Upfront HDRIBT followed by IMRT for the Definitive Treatment of Tongue SCC
Gokula Kumar Appalanaido,
Malaysia
OC-0631
Abstract
Upfront HDRIBT followed by IMRT for the Definitive Treatment of Tongue SCC
Authors: Gokula Kumar Appalanaido1, Muhamad Yusri Musa2, Ewe Seng Chng3, Syadwa Abdul Shukor4, Soon Eu Chong5, Siti Noor Fazliah Mohd Noor6, Ahmad Naqiuddin Azahari1, SIti Hajariah Kamaruddin1, Nor Hafizah Ishak1, Mohd Zahri Abdul Aziz1, Jasmin Jalil1
1Advanced Medical & Dental Institute, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Radiotherapy & Oncology, Penang, Malaysia; 2Advanced Medical & Dental Institute, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Head & Neck Surgery, Penang, Malaysia; 3Advanced Medical & Dental Institute, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Pathology, Penang, Malaysia; 4National University Cancer Institute, Radiation Oncology, Singapore, Singapore; 5School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care, Kelantan, Malaysia; 6Advanced Medical & Dental Institute, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Dentisry & Oral Health, Penang, Malaysia
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
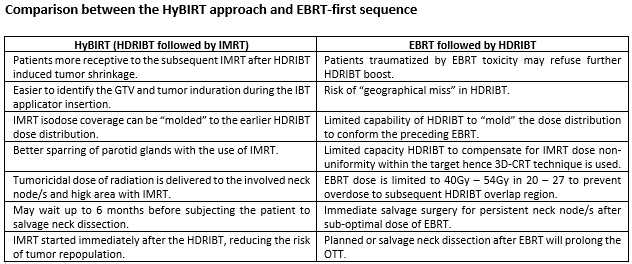
The sequential EBRT followed by HDRIBT for definitive treatment of tongue SCC (TSCC) often advocate planned nodal dissection due to the lower EBRT doses delivered to the involved nodes and HDRIBT is usually performed around 4 weeks (w) after completion of IMRT to the residual TSCC causing prolongation of overall treatment time (OTT). A reversed sequence with HDRIBT first followed by IMRT has the advantage of easier GTV identification for HDRIBT, reduced overall OTT, ability to "mold" and optimize the IMRT dose levels according to the preceding HDRIBT isodoses and can deliver tumoricidal dose to involved nodes. This is the first report on the clinical outcome of patients treated in this reversed sequence that we named as Hybrid Brachytherapy followed by IMRT (HyBIRT)
Material and Methods
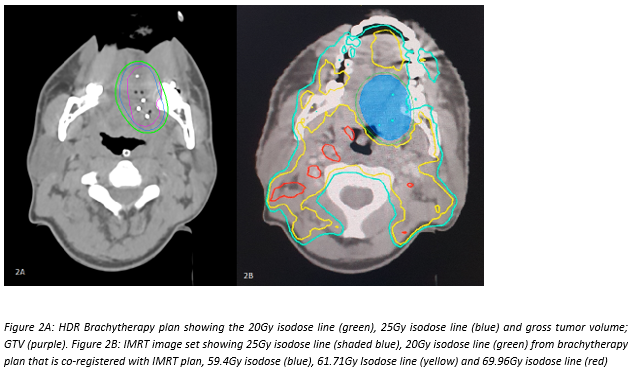
Eleven patients who refused or unfit for surgery and underwent HyBIRT treatment [HDRIBT 20Gy in 5 fractions (F) to tongue GTV followed by definitive IMRT within 10 days (d) to a dose of 69.96Gy to the involved nodes; 61.71Gy to the high risk volume; 59.4Gy to the ipsilateral hemi-tongue and 20Gy HDRIBT volume; and 56.1Gy to the low risk volume over 33F] with or without concurrent weekly Cisplatinum in our centre from 1st January 2019 till 1st January 2021 were prospectively followed up and analysed for tumor control rate and toxicity.
Results
All 11 patients with age range of 20 – 71 years had concurrent chemotherapy. T stage (TNM7) range from T2 – T4a of the anterior mobile tongue and 7 patients had nodal disease. Follow up period range from 2w – 26 months (m). OTT (initiation of HDRIBT to IMRT completion) range from 56 – 63d. One patient had PD and succumbed to the disease while another patient who attained clinical (c) complete response (CR) died of severe dehydration 2w after IMRT. The 12m LR-PFS was 90% (95% CI: 73.2%-100%). Eight patients achieved radiological CR (rCR) at both the primary site and nodes and one of them developed distant metastasis during follow up. The 18m DFS for these 8 patients was 66.7% (95% CI: 30%-100%) with censored data analysis for insufficient follow up. All 11 patients achieved cCR at the primary site and 9 out of 11 patients with available radiological imaging had rCR. Median time for cCR and rCR at primary site is 3.91m and 4.34m respectively and 4.58m for rCR in the nodes for 7 out of 8 patients with nodal disease at presentation. The most common CTCAE 5.0 grade 2 or more early toxicity is oral mucositis, dry mouth, dysphagia and altered taste which resolved to grade 1 by 6m. However, the grade 1 dry mouth and dysarthria which developed much later tend to persist even at 2 years of follow up.
Conclusion
Organ preservation approach with HyBIRT technique in TSCC of mobile tongue showed a promising result both in terms of disease control and toxicity profile. A larger multicentre trial is needed to confirm the efficacy of this regimen. The advantages of the reverse order of HyBIRT technique is summarized in table below.