Toxicity analysis of breast cancer patients treated with VMAT and 3D-CRT
PO-1255
Abstract
Toxicity analysis of breast cancer patients treated with VMAT and 3D-CRT
Authors: Jan Seppälä1, Kalle Vuorinen2, Nea Miettinen3, Janne Heikkilä1, Maria Tengström1
1Kuopio University Hospital, Cancer Centre, Kuopio, Finland; 2University of Eastern Finland, Faculty of Health Sciences, Kuopio, Finland; 3University of Eastern Finland, Department of Applied Physics, Kuopio, Finland
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
The purpose of this study was to report the clinical outcomes and toxicity after VMAT and 3D-CRT delivery techniques as adjuvant treatment after breast-conserving surgery.
Material and Methods
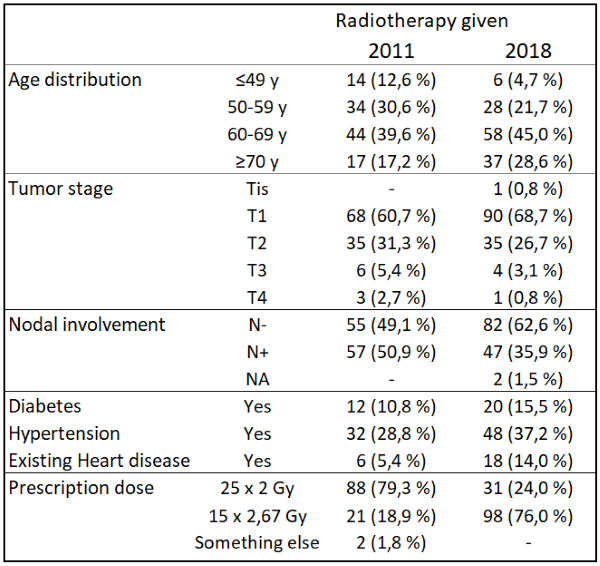
We retrospectively analyzed 239 left or right sided breast cancer patient divided in two cohorts: patients treated in 2011 with 3D-CRT technique (n=111) and patients treated in 2018 with VMAT technique (n=128) [1]. In addition, in 2018 most (82%) of the left sided patients were treated in DIBH. The patient characteristics are presented in Table 1. Of the 2011 group 79.3% were treated with conventional fractionation (25x2Gy ad 50Gy) and the rest with hypofractionation (15x2.67Gy ad 40.05Gy) as in the 2018 group 24% were treated with conventional fractionation and 76% with hypofractionation. Besides the whole breast, also the axillary lymph node area was treated in 39% and 28% of the 2011 and 2018 patients, respectively. Clinical information, such as patients' skin toxicity, lymphedema, and cardiac toxicity, was collected from the patient medical records and acute and late (≥ 6 months) toxicity and cosmetic data were analyzed. All the cardiac complications were recorded in 2021, thus the 2011 patient group had longer follow-up than the 2018 group. The severities of all the symptoms were assessed based on the record of the attending physician.
Table 1: Characteristics of the patients treated in 2011 and 2018.
Results
Of the patients treated in 2011 95.5% had some acute toxicity, redness of the skin being the most common (85%) as of the patients treated in 2018 the corresponding figures were 82.9% and 75%. Dermatitis was observed in 21.6% and 6.2% for the patient groups of 2011 and 2018 and symptoms of hypoesthesia were recorded for 14.4% and 21.7% of the 2011 and 2018 patient groups, respectively.
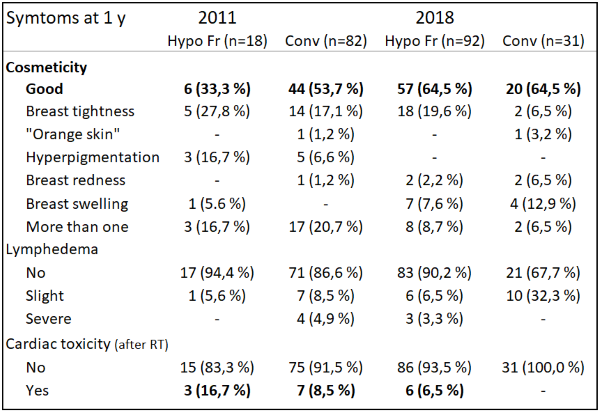
The recorded late complications are presented in Table 2. Overall, the late cosmetic outcomes were better with the patients treated with the VMAT technique in 2018. The recorded lymphedema between the groups of 2011 and 2018 were 12% and 15%, respectively. Locoregional relapse and/or distant metastasis was observed in 3.6% and 1.6% or 13.5% and 3.1% of the patients treated in 2011 and 2018, respectively.
Table 2: Recorded symptoms at one year after the start of RT of the patients treated in 2011 and 2018. The patient groups are sorted by RT fractionation (hypofractionation and conventional fractionation).
Conclusion
The patients treated in 2018 with the VMAT technique had less acute toxicities compared to the patients treated in 2011 with 3D-CRT. In addition, the late overall toxicity was lower, and the late cosmetic results were better in 2018 patient group treated with the VMAT technique than the 2011 patient group treated with 3D-CRT.
References:
[1] Virén T, Heikkilä J, Myllyoja K, Koskela K, Lahtinen T, Seppälä J. Tangential volumetric modulated arc therapy technique for left-sided breast cancer radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol. 2015 Apr 8;10:79.