Pretreatment Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Factor for Cervical Cancer
Fátima Aurora Lima Aires,
Portugal
PO-1435
Abstract
Pretreatment Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Factor for Cervical Cancer
Authors: Fátima Aurora Lima Aires1, Lurdes Salgado2, Lurdes Trigo3, Luísa Carvalho4
1Centro Hospitalar Universitário São João, Radiotherapy, Porto, Portugal; 2Instituto Português de Oncologia , Radiotherapy, Porto, Portugal; 3Instituto Português de Oncologia, Brachytherapy, Porto, Portugal; 4Instituto Português de Oncologia, Radiotherapy, Porto, Portugal
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
We analyzed the prognostic significance of pretreatment serum platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), hemoglobin (Hg) and squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCC) affecting the progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in cervical cancer patients treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy (CRT).
Material and Methods
The clinical data of 170 patients that were treated with definitive CRT was retrospectively analyzed. The inclusion criteria were cervical cancer patients treated for curative intent who were receiving concurrent CRT.
Patients with diseases that could affect the lymphocyte and platelet levels, such as chronic inflammatory disease, distant metastasis or other malignancies, and patients who were undergoing a hysterectomy were excluded. The prognostic factors for OS and PFS were investigated according to cut-off values determined by receiver operating curve analyses.
Results
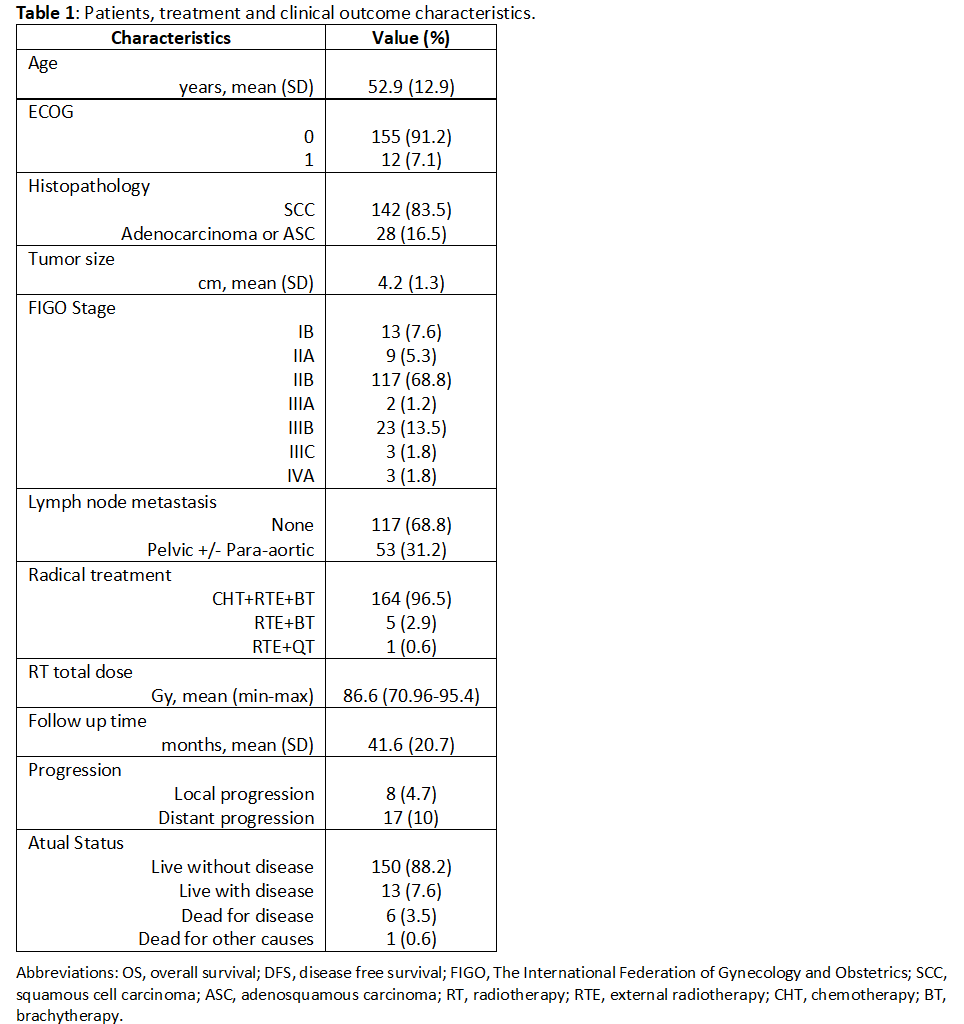
At a mean follow-up time of 41.6 months (stand variation 20 months), the 5-year OS and PFS rates were 96.3% and 85.6%, respectively.
Median pretreatment serum PLR, NLR, hemoglobin (Hg) and SCC were 133.46, 2.42, 12.75g /dl and 3.14 ng/mL, respectively.
The optimal cut off points were 166.3 for PLR with area under the curve (AUC) of 0.596 (p = 0.189); 3.21 for NLR with AUC of 0.505 (p=0.955); 11.5 g/dl for Hg with AUC of 0.568 (p=0.621), and 3.8 ng/mL for SCC with AUC of 0.576 (p=0.346).
In univariate analysis, pathology type and Hg were significant prognostic factors for OS and PLR and SCC for PFS. In multivariate analysis, PLR was significant prognostic factor for PFS. No prognostic factors were found for OS.
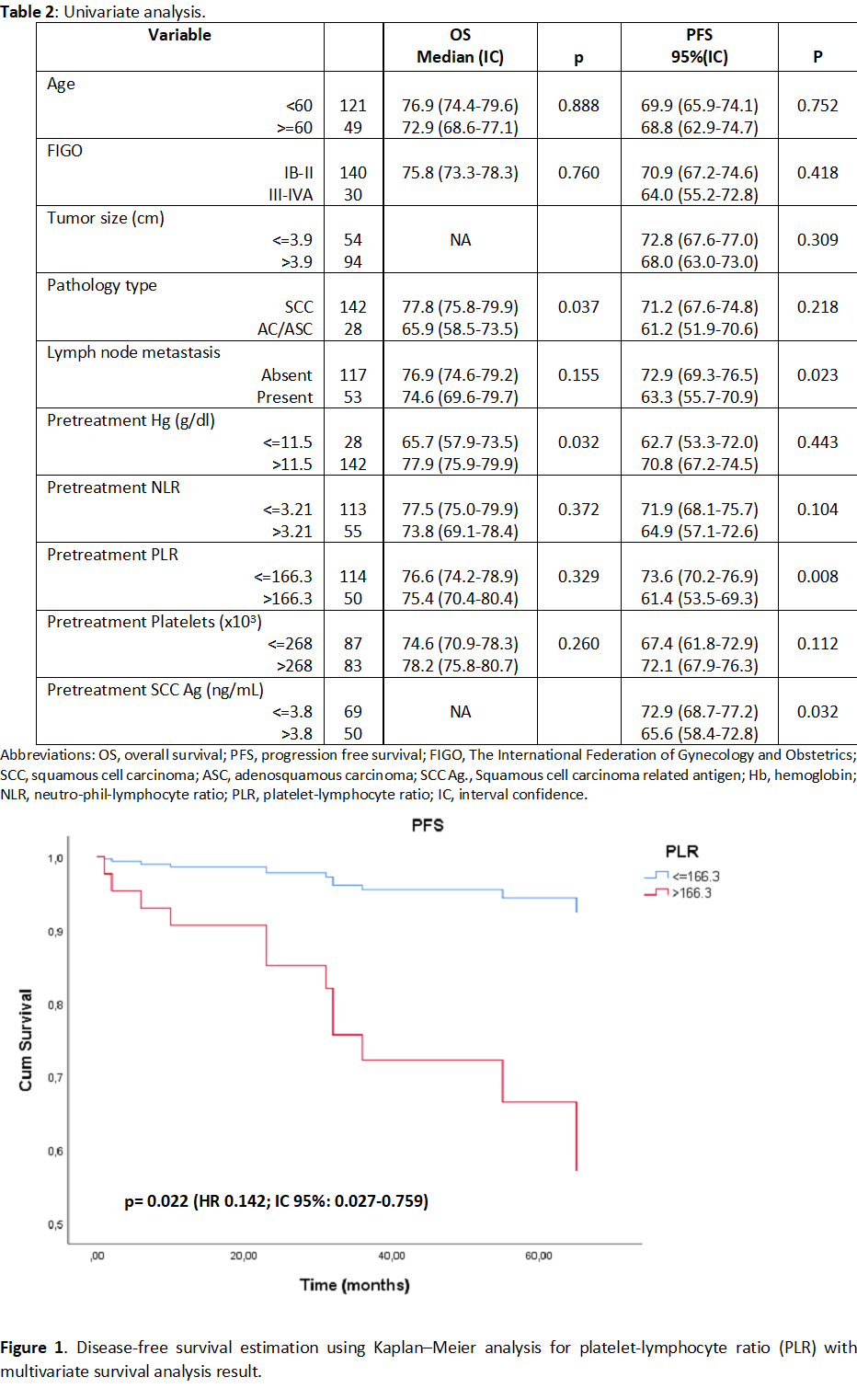
Conclusion
Elevation in PLR before initiation of CRT may be useful biomarker for predicting clinical outcomes.