MR-Guided stereotactic radiotherapy for pancreatic oligometastases from renal cell carcinoma
Jonna van Vulpen,
The Netherlands
PO-1353
Abstract
MR-Guided stereotactic radiotherapy for pancreatic oligometastases from renal cell carcinoma
Authors: Jonna van Vulpen1, Hidde Eijkelenkamp1, Gert Meijer1, Martijn Intven1
1UMC Utrecht, Radiation Oncology, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Patients with pancreatic metastases from clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) have been reported to have an extraordinarily favourable prognosis. Traditionally, treatment for these pancreatic oligometastases comprises either surgical resection or systemic therapy. However, SBRT may be an effective, non-invasive alternative strategy, provided that it shows good local control rates and acceptable toxicity among treated patients.
Material and Methods
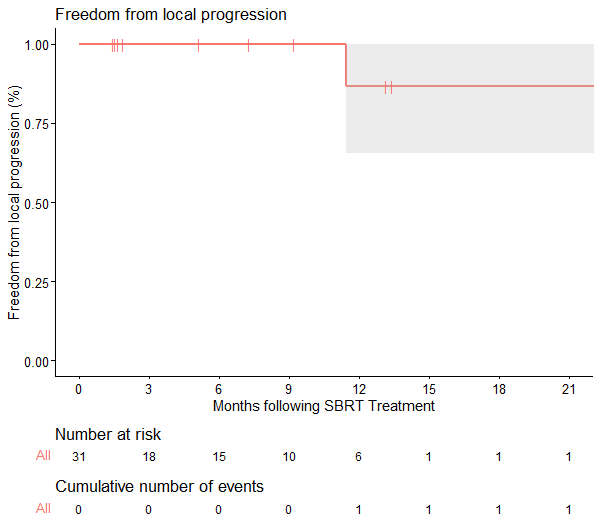
We reviewed all patients treated with MR-guided SBRT for pancreatic oligometastases from renal cell carcinoma at the University Medical Center Utrecht. We explored freedom from local progression (FFLP), progression-free survival (PFS), freedom from start of systemic therapy (FFST), and adverse events (AEs) among treated patients. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to describe the time-to-event endpoints, with estimates at 1 year calculated using logarithmic transformation of the survival function. FFLP was assessed per lesion, adding patient as a cluster effect.
Results
From June 2019 to September 2022, we identified 11 patients treated with MR-guided SBRT to 31 pancreatic oligometastases from RCC. Patients had a mean age of 65.6 years (±6.8) and had a median of 3 irradiated pancreatic metastases (range 1-7). Metastases were treated with 5 fractions of 7 Gy (n=1 metastasis) or 8 Gy (n=30 metastases) per fraction. At a current median follow-up of 9.5 months (range 1-42 months), estimated FFLP at 1 year was 87% (95% CI 66-100%). 1y-PFS was 83% (95% CI 58-100%), and 1y-FFST was 100%. No grade ≥3 AEs were observed.
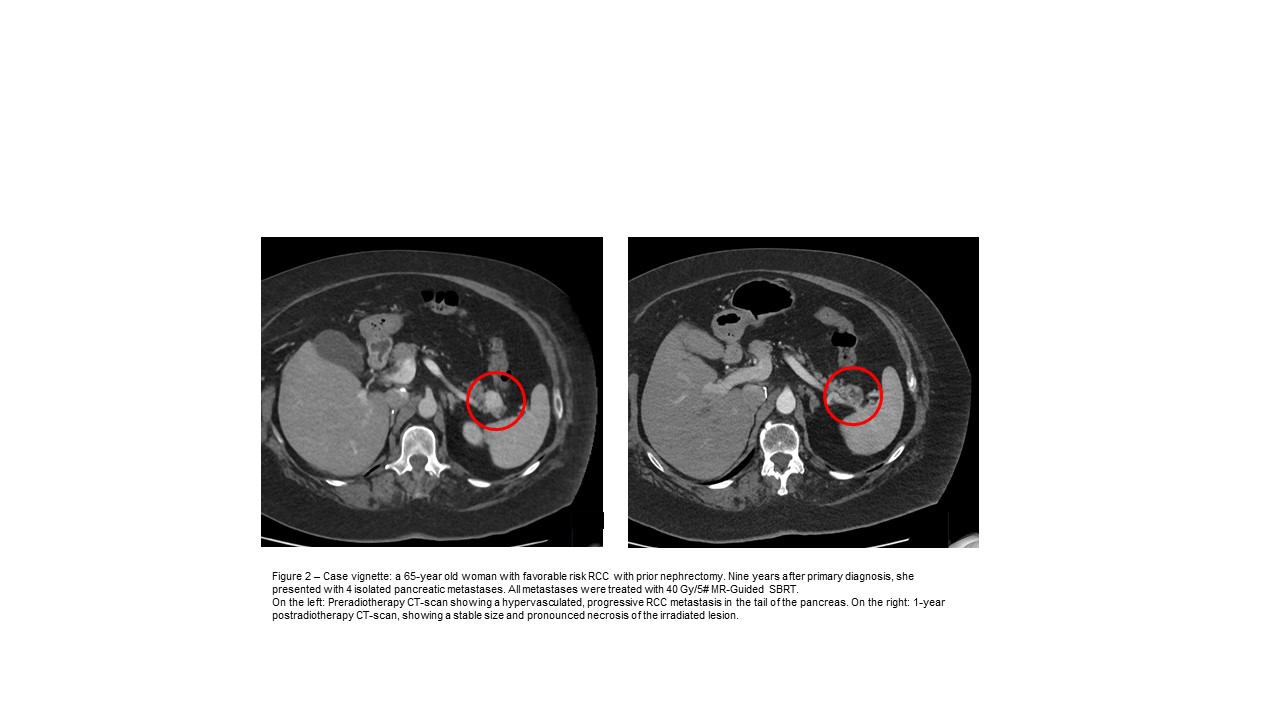
Conclusion
First exploration of MR-guided SBRT to pancreatic oligometastases of RCC indicates that it can be an effective and safe treatment option. Moreover, MR-guided SBRT may facilitate deferral of systemic therapy initiation in this select group of patients with favourable prognosis.