T-score evaluation as prognostic factor in locally advanced cervical cancer
Sofia Cordoba Largo,
Spain
PO-2160
Abstract
T-score evaluation as prognostic factor in locally advanced cervical cancer
Authors: Sofia Santana Jimenez1, Sofía Córdoba Largo1, Beatriz Gil Haro1, Jesús Romero Fernández1, Cristina De La Fuente Alonso1, Joaquín Velasco Jiménez1, Álvaro Perales Molina2, Patricia Sarrión Rubio de La Torre1, Uriel Alexander Corro Verde3, Raquel Benlloch Rodríguez1, Marta López Valcárcel1, María Hernández Miguel1
1Puerta de Hierro Majadahonda University Hospital, Radiation Oncology, Madrid, Spain; 2Puerta de Hierro Majadahonda University Hospital, Medical Physics, Madrid, Spain; 3Marqués de Valdecilla University Hospital, Radiation Oncology, Santander, Spain
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Current FIGO and TMN staging in cervical cancer allow adequate staging but do not provide sufficient prognostic information. Findings based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of patients with locally advanced cervical cancer (LACC) may provide prognostic information. Purpose: To investigate the application of a simple but comprehensive tumor score (T-score) in LACC.
Purpose or objective: To investigate the application of a simple but comprehensive tumor score (T-score) in locally advanced cervical cancer (LACC).
Material and Methods
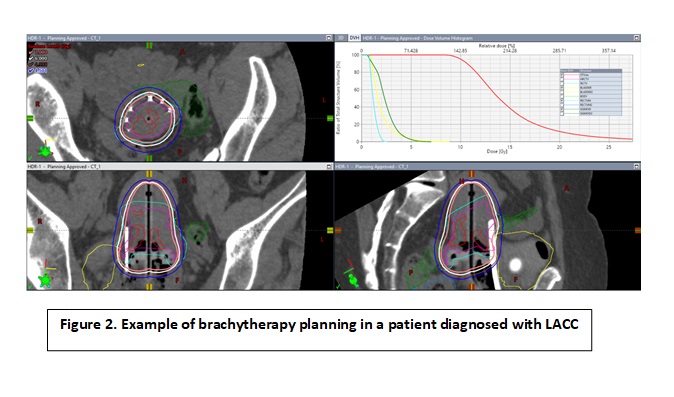
Twenty-six patients diagnosed of LACC treated between Dec 2019 and Feb 2022 with chemoradiotherapy and image-guided adaptive brachytherapy (IGABT),
were analyzed. FIGO stage: IB 11.5%, IIA 11.5%, IIB 11.5%, IIIA 3.8% and IIIC 61.6%. The involvement of 8 anatomical locations (cervix, left parametrium, right parametrium, vagina, bladder, ureter, rectum and uterine body) was scored according to an ordinal scale from 0 to 3 points. The total sum of points constituted the T-score. Statistics: T-test, chi-square, Kaplan-Meier and log-Rank test.
Results
Median follow-up: 8.5 months (1-28). Median volume HRCV: 32,9cc (12-51.3), median D90: 91,30Gy (80-94.90) and median T-score: 4 (2-9). T-score >4 correlated with larger IGABT target volume (HRCTV) (35cc vs 32cc for T-score ≤4; p= 0.053), and the use of interstitials needles (61% vs 15% for T-score ≤4; p=0.041). Two-y overall survival was 76%. There were a non-significant trend toward worse 2-y distant metastasis-free survival and pelvic relapse-free survival for T-score >4 (60% vs 75%, p=0.1; and 75% vs 100%, p=0.07, respectively)
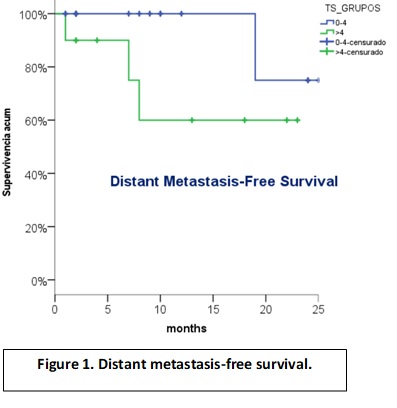
Conclusion
In this small single-center series T-score, has showed clinical utility as prognostic factor and can predict parameters for IGABT such as volume and interstitial needle application.