Clinical evaluation of Exactrac Dynamic surface guided pre-positioning system for cranial treatments
PO-1909
Abstract
Clinical evaluation of Exactrac Dynamic surface guided pre-positioning system for cranial treatments
Authors: Jorge Alonso Muriedas1, Rosa Fabregat Borras1, Rodrigo Astudillo Olalla1, Marina Gutiérrez Ruiz1, Fernando Gómez Enríquez1, Diego Bruzos López1, Samuel Ruiz Arrebola1, Guillermo Camacho de la Vega1, Ana Reguilón Martín1, Verónica Cañón García1, María Ferri Molina1, Ana Laura Rivero Pérez1, Javier Albendea Roch1, Frandeina Pinto Guevara1, Mara García Lamela1
1Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, Radiotherapy, Santander, Spain
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The Brainlab Exactrac Dynamic system (ED) is composed of two kV X-ray tubes on the floor, two ceiling mounted flat panel detectors and a single ceiling mounted receptacle, which contains a structured light projector, two high resolution cameras and an integrated thermal camera.
The system automatically performs the pre-positioning of the patient by matching the live 3D surface with the external contour generated by the treatment planning system. Final positioning is achieved by the fusion of stereoscopic X-Ray images and reference computed tomography images. During treatment, thermal data is combined with surface information to monitor the patient.
The goal of this work was to evaluate the surface guided pre-positioning system accuracy for cranial treatments.
Material and Methods
The ED system incorporated in a Varian TrueBeam STX linear accelerator was tested using the data from 13 patients who received from 1 to 5 cranial stereotactic radiotherapy fractions. A database of 10 more patients is pending analysis to complete this study.
Every treatment day, patients were immobilized with 4PI stereotactic mask system. After performing the pre-positioning of the patients with the ED surface guided system, residual errors calculated from kV X-ray stereoscopic images were registered in vertical, longitudinal and lateral axis.
The modulus of the vector composed by the vertical, longitudinal and lateral axis was calculated for each fraction of treatment.
Results
Figure 1 shows the histogram of the vector modulus from all the registered treatment day. It is observed that most of the displacement are between 3.5 and 4.5 mm. The mean value was 4.4±1.9 mm (k=1).
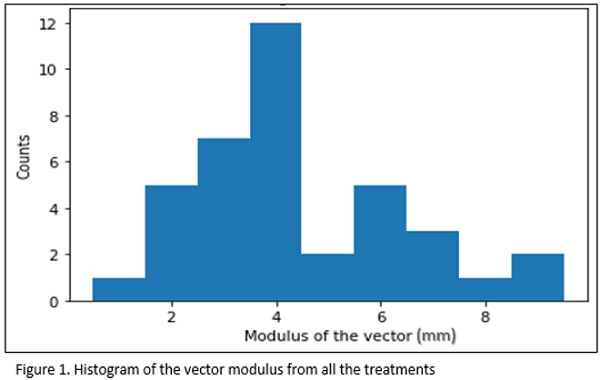
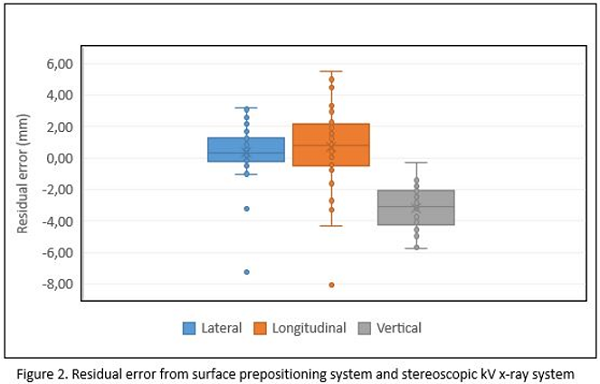
Figure 2 shows each axis residual errors for all patients and for all treatment day. The mean value was 0.4±1.8 mm, 1±3 mm and -3.2±1.3 mm for lateral, longitudinal and vertical position (k=1), respectively.
Conclusion
Preliminary results obtained for surface guided ED prepositioning system show, in average, submillimeter accuracy for lateral and longitudinal axis for patients immobilized with 4PI stereotactic mask. However, less accuracy has been found for vertical axis, probably because of the external contour generation inaccuracy due to the thermoplastic mask.
Consequently, it is necessary internal information from Cone Beam Computed Tomography or kV X-Ray images to achieve total submillimeter accuracy necessary for example in radiosurgery treatments.