Comparison of Varian Halcyon and Elekta Synergy for HA-WBRT+SIB in multiple brain metastases
PO-2010
Abstract
Comparison of Varian Halcyon and Elekta Synergy for HA-WBRT+SIB in multiple brain metastases
Authors: Johannes Kraft1, Stefan Weick1, Kathrin Breuer2, Paul Lutyj2, Klaus Bratengeier1, Florian Exner1, Anne Richter2, Jörg Tamihardja1, Dominik Lisowski1, Bülent Polat2, Michael Flentje3
1University Hospital Wuerzburg, Department of Radiation Oncology, Wuerzburg, Germany; 2University Hospital Wuerzburg, Department of Radiation Oncology , Wuerzburg, Germany; 3University Hospital Wuerzburg, Department of Radiation Oncology Wuerzburg, Wuerzburg, Germany
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Treatment plan comparison of hippocampal-avoidance whole brain radiotherapy with simultaneous integrated boost (HA-WBRT+SIB) for treatment of multiple brain metastases between an O-ring and a conventional C-arm linac regarding overall plan quality, dose distribution and adherence to a specified study protocol.
Material and Methods
12 treatment plans for irradiation of multiple brain metastases with HA-WBRT+SIB planned with Pinnacle at a C-arm Elekta Synergy Agility linac were replanned with Eclipse for treatment at an O-ring Varian Halcyon linac. Radiotherapy was applied with a 4-arc volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) and treatment planning was performed on both units according to the experimental arm of the HIPPORAD study protocol (30 Gy in 12 fractions to the whole brain, 51 Gy integrated boost for brain metastases and sparing of the bilateral hippocampal region). Dose-volume histogram metrics for target volume coverage and organ at risk sparing was performed and evaluated regarding their compliance with the study protocol requirements. Additionally, gradient index, homogeneity index and conformity index were calculated.
Results
12 patients with a median age of 58.5 (36 to 88) years and a median number of 9 (6 to 17) metastases were included in this analysis. The most common entity was NSCLC (n=6), followed by breast cancer (n=3). For both linacs the required specifications of the HIPPORAD study protocol were fully met for the target volumes (PTVwholebrain and PTVmetastases). There were only minor statistical differences within the achieved planning goals for both linacs, including better performance of meeting the required 30 Gy in PTV wholebrain for the Halcyon-Eclipse plans compared to the Synergy-Pinnacle plans (Dmean: Halcyon 30.27 vs Synergy 31.43 Gy, p < 0.001). However, violations of the study protocol demands were observed for some organs at risk constraints. In total, we observed 8 major deviations and 3 minor deviations for the Halcyon treatment plans and 8 major and 5 minor deviations for the Synergy plans. For the conformity index (CI), homogeneity index (HI) and the gradient index (GI), Synergy-Pinnacle plans were slightly in favour, except for the CI for PTVmetastases, where Halcyon-Eclipse plans were superior.
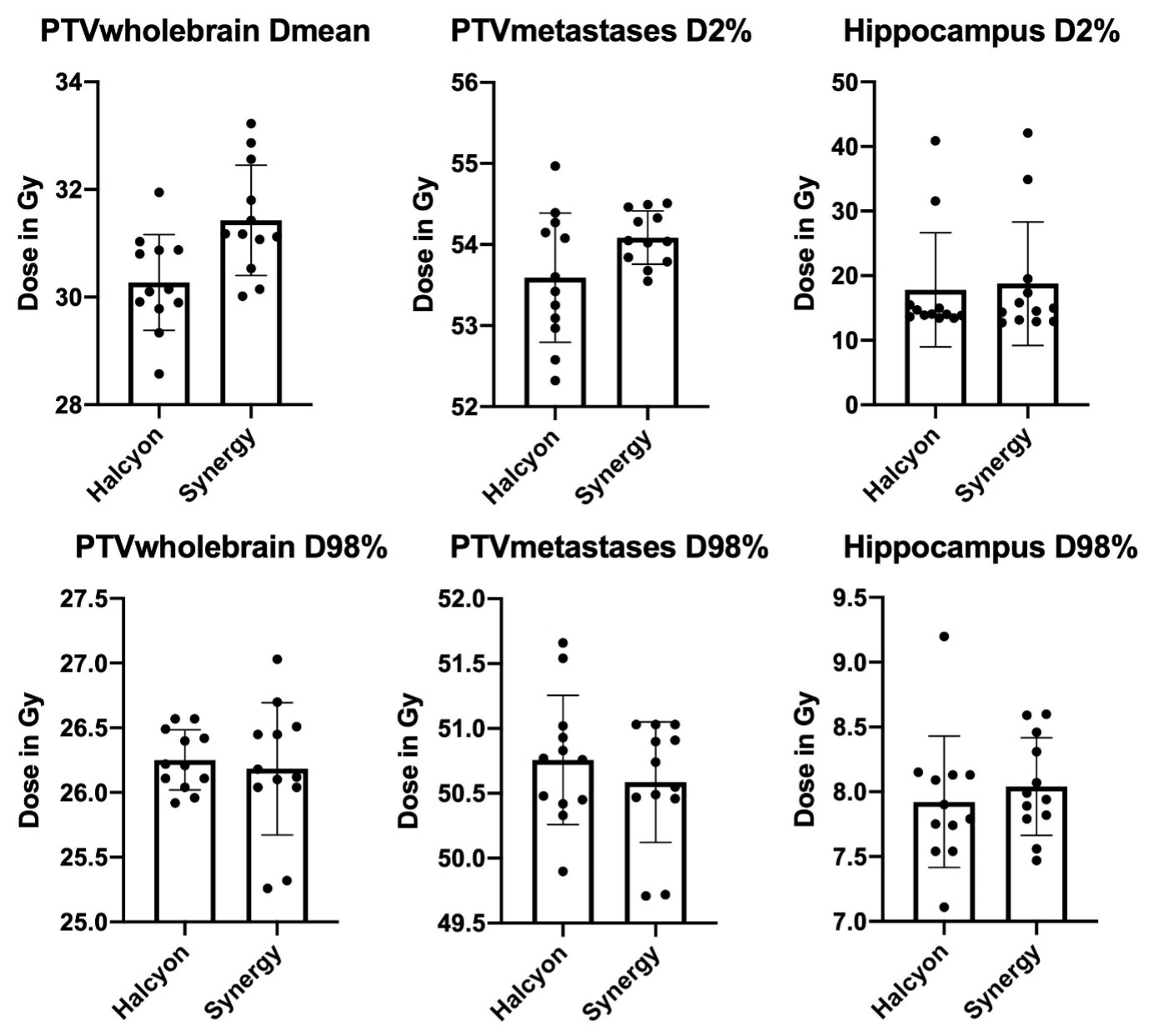
Box plots showing dose-values of target structures (PTVwholebrain, PTVmetastases) and Hippocampus
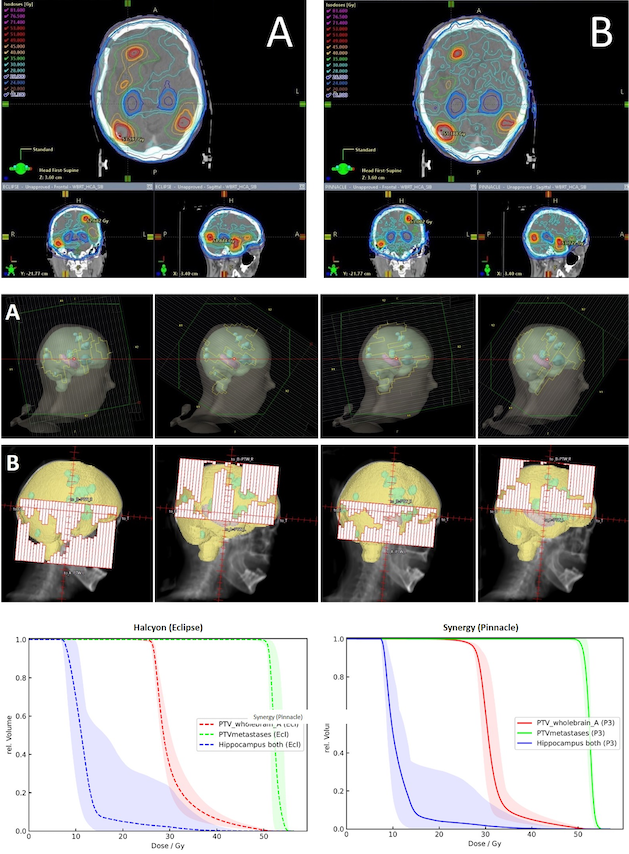
Typical dose distribution, beams eye view of treatment fields and average dose volume histogram (A = Halcyon-Eclipse, B = Synergy-Pinnacle)
Conclusion
Based on the planning requirements of the HIPPORAD study protocol, whole-brain irradiation with hippocampal avoidance and simultaneous integrated boost is feasible with comparable plan quality on the Varian Halcyon compared to treatment plans of a standard C-arm Elekta Synergy Agility linac.