Reirradiation by stereotactic radiotherapy of brain metastases in case of local recurrence
PO-1136
Abstract
Reirradiation by stereotactic radiotherapy of brain metastases in case of local recurrence
Authors: François Lucia1, Ruben Touati1, Vincent Bourbonne1, Gurvan Dissaux1, Gaelle Goasduff1, Olivier Pradier1, Romuald Seizeur2, Ulrike Schick1
1University Hospital of Brest, Radiation Oncology, Brest, France; 2University Hospital of Brest, Neurosurgery, Brest, France
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a second course of SRT (SRT2) treatment for local recurrence of brain metastases previously treated with SRT (SRT1), using Hypofractionated Treatment Effects in the Clinic (HyTEC) reporting standards.
Material and Methods
From December 2014 to May 2021, 32 patients with 34 brain metastases received salvage SRT2 after failed SRT1. A total dose of 21 to 27 Gy in 3 fractions or 30 Gy in 5 fractions was prescribed to the periphery of the PTV (99% of the prescribed dose covering 99% of the PTV). After SRT2, multiparametric MRI, sometimes combined with 18F-DOPA PET-CT, was performed every 3 months to determine local control (LC) and radionecrosis (RN).
Results
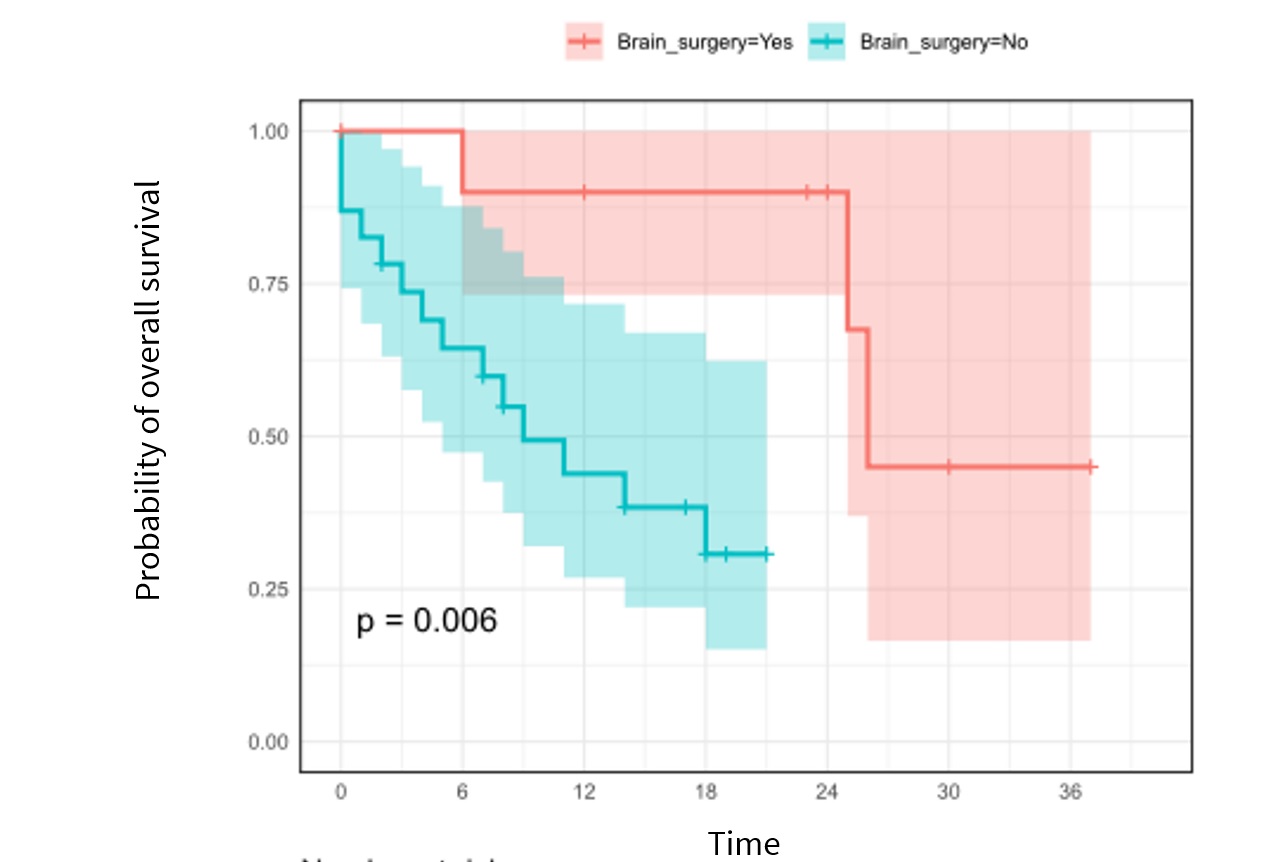
The median interval between SRT1 and SRT2 was 12 months. The median delivered dose (BED with an α/β ratio of 10) at 100% of GTV at SRT2 was 40.89 Gy (range 24.87-50.36 Gy). The median cumulative delivered dose (BED) at 100% of GTV was 81.78 Gy (range 76.59-91.25 Gy). After a median follow-up of 12 months (range 1-37 months), the crude LC and RN rates were 68% and 12%, respectively, and the median overall survival was 25 months. In multivariate analysis, the performance of surgery was predictive of a significant better LC (p = 0.002) and survival benefit (p = 0.04). The volume of normal brain receiving 5 Gy during SRT2 (p = 0.04), dose delivered to the PTV in SRT1 (p = 0.003), and concomitant systemic therapy (p = 0.04) were associated with increased risk of RN.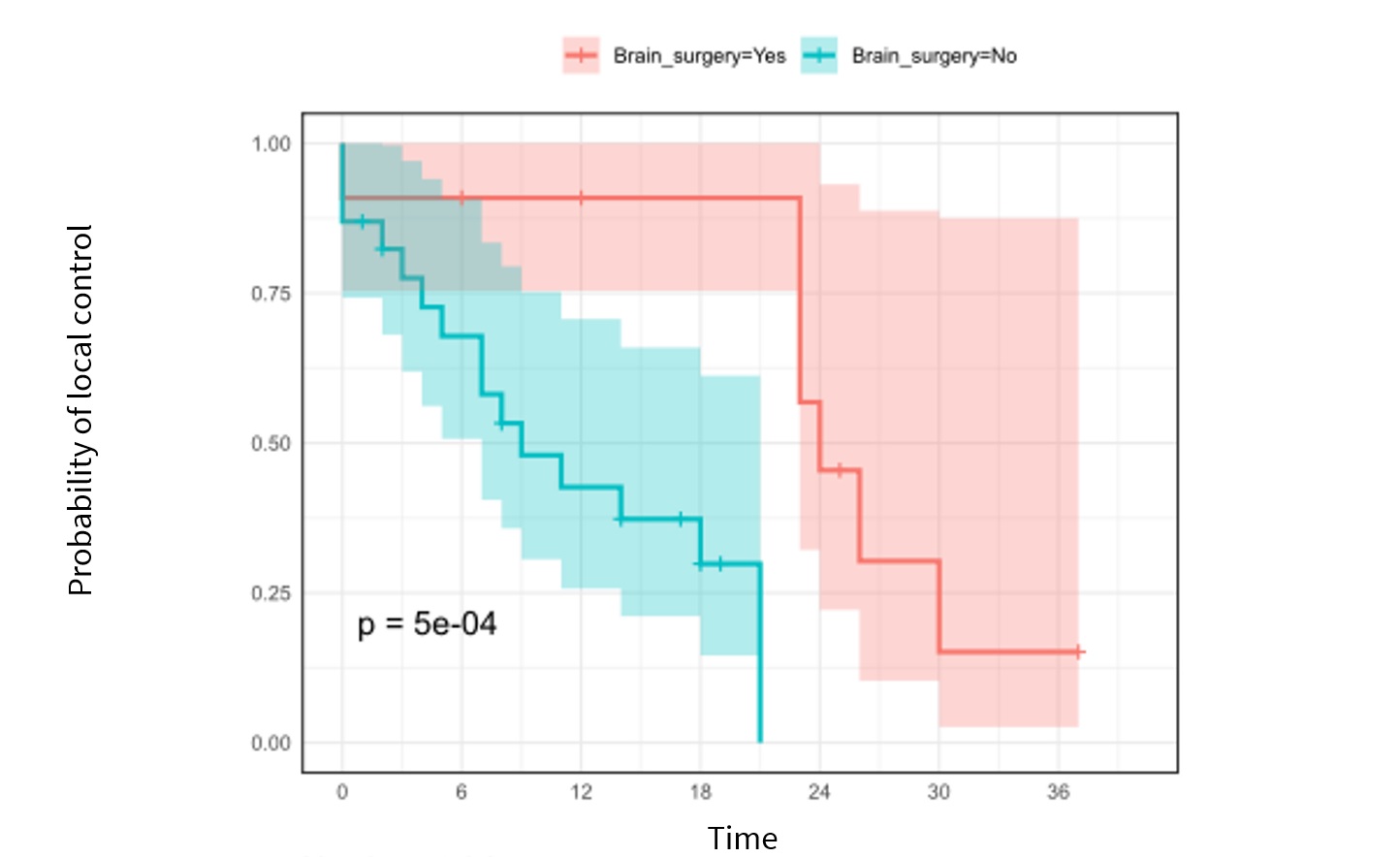
Conclusion
SRT2 is an effective approach for local recurrence of BM after initial SRT treatment and is a potential salvage therapy option for well-selected people with good performance status. Surgery was associated with a higher LC.