FIRST BRC AFTER RP: choline/PSMA-PET or mpMRI guided-SBRT on DETECTABLE PROSTATE BED RECURRENCE
Maria Giulia Vincini,
Italy
PO-1506
Abstract
FIRST BRC AFTER RP: choline/PSMA-PET or mpMRI guided-SBRT on DETECTABLE PROSTATE BED RECURRENCE
Authors: Riccardo Santamaria1,2, Lorenzo Colombi1,3, Giulia Corrao1, Mattia Zaffaroni1, Maria Giulia Vincini1, Dario Zerini1, Lorenzo Muraglia4, Sarah Alessi5, Giulia Marvaso1,3, Francesco Ceci4,3, Giuseppe Petralia5,3, Gennaro Musi6, Barbara Alicja Jereczek-Fossa1,3
1IEO, European Institute of Oncology IRCCS, Division of Radiation Oncology, Milan, Italy; 2University of Milan, Department of Oncology and Hemato-Oncology, Milan, Italy; 3University of Milan, Department of Oncology and Hemato-Oncology, Milan, Italy; 4IEO, European Institute of Oncology IRCCS, Division of Nuclear Medicine, Milan, Italy; 5IEO, European Institute of Oncology IRCCS, Division of Radiology, Milan, Italy; 6IEO, European Institute of Oncology IRCCS, Division of Urology, Milan, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Local recurrence on prostate bed occurred in about 30% of PCa patients after surgery. Diagnostic imaging has made significant advances in recent years, expanding and refining the diagnostic potential and enabling precise detection of disease recurrence. However, the most appropriate diagnostic approach and salvage radiotherapy for this clinical setting remains a matter of debate. Stereotactic RT (SBRT) treatments made it possible to target only the tissue affected by the recurrence, achieving excellent local control with an optimal safety profile.
The aim of the present study (Ethical Committee notification Nr 79) is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of our cohort of patients treated with SBRT on the detectable prostate bed recurrence.
Material and Methods
Patients who underwent SBRT to macroscopic bed recurrence were retrospectively considered. All patinets were treated based on multiparametric (mp) MRI or choline/PSMA PET. Continuous variables were summarized as mean/median and interquartile range/range, while categorical variables were presented with absolute and relative frequencies. Toxicities were collected according RTOG scale.
Results
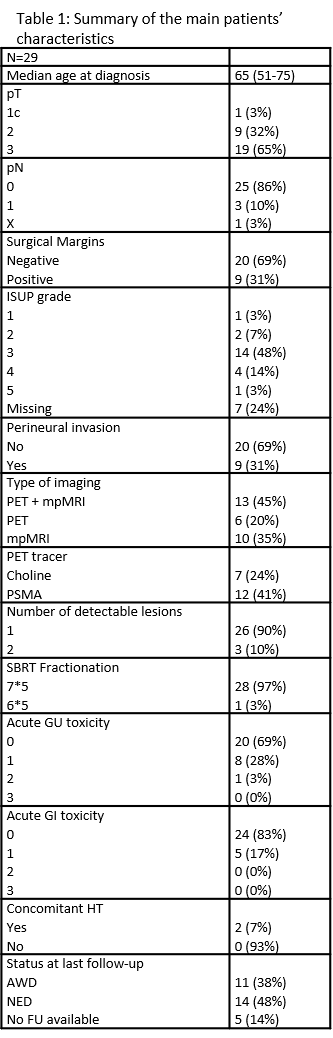
A total of consecutive 29 patients were included for the analysis. Among them 19 (65.5%) presented a T3 disease at surgery, 20 (69%). Nine (31%) and 20 (69%) had negative and positive surgical margins and the majority without perineural invasion (69%). Fourteen (48.3%) patients were diagnosed with a grade 3 ISUP. Median time to biochemical relapse was 47.9 months (3.4-157.2). Median PSA at restaging was 0.5 ng/ml (0.08-26.89). Thirteen patients (45%) were staged with both mpMRI and choline/PSMA PET, while 6 (20%) and 10 (35%) were treated based on PET or MRI only, respectively. All patients underwent SBRT on prostate in 5 fx every other day with a dose/fx within 6 or 7 Gy. Only 2 (7%) patients underwent concomitant hormonal therapy.
After a median follow-up of 11.8 months (6.8-53.9), 10 (35%) patients experienced a biochemical relapse. Among them, 8 (27.5) developed a clincal recurrence (4 local recurrences and 4 oligorelapses). At last censored follow-up, 11 (38%) patients are alive with disease while 14 (48.3%) are alive with no evidence of disease.
Five (17%) G1 gastrointestinal (GI) acute toxicity were observed and 8 (27.5%) G2 genitourinary (GU) toxicities were reported. No G≥3 GU/GI acute toxicities were noted. One acute G2 toxicity occurred. All toxicities were solved at last follow up.
Conclusion
Targeting macroscopic bed recurrence with SBRT results to be a safe and efficacy treatment. Further analysis, additional data and longer follow-up will provide a clearer indication on the right way to treat these patients and on the more appropriate staging methodology for this cohort of patients.