A new light on dose verification of high modulated spine SBRT plans with FFF
Michel Oellers,
The Netherlands
PO-1721
Abstract
A new light on dose verification of high modulated spine SBRT plans with FFF
Authors: Michel Oellers1, Ans Swinnen1, Marcel Walpot1, Frank Verhaegen1
1MAASTRO, Medical Physics, MAASTRICHT, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for spine is related to complex highly modulated plans in a heterogenous tissue environment. Treatment with 10 MV flattening filter free (FFF) beams ensures fast treatment times and consequently less chance of intra-fraction movement. In recent literature dose verification anomalies up to 10% have been seen for these plans and these were contributed to plan complexity and inaccurate dosimetric leaf gap (DLG) values in Eclipse TPS [1,2]. However we will show that, in high density tissue like bone, the dose anomalies are more likely to be related to the dose reporting mode in Acuros, being either dose-to-medium (D2M) or dose-to-water (D2M) in relation to homogeneous and heterogeneous dose verification phantoms. This is supported by recent findings in [3].
Material and Methods
In total 13 spine SBRT patients were selected and planned with VMAT, 10MV FFF and Acuros using D2M in Eclipse TPS (v16.1). Patients were treated on a Truebeam STx linac. Dose verification plans were calculated in D2M and D2W. The homogeneous PTW Octavius phantom with 1000 SRS detector and heterogeneous CIRS E2E SBRT phantom using EBT-XD film were used for the verification measurements. Verisoft (PTW) and FilmQA pro (Ashland) software was used for analysis based on gamma pass rates. Pass rates above 90% with 2%/2mm at the 80% isodose were considered as clinically acceptable.
Results
Verification plans calculated with
D2M and D2W and measured in Octavius/1000 SRS showed clinically acceptable gamma pass rates in 4 (31%) and 12 (92%) patients, respectively. Verification plans calculated with D2M and measured in a heterogeneous anthropomorphic phantom showed clinically acceptable plans in all 13 (100%) patients [Fig.1].
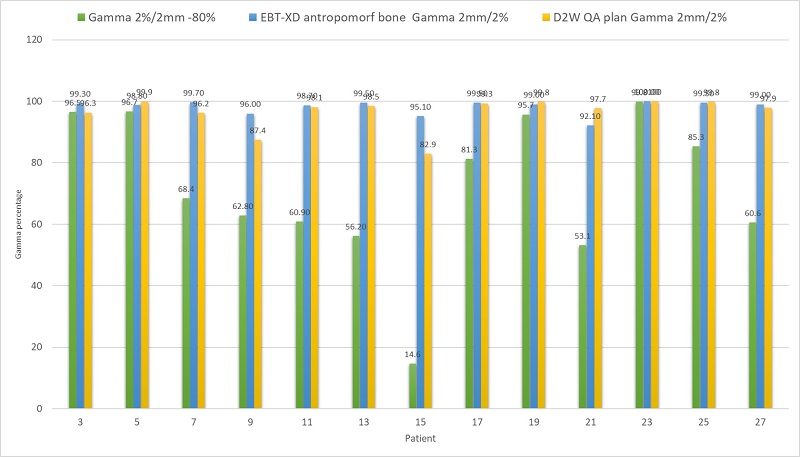
Conclusion
Water-equivalent phantoms like Octavius/1000 SRS should be used with caution for dose verification in bone tissue like spine. Acceptable results were however acquired if D2W was used as dose reporting mode in Acuros. The most realistic and accurate dose verification method for spine SBRT is to report in D2M and perform the dose verification in a heterogeneous anthropomorphic phantom.
[1] Kim J, Han JS, Hsia AT, Li S, Xu Z, Ryu S. Relationship between dosimetric leaf gap and dose calculation errors for high definition multi-leaf collimators in radiotherapy. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2018 Feb 20;5:31-36. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2018.01.003.
[2] Vieillevigne L, Khamphan C, Saez J, Hernandez V. On the need for tuning the dosimetric leaf gap for stereotactic treatment plans in the Eclipse treatment planning system. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019 Jul;20(7):68-77. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12656. Epub 2019 Jun 21. PMID: 31225938; PMCID: PMC6612699.
[3] Shaw M, Lye J, Alves A, Hanlon M, Lehmann J, Supple J, Porumb C, Williams I, Geso M, Brown R. Measuring the dose in bone for spine stereotactic body radiotherapy. Phys Med. 2021 Apr;84:265-273. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.03.011. Epub 2021 Mar 25. PMID: 33773909.