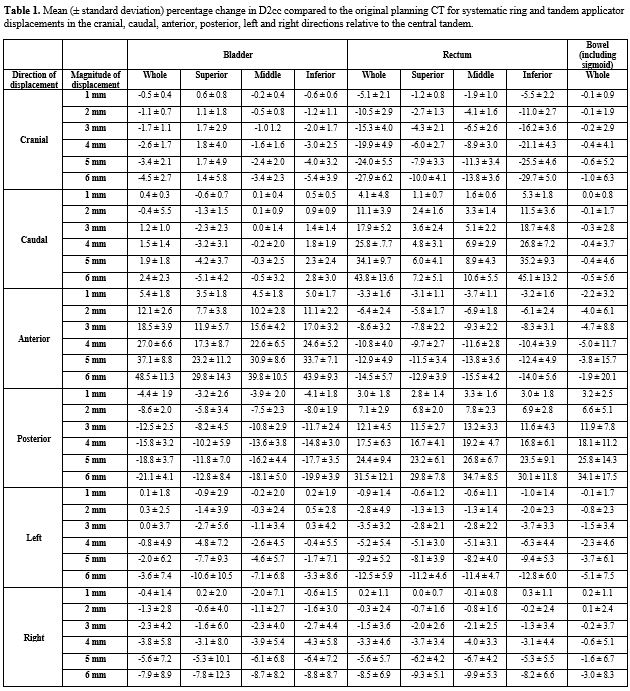
The greatest mean increases in D2cc occurred in the anterior direction for bladder and posterior direction for rectum, with increases of 5.4±1.8%, 18.5±3.9% and 37.1±8.8% to bladder and 3.0±1.8%, 12.1±4.5% and 24.4±9.4% to rectum for 1, 3 and 5 mm shifts in each respective direction. The greatest mean increases in bowel D2cc occurred with posterior displacement with increases of 3.2±2.5%, 11.9±7.8% and 25.8±14.3% for 1, 3 and 5 mm shifts respectively.
The inferior bladder experienced the greatest percentage change in D2cc with 1, 3 and 5 mm anterior shifts resulting in mean increases of 5.0±1.7%, 17.0±3.2% and 33.7±7.1% respectively. The middle part of the rectum experienced the greatest percentage change in D2cc with 1, 3 and 5 mm posterior shifts resulting in mean increases of 3.3±1.6%, 13.2±3.3% and 26.8±6.7% respectively.
Wide deviations in mean D2cc occurred with increasing displacement, with shifts of 6 mm resulting in changes of 48.5±11.3%, -21.1±4.1% and -7.9±8.9% in the anterior, posterior and right directions for the bladder, 27.9±6.2%, 43.8±13.6%, -14.5±5.7%, 31.5±12.1%, -12.5±5.9% and -8.5±6.9% in cranial, caudal, anterior, posterior, left and right directions for the rectum and 34.1±17.5% in the posterior direction for the bowel. Displacements in the caudal and left directions had the least mean changes for bladder at 2.4±2.3% and 3.6±7.4% at 6 mm respectively. Displacements in the cranial and caudal directions had the least mean changes for bowel at -1.0±6.3% and -0.5±5.6% at 6 mm respectively (Table 1).