We collected 104 responses from 78 institutions (57 public and 21 private). Of the 118 centers in Spain, 79% of the public institutions and 46% of the private ones answered this survey. From these 78 institutions, 54% perform breast treatments with DIBH, and 46% do not have this technique. The principal reasons for not adopting DIBH for breast treatments are no equipment available (50%), having the equipment but not implemented (44%), and other reasons in 6% of the cases.
The use of IMRT/VMAT for left or right breast treatment planning varies widely among centers (with or without DIBH): 42% of the centers perform IMRT/VMAT in more than 75% of the cases, and 32% of the centers in less than 10%.
Figure 1 summarizes DIBH equipment, treatment planning technique, and treatment time for those centers that perform DIBH.
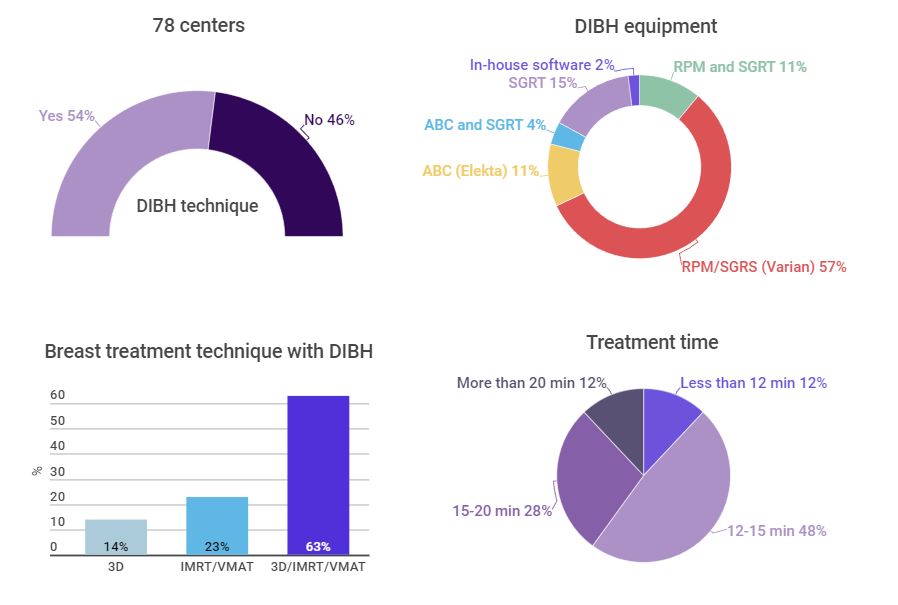
Figure 1. Questions grouped by center
Most centers performed one training session (66%), 17% none, and 17% between 2-3 sessions. The main reason for not treating all left breasts with DIBH was patient-related factors (42%), followed by lack of equipment/resources/time (29%), and not considering it necessary (29%). The following questions (Figure 2) regarding complexity were analyzed individually (only those with DIBH in their centers).
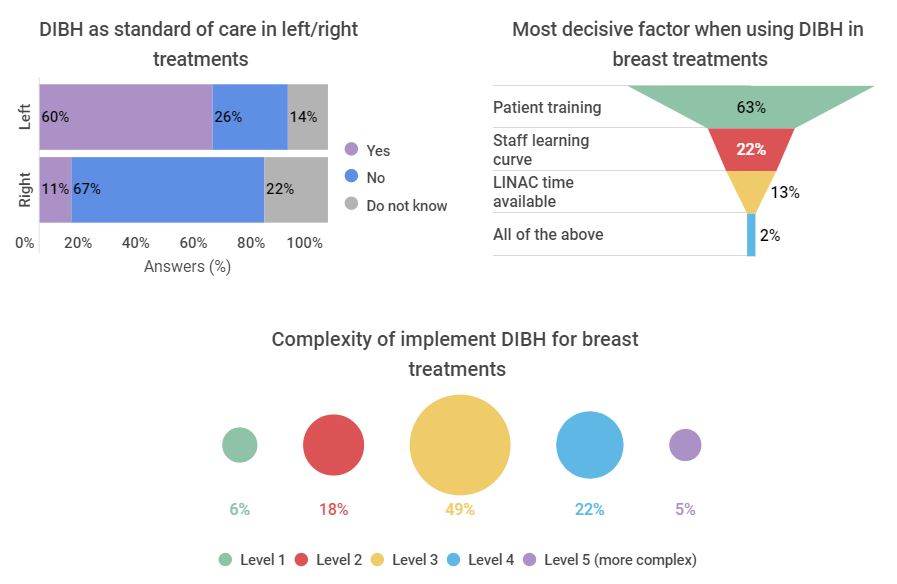
Figure 2. Using and implementing DIBH
For left-breast treatments, 60% of the surveyed would use DIBH as a standard of care, but only 11% would use it routinely for right-breast treatments. Patient training is the most decisive factor when using DIBH, and most respondents consider a level 3 of complexity when implementing DIBH.