Establishing a reliable DIR methodology applied to pancreatic recurrence evaluation
PO-1686
Abstract
Establishing a reliable DIR methodology applied to pancreatic recurrence evaluation
Authors: Sara Poeta1, Martin Manderlier2, Christelle Bouchart2, Akos Gulyban1, Younes Jourani1, Nick Reynaert1
1Institut Jules Bordet, Medical Physics, Brussels, Belgium; 2Institut Jules Bordet, Radiation Oncology, Brussels, Belgium
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The aim of this work is to establish a reliable methodology for pancreatic recurrence (PR) back propagation from recurrence to initial image sets, using deformable image registration (DIR) including evaluation metrics, use of regions of interest (ROI) and define limitations.
Material and Methods
Loco-regional PR after isotoxic high-dose stereotactic body radiotherapy (iHD-SBRT) (Bouchart C. et al TAM 2021) was identified in seventeen patients included in this retrospective study. The iHD-SBRT treatment was based on CT and MRI with abdominal compression. An additional oncological resection of the primary tumor was performed in ten patients.
At the time of recurrence, CT or MRI was performed for ten and seven patients respectively. Single modality antichronologic image registration was applied (CT <- CT or MR <- MR), for recurrence mapping using MIM (version 7.1.5, MIMvista Inc, Cleaveland OH USA). An initial local rigid registration (RIR) was performed guided by either the great vessels (GVs) or pancreas, followed by automatic DIR.
For each patient the pancreas (corresponding residual anatomical segments in case of surgery) and GVs were defined on both image sets, while initial tumour and recurrence only in the corresponding ones.
The automatic DIR was verified and adjusted by a physicist and a specialized physician using MIM’s Reg Refine tool (Johnson et al, JACMP, 2016).
All delineated structures were propagated to the initial image set using the final DIR.
All corresponding structures (initials and deformed) were evaluated using DICE similarity coefficient (DICE) for volumetric assessment, additional to symmetric Hausdorff distance 95% (HD95%) and mean distance to agreement (MDA). Furthermore, Jacobian determinant (JD) was used for DIR plausibility and finally visual inspection as qualitative assessment.
Results
For every case the initial RIR and automatic DIR required manual adjustment.
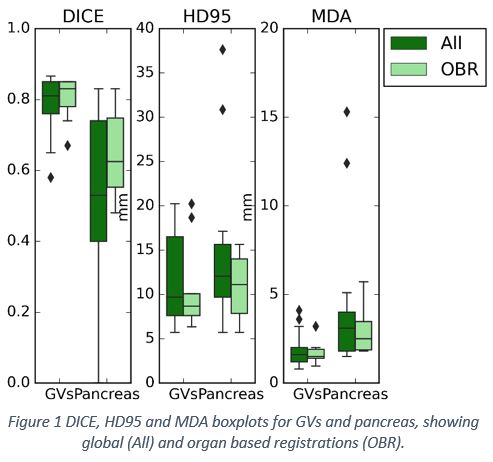
GVs provided a consistent guide for DIR adjustments, while pancreas could help small DIR adjustments whenever used for initial RIR. DICE showed good and moderate agreement for GVs and pancreas, respectively. HD95 showed large variation for both structures up to 21mm and 16mm while it remained reasonable for MDA with values up to 3.2mm and 5.7mm for GVs and pancreas, respectively. Mean Jacobian confirmed plausible DIR, with values ranging from 0.2 - 1.3, 0.6 – 1.5 and 0.4 – 1.2, for recurrence, GVs and pancreas, respectively. Recurrence and pancreas had a predisposition for shrinkage while GVs remained stable, reinforcing the role of GVs as a reliable landmark. Visual inspection resulted in clinically satisfactory agreement within the ROI.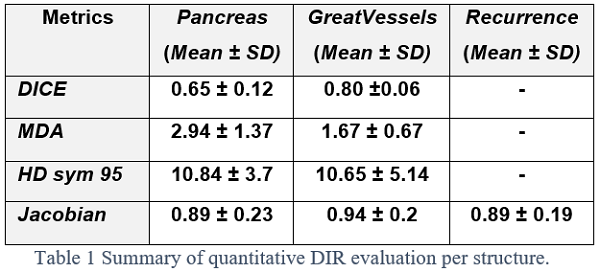
Conclusion
Great Vessels area is a proper guide for organ based deformation, while MDA combined with visual inspection are most suitable methodology to evaluate DIR in pancreatic recurrence back propagation to initial CT/MR.