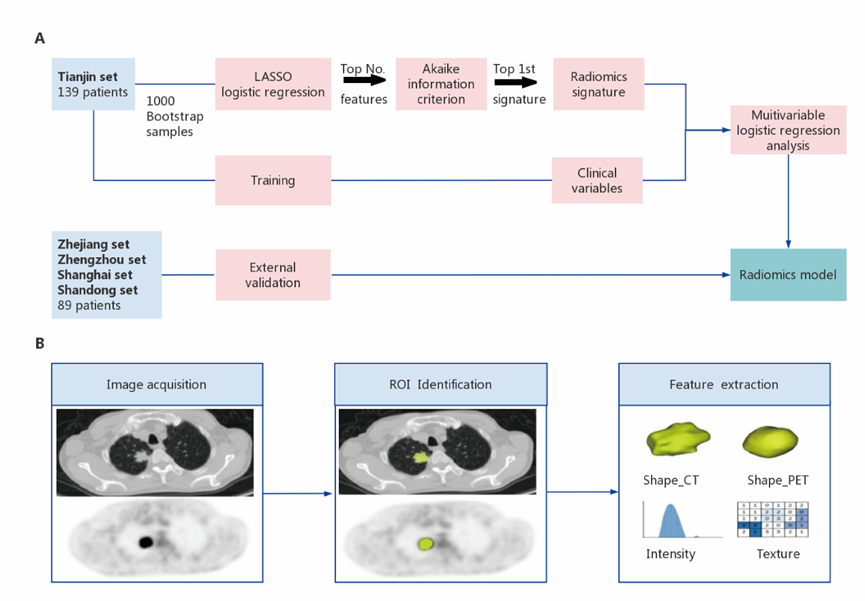
Figure 1. The study flowchart and the radiomics workflow. A, The study flowchart, B, The radiomics workflow.
Model
| Training set
(95%CI)
| Over-optimistic correction
(95%CI)
| External validation set
(95%CI)
|
CT
| 0.819
(0.745-0.892)
| 0.804
(0.728-0.880)
| 0.786
(0.641-0.931)
|
PET
| 0.763
(0.678-0.848)
| 0.735
(0.646-0.824)
| 0.804
(0.681-0.927)
|
CT + PET
| 0.835
(0.780-0.891)
| 0.828
(0.757-0.898)
| 0.819
(0.692-0.947)
|
Table 1. Discrimination of radiomics signature.
Conclusion
The proposed radiomics model can be used for the personalized prediction of distant failure and stratify the prognosis in early-stage NSCLC patients treated with SBRT.