Impact of COVID-19 pandemic to radiotherapy activities: a monoinstitutional evaluation
PO-1081
Abstract
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic to radiotherapy activities: a monoinstitutional evaluation
Authors: Cristina Mariucci1, Elena Galofaro1, Eleonora Arena1, Clelia Di Carlo1, Valeria Panni1, Mohamed Vincenzo Agbaje Olufemi1, Maika di Benedetto1, Lisa Vicenzi1, Maria Montisci1, Vittoria Emanuela Morabito2, Francesca Cucciarelli1, Francesco Fenu1, Marco Valenti2, Giovanna Mantello1
1Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria delle Marche, Radiotherapy Department, Ancona, Italy; 2Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria delle Marche, Medical Physics, Ancona, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
In the 2020, COVID-19 pandemic had an indirect impact on all hospital services, as well as oncology activities. This impact, particularly in the early months of 2020, posed a problem for radiation oncology departments because medical staff were often unprepared to face COVID -19 pandemic. The aim of this study was to evaluate the indirect impact of COVID-19 on all activities in our radiation oncology department.
Material and Methods
We retrospectively compared the development of clinical activities in the following periods: January-December 2019, January-December 2020, and January-December 2021. Data related to clinical visits (first evaluation, follow-up), planning CT and PET /CT, treatment planning, and radiotherapy sessions at our 4 LINACs were examined.
Results
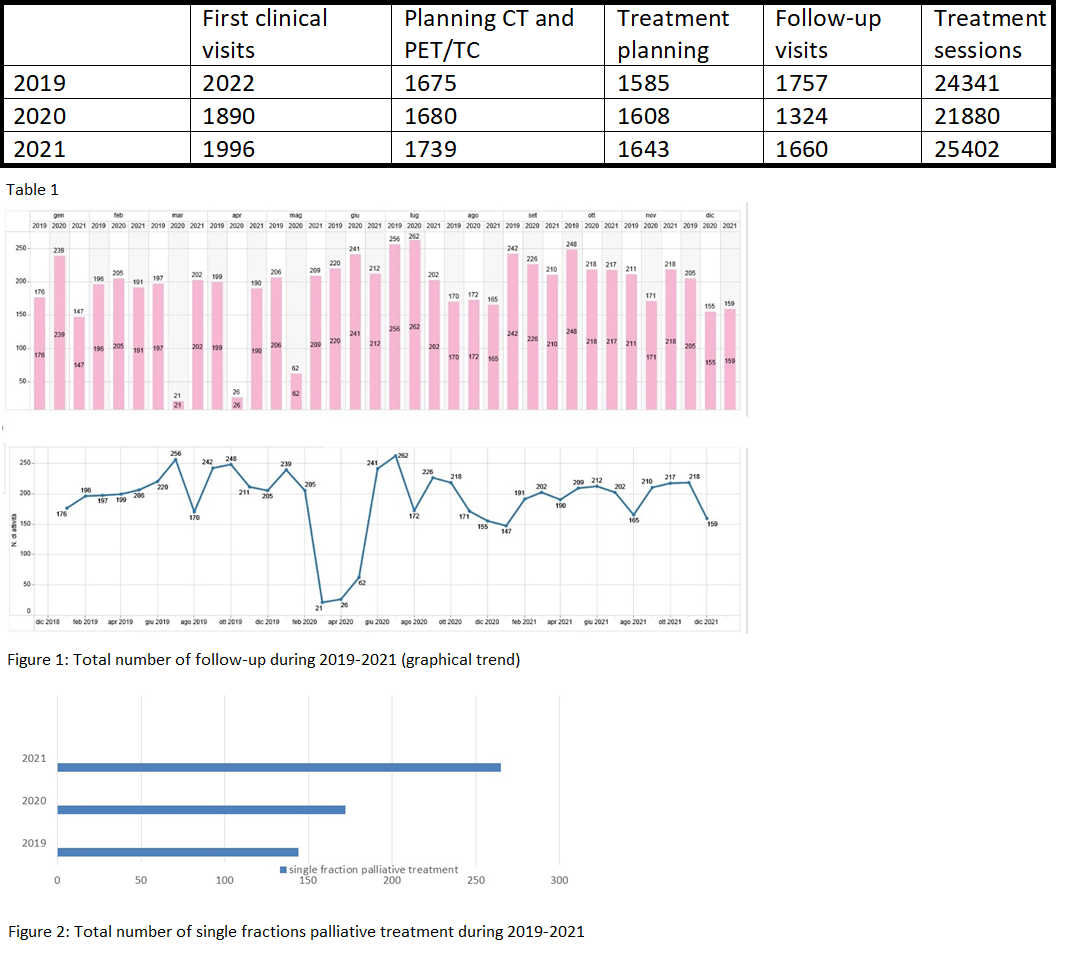
The results are shown in Table 1. In 2019 and 2020, the first clinical visits were 2022 and 1890, respectively, representing a 5.6% increase in 2021. Planning CT and PET/CT in 2020 was 1680, similar to 2019 (n=1675), whereas in 2021 we recorded 1739 CT and PET/CT. Treatment plans generated in 2020 were 1608 (compared with 1585 in 2019, +1.45%) and reached 1643 in 2021 (+2.2%). As shown in Figure 1, follow-up decreased rapidly in March and April 2020 (n=1324 in 2020 vs 1757 in 2019, -24.6%), while follow-up in 2021 was similar to pre-pandemic levels (1660, +25.4%). During COVID -19 first (March, April 2020) and second (October, November 2020) peak follow-up visits were conducted via tele-visits (n=628); no tele-visits were conducted in 2021. The total number of treatment sessions was 21880 in 2020 compared with 24341 in 2019 (-10.1%); in 2021, there was a 16.1% increase in treatment sessions (25402). Hypofractionated regimens were preferred to reduce patient treatment time (171 in 2020 versus 141 in 2019, with percentage variation + 21.3%), this trend was confirmed in 2021 for all pathologies, in particular palliative treatment with one fraction reached +54% (267, Figure 2).
Conclusion
In the last 3 years, the activity of our radiotherapy department has never stopped. Compared to 2019, our activity has decreased, especially in the first months of 2020. This decrease was mainly related to clinical visits of patients because people were afraid of spreading COVID -19. During 2021, all activities gradually increased, favouring the use of hypofractionated regimens for all pathologies.