Improvement in plan quality after Clinical Goals implementation in a large network of cancer centers
PO-2067
Abstract
Improvement in plan quality after Clinical Goals implementation in a large network of cancer centers
Authors: Hefei Liu1, Praveen Nuksani2, Malolan Rajagopalan3, Mangesh Patil4, Krishna Komanduri2, Brent Murphy2, Deepak Khuntia2, Sushil Beriwal2
1Medical College of Wisconsin, Department of Radiation Oncology, Milwaukee, USA; 2Varian Medical Systems, Medical Affairs, Palo Alto, USA; 3Mount Carmel Health System, Department of Radiation Oncology, Columbus, USA; 4American Oncology Institute, Department of Radiation Oncology, Hyderabad, India
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Clinical Goals is a tool available in the Varian Eclipse planning system to objectively and visually evaluate the quality of treatment plans based upon user-defined dose-volume parameters. We defined a set of Clinical Goals for Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT) based on published data and guidelines and implemented this in a network of cancer centers in India. A dosimetric study was performed to compare brain SRS and breast IMRT plan quality before and after Clinical Goal implementation.
Material and Methods
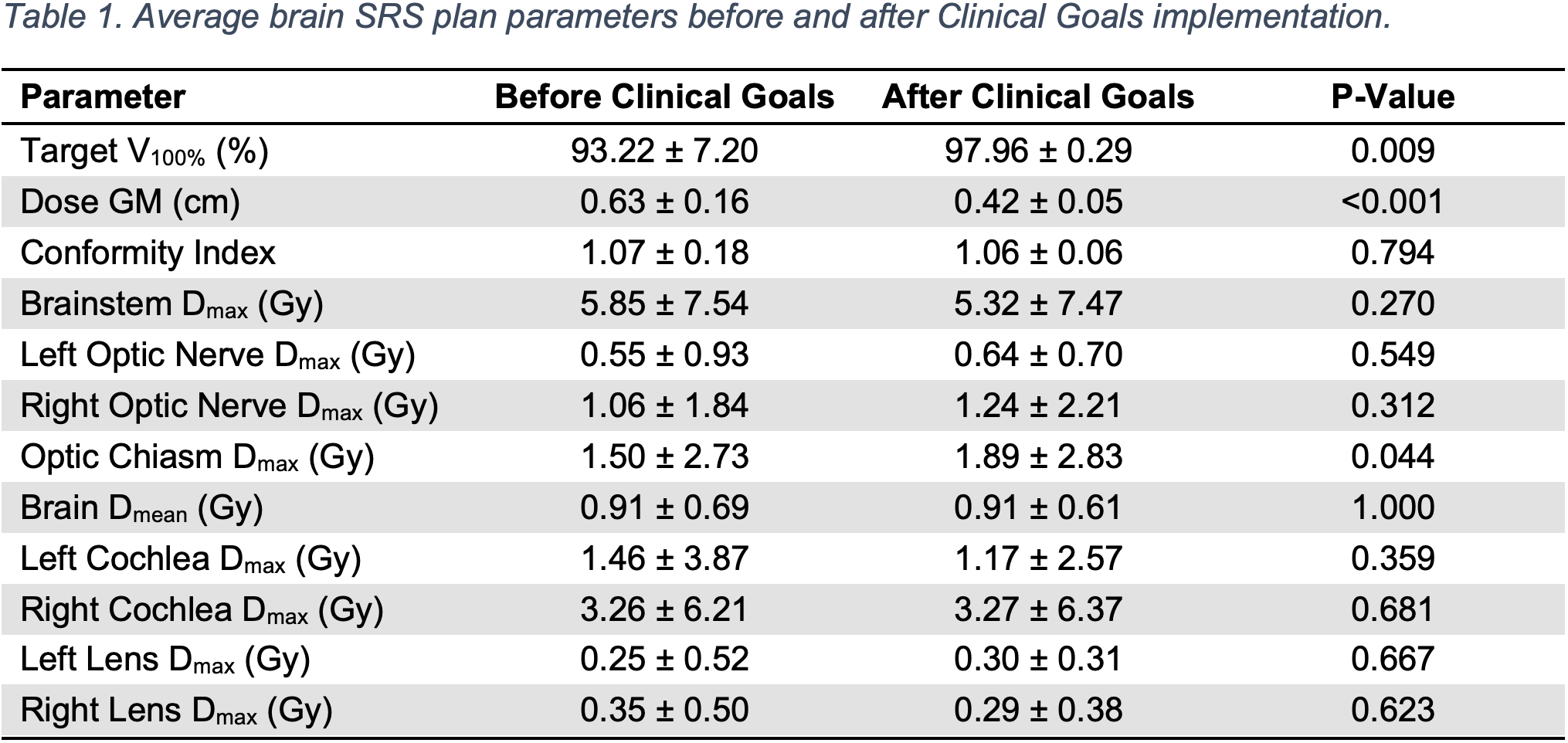
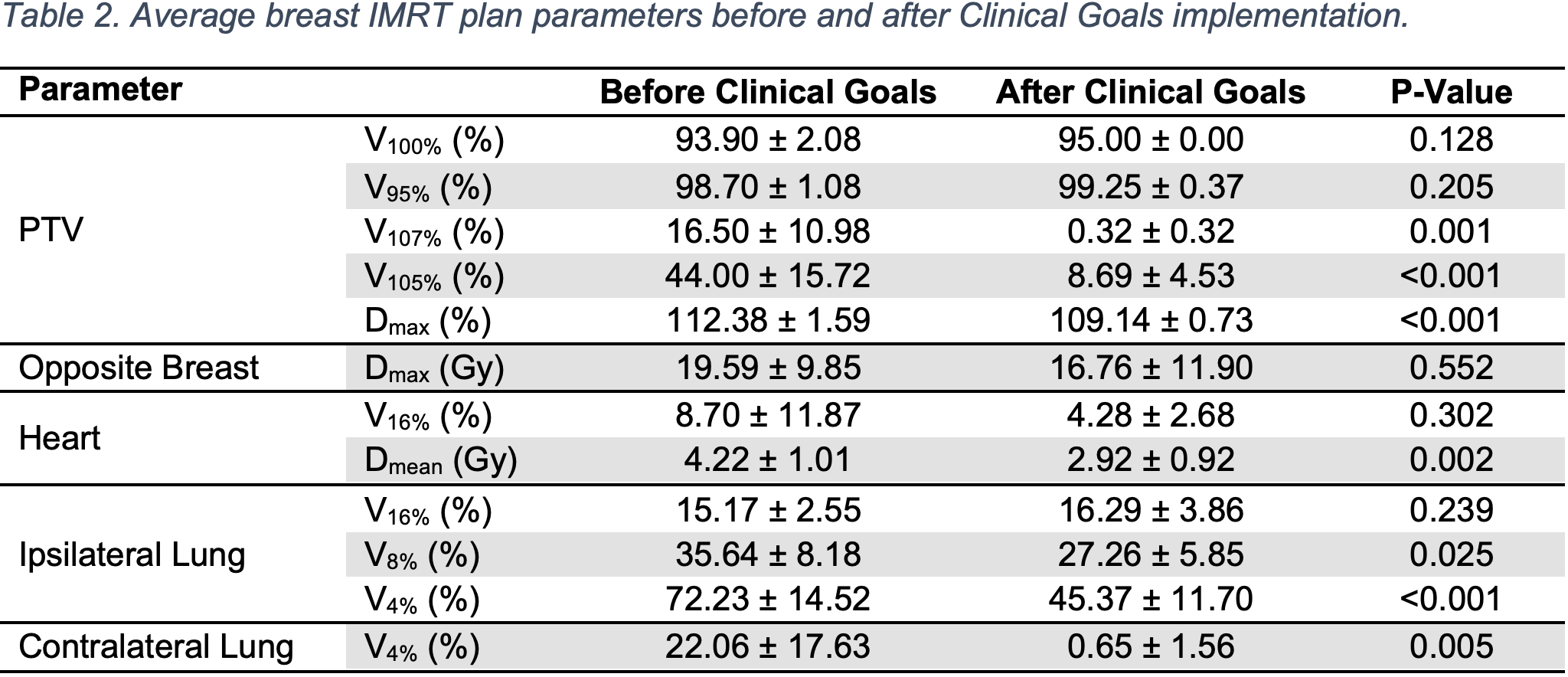
The Clinical Goals defined for SRS plans were target V100% ≥ 98%, dose gradient measure (GM) ≤ 0.5 cm, conformity index (CI) 1.0-1.2. For breast IMRT plans, Clinical Goals defined target V100% ≥ 97%, V95% ≥ 95%, V107% ≤ 2%, V105% ≤ 10%, and Dmax ≤ 2.4 Gy. Dose limits to organs-at-risk (OAR) were summarize in supplemental materials. Twenty brain SRS and ten breast IMRT treatment plans that were previously delivered on patients were selected and re-planned using Clinical Goals. The pre- and post-optimized plan parameters were compared using student t-tests.
Results
For brain SRS plans, the V100, GM, and CI for the pre- and post-Clinical-Goals plans were 93.22% ± 7.2% vs. 97.96% ± 0.28% (p=0.008), 0.63 ± 0.16 vs. 0.42 ± 0.05 (p<0.001) and 1.07 ± 0.18 vs. 1.06 ± 0.06 (p=0.79), respectively. There were no differences in max dose to OARs. In breast IMRT plans, the target V107% for pre- and post-implemented plans were 16.50 ± 10.98% vs. 0.32 ± 0.32%, respectively (p=0.001). The average target V105% were 44.00 ± 15.72% and 8.69 ± 4.53%, respectively (p<0.001). No differences were found in the average target V100% (p=0.128) and V95% (p=0.205). The average target Dmax were 112.28 ± 1.59% and 109.14 ± 0.73%, respectively (p<0.001). There were only minor differences in doses to OARs.
Conclusion
The implementation of Clinical Goals in Varian Eclipse significantly improved SRS and IMRT plan quality with enhanced coverage, dose GM, and CI without increased dose to OARs.