Can SunCHECK™ Patient replace phantom based SRS plan verification?
Sam Wheeler,
United Kingdom
PO-1719
Abstract
Can SunCHECK™ Patient replace phantom based SRS plan verification?
Authors: Neda Shiravand1, Alison Starke1, Jackie Poxon1, Sam Wheeler1, Niall Macdougall1
1Barts Health NHS Trust, Radiotherapy Physics, London, United Kingdom
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
SRS plans require high delivery accuracy due to the small volumes and steep dose gradients involved. The accuracy of both TPS calculation and treatment delivery are verified by a pre-treatment measurement with a detector array: a time consuming process. The SunCHECK Patient platform offers an independent 3D dose calculation module (DoseCHECK) and EPID based measurement for pre-treatment verification (PerFRACTION). The aim was to establish if DoseCHECK and PerFRACTION are sufficiently sensitive to detect clinically significant errors in SRS HyperArc plans and thereby replace array verification.
Material and Methods
Six previously treated, single lesion, SRS HyperArc patient plans were selected, covering a range of PTV volumes (1.2 - 15.3 cc), fraction doses (8 - 20Gy) and beam energies (6MV and 10FFF). Deliberate errors were written into treatment DICOM plan files to simulate potential corruption in the planning process and plan delivery errors. Plans were exported to MATLAB to introduce MLC errors into one leaf bank to simulate patient plan corruption. Six erroneous plans were created for each patient:
• central MLC leaf retracted by 1.0 mm and 2.0 mm;
• central five MLC leaves retracted by 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm
• all MLC leaves retracted by 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm.
The modified plan files were sent to SunCHECK (with their original dose, structure set and CT files). DoseCHECK compared its dose calculation on the corrupted plan file(s) with the original TPS dose. PerFRACTION compared its corrupted plan dose calculation with measured EPID dose from the original plan. Plans were reported as a pass or fail using local gamma analysis parameters: 5% dose difference, 1mm DTA, 30% threshold, 95% pass rate.
Results
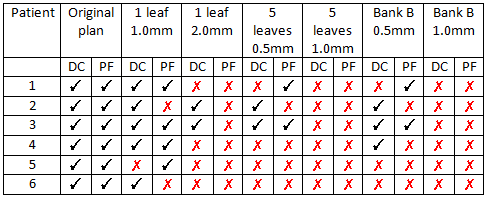
Table 1: DoseCHECK (DC) and PerFRACTION (PF) results: ✗represents a fail and ✓represents a pass.
For all six plans DoseCHECK produced a failure when the central five leaves were changed by 1.0mm. PerFRACTION analysis of EPID measurements produced a failure for all six patients when a single leaf was displaced by 2mm, and when 5 leaves were changed by 1.0mm. Four out of six patient plans failed with a leaf error of only 0.5mm. 31/36 of all generated error plans failed DoseCHECK, PerFRACTION or both, demonstrating that used together they have a high degree of sensitivity for detecting errors.
Conclusion
DoseCHECK and PerFRACTION modules of SunCHECK Patient are highly sensitive at detecting MLC positional errors introduced into SRS plans, demonstrating that errors in TPS calculations and machine delivery can be detected at the pre-treatment stage. PerFRACTION can be safely implemented for SRS patient specific QC, replacing time consuming phantom measurements and thus reducing staff and machine clinical workload.