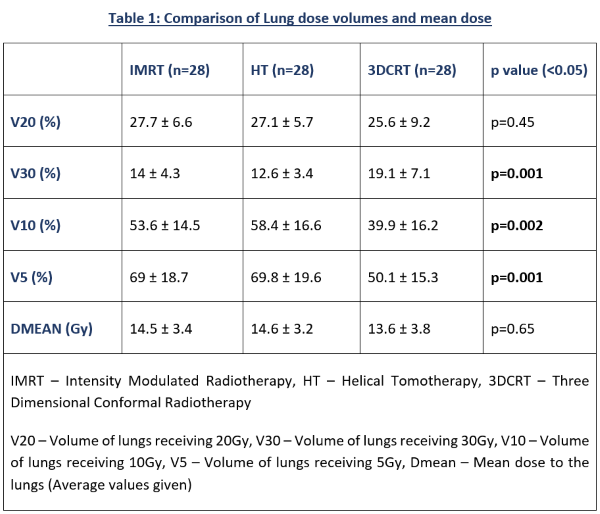
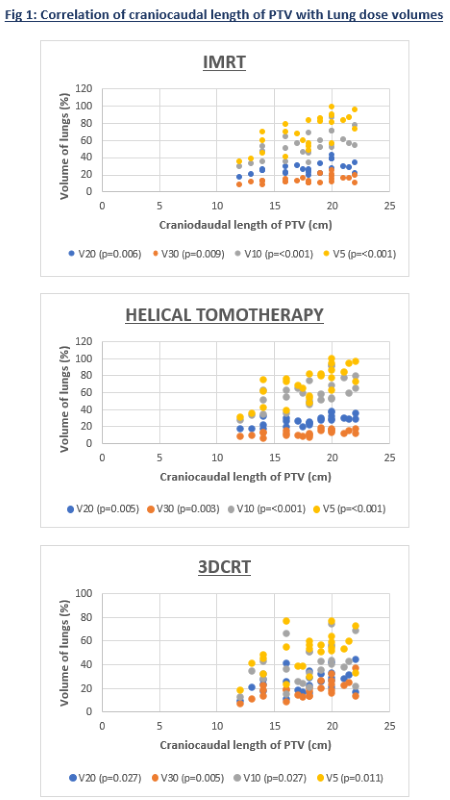
The Dmean and V20 lung volumes were similar between IMRT, HT and 3DCRT (Table 1). IMRT and HT had significantly lower V30 when compared to 3DCRT (14 ± 4.3, 12.6 ± 3.4, 19.1 ± 7.1 respectively; p=0.001), whereas V5 (69 ± 18.7, 69.8 ± 19.6, 50.1 ± 15.3 respectively; p=0.001) and V10 (53.6 ± 14.5, 58.4 ± 16.6, 39.9 ± 16.2 respectively; p=0.002) were significantly lower in 3DCRT. All lung dose volumes had significant moderately positive to strongly positive correlation with craniocaudal length of the PTV across the three different techniques (Figure 1). Volume of PTV had no significant correlation with lung dose volumes, whereas volume of GTV had moderately positive correlation with V20 of IMRT (Correlation Coefficient Factor(R)=0.43; p=0.02). IMRT had significantly less low dose region in upper third esophageal tumors (GTV - Gross Tumor Volume) compared to mid and lower thoracic location in V5 (55.1 ± 15.7, 80.2 ± 14.8, 70.2 ± 12.3 respectively; p=0.016), V10 (44.3 ± 12.4, 60.4 ± 13.2, 57.3 ± 11.5 respectively; p=0.017), and Dmean (12.3 ± 3, 16.3 ± 3.3, 14.7 ± 1.1 respectively; p=0.015). HT also had lower V5 (55.5 ± 16.7, 81.3 ± 16.1, 71.8 ± 9.1 respectively; p=0.011), V10 (47.7 ± 12.7, 65.3 ± 17, 66.4 ± 7 respectively; p=0.042), and Dmean (12.5 ± 2.5, 16.5 ± 3.2, 16.3 ± 1 respectively, p=0.01) in upper third esophageal tumors.