Film dosimetry of single isocenter stereotactic radiotherapy for multiple brain metastases
Laura Bogers,
The Netherlands
PO-1723
Abstract
Film dosimetry of single isocenter stereotactic radiotherapy for multiple brain metastases
Authors: Laura Bogers1, Jaap Zindler2, Marc de Goede1, Ivonne Mudde-van der Wouden2, Anna Petoukhova1
1Haaglanden Medical Center, Department of Medical Physics, Leidschendam, The Netherlands; 2Haaglanden Medical Center, Department of Radiation Oncology, Leidschendam, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) is a promising treatment option for patients with multiple brain metastases. Optimal treatment quality with sparing of healthy brain tissue is essential to avoid SRT complications such as brain necrosis. The use of a single isocenter instead of separate isocenters for each metastasis reduces the treatment time without quality loss¹. The aim of this work was to evaluate the quality and the dosimetric accuracy of one-isocenter treatment plans using GafChromic EBT3 film measurements. This is relevant to investigate whether the delivered dose is equal to the calculated dose in the treatment planning system (RayStation, RaySearch laboratories, v10B).
Material and Methods
28 patients with multiple brain metastases median= 8 (4-18) were treated with SRT (18 - 25.5 Gy in 1 or 3 fractions). Non-coplanar LINAC-based treatment planning was performed with 6 MV FFF. Single isocenter treatment technique consisted of 6 VMAT arcs with 3 couch rotations (0°, 60° and 300°). The used gross tumour volume to PTV margin was 1 mm. The PTV coverage should have been at least 98%.
Treatment plans were recalculated on a home-made phantom consisting of 4 layers of plastic (15x15x2 cm³), in between the layers films were placed. After irradiation, 24 hour waiting time is used before results were analysed using DoseLab 4.11. Gamma pass rate was calculated with 3% absolute global dose difference and 1 mm distance-to-agreement criteria. Additionally, dose calculations in Mobius3D were performed with the same gamma criteria. To assess SRT plan quality, the Paddick conformity index (CI), the Paddick gradient index (GI), the total V12Gy of uninvolved brain, the number of monitor units (MU) and irradiation time were studied and reported as MEAN±1SD.
Results
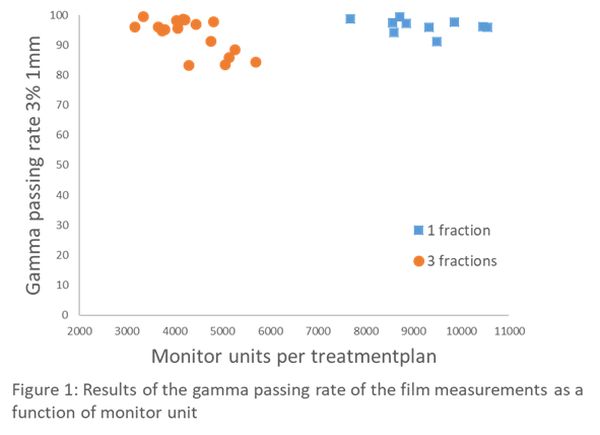
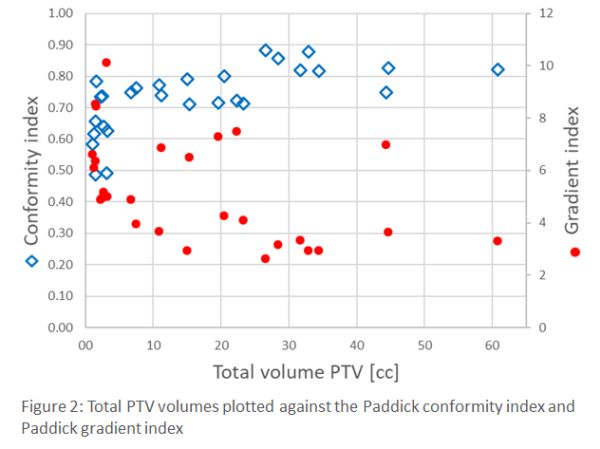
The mean pass rate for all measured films was 94.6±0.4% with 3%/1 mm criteria. The mean pass rate for patients with 1 fraction was 96.4±0.4% and for 3 fractions 91.0±0.4% (see figure 1). The mean pass rate of the secondary dose calculations in Mobius3D was 98.2±1.0% with the same criteria. The mean total CI and GI were 0.73±0.10 and 5.35±2.05, respectively. The total V12Gy was 5.31±5.56%. The number of monitor units and the irradiation time were 6057±2505 MU and 597±56 seconds, respectively. Additionally, we studied the CI and GI as a function of total PTV volume (see figure 2).
Conclusion
The dosimetric results obtained with film measurements and secondary dose calculations are in good agreement with our criteria. High plan quality was observed with a dependence on total volume of the metastases: increasing CI and decreasing GI. These results give confidence in the accuracy of the method and our treatment plans. Measurements where multiple fractions (with lower fraction dose) was used had a lower mean pass rate compared to 1 fraction with higher dose. This was due to the difference in global gamma dose criteria.
1. Petoukhova A, Snijder R, Wiggenraad R, et al. Cancers. 2021 10;13(14):3458.