Radiation affects bronchial epithelial progenitor function as assessed by organoid formation assay
Merian Kuipers,
The Netherlands
PO-2204
Abstract
Radiation affects bronchial epithelial progenitor function as assessed by organoid formation assay
Authors: Merian Kuipers1, Dennis Ninaber1, Annelies Slats1, Pieter Hiemstra1
1Leiden University Medical Centre (LUMC), Pulmonology, Leiden, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) is a serious side-effect of radiotherapy for lung cancer. We hypothe that radiation-induced effects on the normal lung epithelium play a key role in development of RILI. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to study the effect of ionizing radiation (IR) on cultured primary bronchial epithelial cells (PBEC).
Material and Methods
PBEC were cultured submerged/undifferentiated (S-PBEC), at the Air-Liquid-Interface (ALI-PBEC) to allow mucociliairy differentiation, and as 3-dimensional organoids (3D-PBEC). Cells cultured according to these three methods were exposed to ionizing radiation (IR; 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8 Gray (Gy) ), dissociated and reseeded in an organoid model in similar densities 1h, 24h, 7 days and 14 days after IR to observe organoid formation. In addition, in the ALI-PBEC model, a qPCR was performed at 3h, 6h, 24h and 48h after IR, as well as ELISA on conditioned media after 72h after IR, to assess effects of IR. Immunofluorescent staining of γH2Ax-foci was performed to asses DNA-damage of these cells.
Results
IR had a marked effect on organoid formation: organoid formation was severely impaired following IR irrespective of culture model in which cells were exposed to IR and at all time points after IR. The effect was strongest with IR-exposed ALI-PBEC, with already a 50% reduction in organoid formation after 0.25 Gy and hardly any organoid formation with an 8 Gy dose (figure 1).

This effect lasted up to 14 days after radiation of ALI-PBEC (figure 2). In contrast, IR did not increase mRNA levels for markers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT; ZEB-1, SLUG, SNAIL, vimentin) or inflammation (IL-1β, IL-8, VEGF) in the ALI-PBEC model. There was also no upregulation of secreted proteins IL-6, IL-8 or fibronectin. Furthermore, there were no changes in morphology and barrier function (Trans Epithelial Electrical Resistance; TEER) following IR, indicating that it did not cause cytotoxicity. IR did cause double stranded DNA breaks, increasing with radiation dose as measured by immunofluorescent staining of γH2Ax-foci.
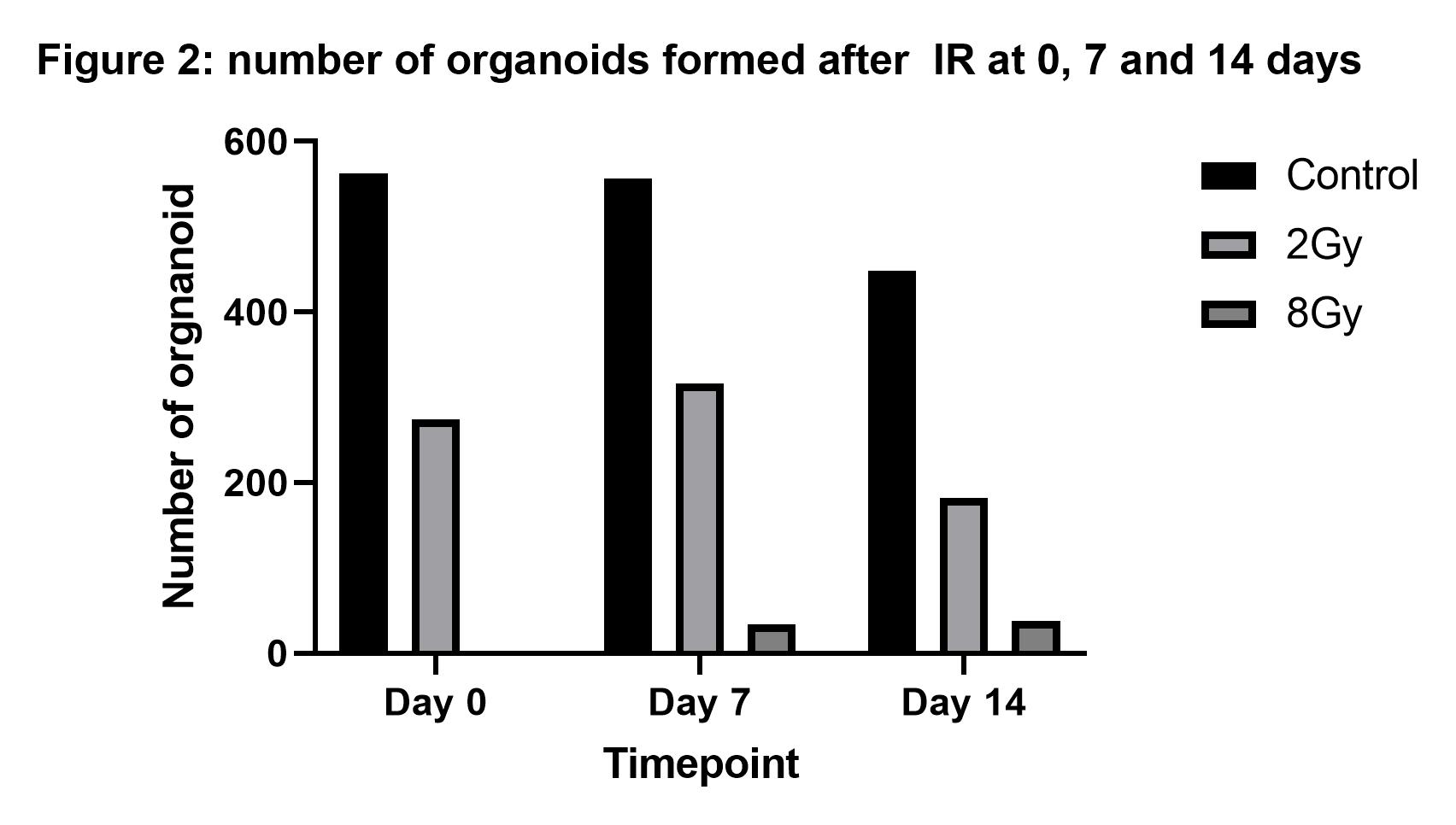
Conclusion
In conclusion, epithelial progenitor cell function as assessed by organoid formation capacity is strongly reduced by IR and persists for at least 14 days. This effect is not accompanied by IR-induced cytotoxicity, release of pro-inflammatory mediators or EMT. This effect on progenitor cell function could be a lead to further delineate RILI.