single application CT-based interstitial high-dose-rate brachytherapy for cervical cancer
PO-2153
Abstract
single application CT-based interstitial high-dose-rate brachytherapy for cervical cancer
Authors: Eugene Yap1, Warren Bacorro1, Teresa Sy Ortin1, Carl Jainar1, Mark Dumago1, Maureen Bojador1, Stellar Cabrera1, Luisa Jacomina1, Gil Gonzalez2, Jocelyn Mariano2, Linda Antonio1, Aida Bautista3, Janell Genson4
1University of Santo Tomas Hospital, Radiation Oncology, Manila, Philippines; 2University of Santo Tomas Hospital, Gynecologic Oncology, Manila, Philippines; 3Manila Doctors Hospital , Gynecologic Oncology, Manila, Philippines; 4Manila Doctors Hospital , Radiation Oncology , Manila, Philippines
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Current literature on single application multifractionated brachytherapy(BRT) is limited. The use of MRI, which provides better soft-tissue delineation, allows more hypofractionated treatment, with a recent study showing acceptable results using three fractions. However, with CT- based treatment, the most commonly used regimen consists of 5-6 fractions with concerns of toxicity if a more hypofractionated regimen was used. The aim of the study is to evaluate the safety and clinical outcomes of single application multifractionated CT-guided interstitial high-dose-rate(HDR) BRT given in four fractions in locally advanced cervical cancer.
Material and Methods
Patients with cervical cancer FIGO 2018 stage IIB-IVA that were treated definitively with external radiation (50Gy/25fractions) ± weekly cisplatin followed by single application multifractionated CT-guided interstitial HDR BRT were included. The protocol involves the use of four fractions of HDR BRT given in 3 consecutive days with 2 fractions given on the second day 6 hours apart with a total planning target of HRCTVD90 of >85Gy EQD2. Dosimetric data, clinical response, and toxicity records were reviewed.
Results
Twenty-three consecutive patients were included. Clinical stage distribution was as follows: IIB: 13.0% (3), IIIB: 26.1% (6), IIIC: 26.1% (6) and IVA: 34.78% (8). Median initial T score at diagnosis was 10 (range 7-15). All patients underwent Intracavitary + Interstitial BT with needles (median 11 ; range, 6-20). The mean ± standard deviation HRCTV volume was 67.88 ± 27.66 cm3 and HRCTV D90 dose was 83± 10.8Gy. The 2 cm3 to bladder, rectum, and sigmoid were 86.37 ± 7.5 Gy, 72.60 ± 6.0 Gy, and 68.18 ± 8.3 Gy, respectively. Mean overall treatment time was 65 ± 21 days. With a median follow up of 9.5 months (range, 1-39), The median survival was 16 months, and the one-year local control rate, progression free survival and overall survival were 73% (54-100, 95% CI), 60% (40-92, 95% CI), and 72% (52-100, 95% CI), respectively. For the acute toxicity, grade 3 radiation-related toxicity was observed in 4 patients: 1 hematologic, 1 diarrhea, and 2 infections. The most severe was one patient with grade 4 toxicity of sepsis. For the late toxicity, grade 3 toxicity was observed in 3 patients: 2 proctitis needing intervention and 1 genitourinary toxicity. There were 3 grade 4 genitourinary toxicity with one needing a nephrostomy tube, and two requiring dialysis.
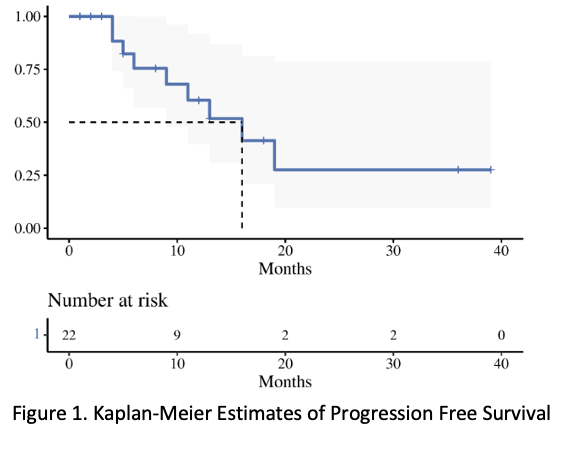
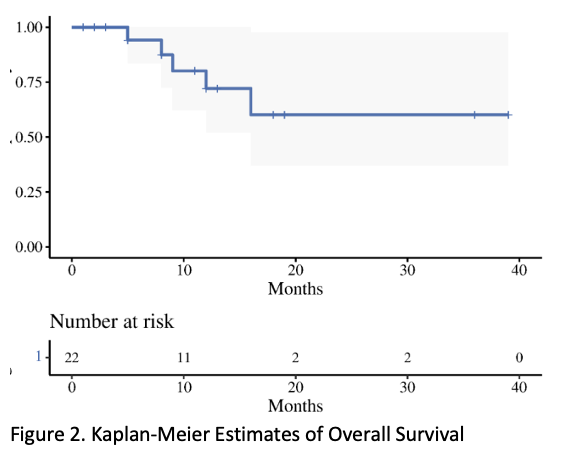
Conclusion
Single application multifractionated CT-Guided Interstitial HDR BRT given in four fractions in locally advanced cervical cancer is feasible and safe showing satisfactory response and acceptable toxicities.