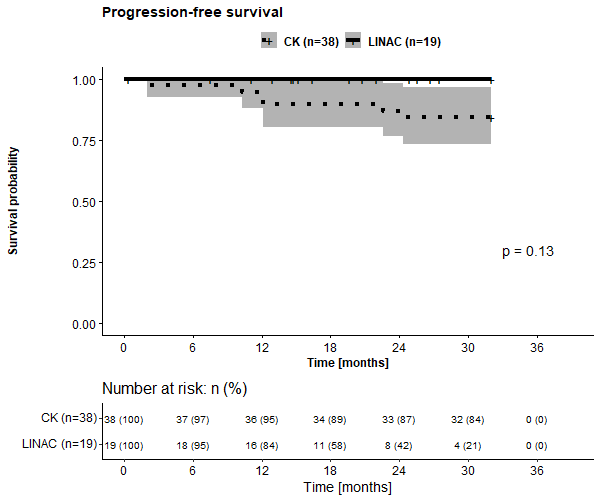
The evaluation of survival showed comparable outcome in LINAC and CK group in terms of overall survival (OS, p=0.15), local control (LC, p=0.62) & PFS (p=0.13). Two-year OS, LC & PFS was 100% vs 87%, 100% vs 100%, & 100% vs 87% for LINAC vs CK group, respectively.
Early gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity was comparable among the groups (G0 & G1 - 82% & 18% vs 68% & 26% for CK vs LINAC, respectively; p=0.22). Only 1 patient in LINAC arm had early GI G2 toxicity. Also, intermediate toxicity was comparable (p=0.44) - G0 & G1-84% & 8% vs 79% & 5% for CK vs LINAC, respectively. Two patients in LINAC arm had higher toxicity (G2 in 1 & G3 in 1 case). The difference between groups was statistically significant in terms of late GI toxicity–0 patients in CK arm, compared to 2 patients with G1 and 1 patient with G2 toxicity in LINAC group (p=0.02).
Early, intermediate and late genitourinary (GU) toxicity in both arms showed no statistical difference between the groups (p=0.19 for early, 0.23 for intermediate & 0.40 for late toxicity). Early GU G0, G1 & G2 was observed in 76%, 21% & 3% vs 63%, 21% & 16% for CK vs LINAC, respectively. Intermediate GU G0, G1 & G2 toxicity was-82%,10% & 0% vs 68%, 16% & 10% for CK vs LINAC, respectively. Late GU toxicity G1/G2 was observed in 2 patients in CK arm (2 cases of G1 toxicity) and in 2 cases in LINAC SBRT arm (1 G1 & 1 G2 toxicity).