The role of combined radiomics features as predictor of response to CRT or BRT in patients with OPC
PO-2111
Abstract
The role of combined radiomics features as predictor of response to CRT or BRT in patients with OPC
Authors: Haruo Inokuchi1, Nobutaka Mukumoto1, Naoki Mukumoto1, Mai Sakagami1, Mutsumi Yamagishi1, Nobunari Hamaura1, Hiroshige Itoyama1, Shogo Matsuda1, Keiko Shibuya1
1Osaka metropolitan university, Radiation oncology, Osaka, Japan
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Minimally invasive therapies have been developed for HPV-associated oropharyngeal carcinoma (OPC), but prognostic factors and optimal patient selection are not clear. We evaluate the prognostic value of radiomics combined features based on 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in patients with locally advanced OPC treated with chemo-radiotherapy (CRT) or bio-radiotherapy (BRT).
Material and Methods
Data of 82 patients with advanced OPC who underwent FDG PET and T2-weighted MRI before definitive CRT or BRT 08/2011 to 12/2019 were retrospectively analyzed. Patients had to meet the following eligibility criteria: histologically proven OPC; treated with definitive radiotherapy (RT) combined with concurrent chemotherapy or cetuximab; curative intent; use of IMRT or VMAT (photons) to a total dose of 70 Gy, respectively. Quantitative 428 PET and MR radiomics imaging characteristics were extracted from the primary and nodal tumor volumes, and multiple clinical variables included sex, age, tumor p16 status, tobacco were assessed. Pearson’s correlation was used to explore possible correlations among them. The radiomics score was constructed according to the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) method. Survival analysis (loco-regional control; LRC, disease-free survival; DFS, distant metastasis free survival; DMFS, and overall survival; OS) was performed using the log-rank test and Cox's proportional hazards regression model. We split the dataset into training and internal validation sets. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve with 5-fold cross validation were used to evaluate their prognostic performance.
Results
The median follow-up period of the training cohort was 41 months (range, 13-72 months). The multivariate survival analysis showed that age (<67) (p = 0.032), HPV positivity (p = 0.022), and the low radiomics score (p = 0.005) were correlated with LRC. In DFS and DMFS, radiomics feature scores were independent prognostic factors. (p < 0.05) In addition, age (p = 0.032) and radiomics feature score (p = 0.004) were predictive of survival in OS. The combined radiomics model based on the multivariate analysis showed the best predictive ability for DFS, with an AUC of 0.828 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.774-0.873] in the training cohort and 0.821 (95%CI: 0.689-0.897) in the validation cohort. As shown in Figure, when stratified by the cutoff value of the radiomics feature score, CRT was superior to BRT for locoregional control in the poor prognosis group. (p = 0.045)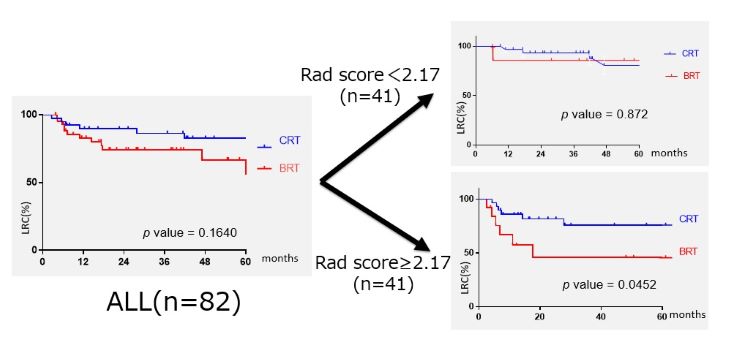
Conclusion
The combined radiomic models based on FDG PET and MR images were independent prognostic factor for DFS and DMFS in patients with OPC. The radiomics score-based nomogram could improve prognostic stratification ability and thus contribute to individualized therapy for HPV-associated OPC patients.