Inter-observer variation in GTV delineation of esophageal cancer on MR, CT and PET CT
Ajra Secerov Ermenc,
Slovenia
PO-1366
Abstract
Inter-observer variation in GTV delineation of esophageal cancer on MR, CT and PET CT
Authors: Ajra Secerov Ermenc1,2, Primoz Peterlin1, Franc Anderluh1, Ana Jeromen Peressutti1, Jasna But Hadzic1, Vaneja Velenik1, Barbara Segedin1,2
1Institute of Oncology, Division of Radiotherapy, Ljubljana, Slovenia; 2University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
In the present study we investigated inter-observer variation in gross tumor volume (GTV) delineation of esophageal cancer on different imaging modalities – CT, PET CT and MR.
Material and Methods
Twenty-three consecutive patients with esophageal cancer treated with preoperative or curative chemoradiotherapy were selected. All patients had CT, PET CT and MR imaging in treatment position prior to radiotherapy. Five experienced observers from our institution independently delineated GTV for the first thirteen patients on CT alone, PET CT, MR alone and with co-registered PET CT and MR (figure 1). Inter-observer agreement, expressed in generalized conformity index (CIgen) and mean volumes of GTV were calculated per patient and imaging modality.
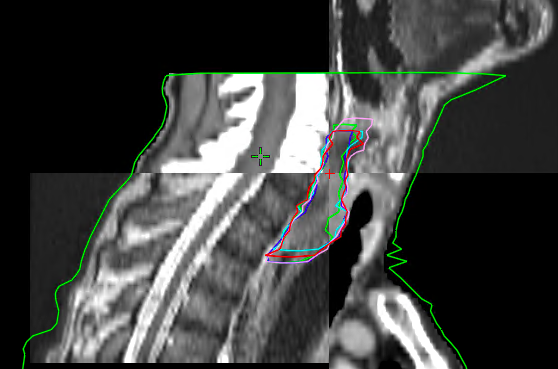
Figure 1. Delineations of five observers on sagital CT with co-registered MR sequences.
Results
In the preliminary analysis we included the first thirteen patients, seven had the tumor in the proximal third of the esophagus, one in the middle and five in the distal third. The analysis showed the smallest mean GTV volume when contoured on MR alone (39.2cm3) and the largest on PET CT alone (54.9 cm3). We observed the best agreement when contouring on all three imaging modalities (CIgen 0.69), the worst agreement on CT and MR alone, CIgen 0.61 for both (table 1).
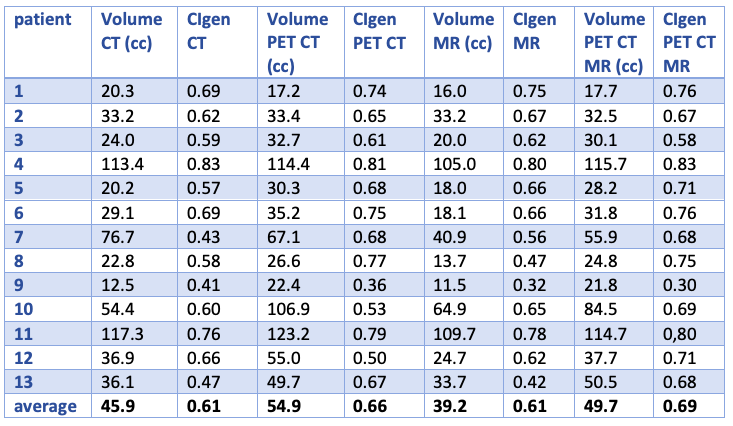
Table 1. Volume of GTV and CIgen per case and modality.
The addition of MR to PET CT reduced inter-observer variation more in patients with tumors of the distal third (CIgen 0.59) in comparison to PET CT alone (CIgen 0.54), than in patients with tumors of the proximal or middle third with CIgen 0.75 on all three imaging modalities and CIgen 0.73 on PET CT alone.
Conclusion
Our preliminary analysis showed the highest agreement in contouring the GTV in esophageal cancer on all three imaging modalities combined, but final results are awaited. The addition of MR to PET CT improved interobserver agreement in tumors of the distal third of esophagus compared to PET CT alone.