Cost of breast cancer treatment: a longitudinal cohort study from tertiary cancer center.
tabassum wadasadawala,
India
PO-1092
Abstract
Cost of breast cancer treatment: a longitudinal cohort study from tertiary cancer center.
Authors: Tabassum Wadasadawala1, Sanjay Mohanty2, Soumendu Sen3, Pijush Kanti3, Rajiv Sarin1, Sudeep Gupta4, Vani Parmar5
1Tata Memorial Centre, Radiation Oncology, Mumbai, India; 2International Institute for population sciences, Department of Fertility Studies, Mumbai, India; 3International Institute for Population Sciences, Department of Fertility Studies, Mumbai, India; 4Tata Memorial Centre, Medical Oncology, Mumbai, India; 5Tata Memorial Centre, Surgical Oncology, Mumbai, India
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Report expenditure on cancer treatment incurred by breast cancer patients
Material and Methods
The study used longitudinal data of 492 breast cancer patients registered at our centre, during June 2019 and March 2022. The direct and indirect cost of treatment was captured from the time of registration till the end of treatment. All the visits of the patients were captured and relevant information on expenditure was collected. At the end of treatment, details regarding reimbursement was collected.
Results
Majority of the cohort comprised of pre/perimenopausal (56.3%), overweight/obese (55.9%) and multiparous (78%) women. The disease was left sided (54.2%) and of advanced stage (66.4%) with one-quarter of patients having prior history of medical ailment other than cancer. Cooking facility was available for 68.8% of the patients and 92.4% of patients stayed in paid or rented accommodation. Mean number of hospital visits were 50 (SD 15.8). The direct and indirect cost of treatment has been tabulated below. Patients in the service category had one third of the direct cost (both non-treatment as well as treatment) while almost half of the indirect cost compared to patients in the paying category. Mean number of days of wage loss was 68 days (SD 245. Mean amount of reimbursement was 64650 (SD 79788) and 160215 (SD 251090) for the service and paying category respectively.
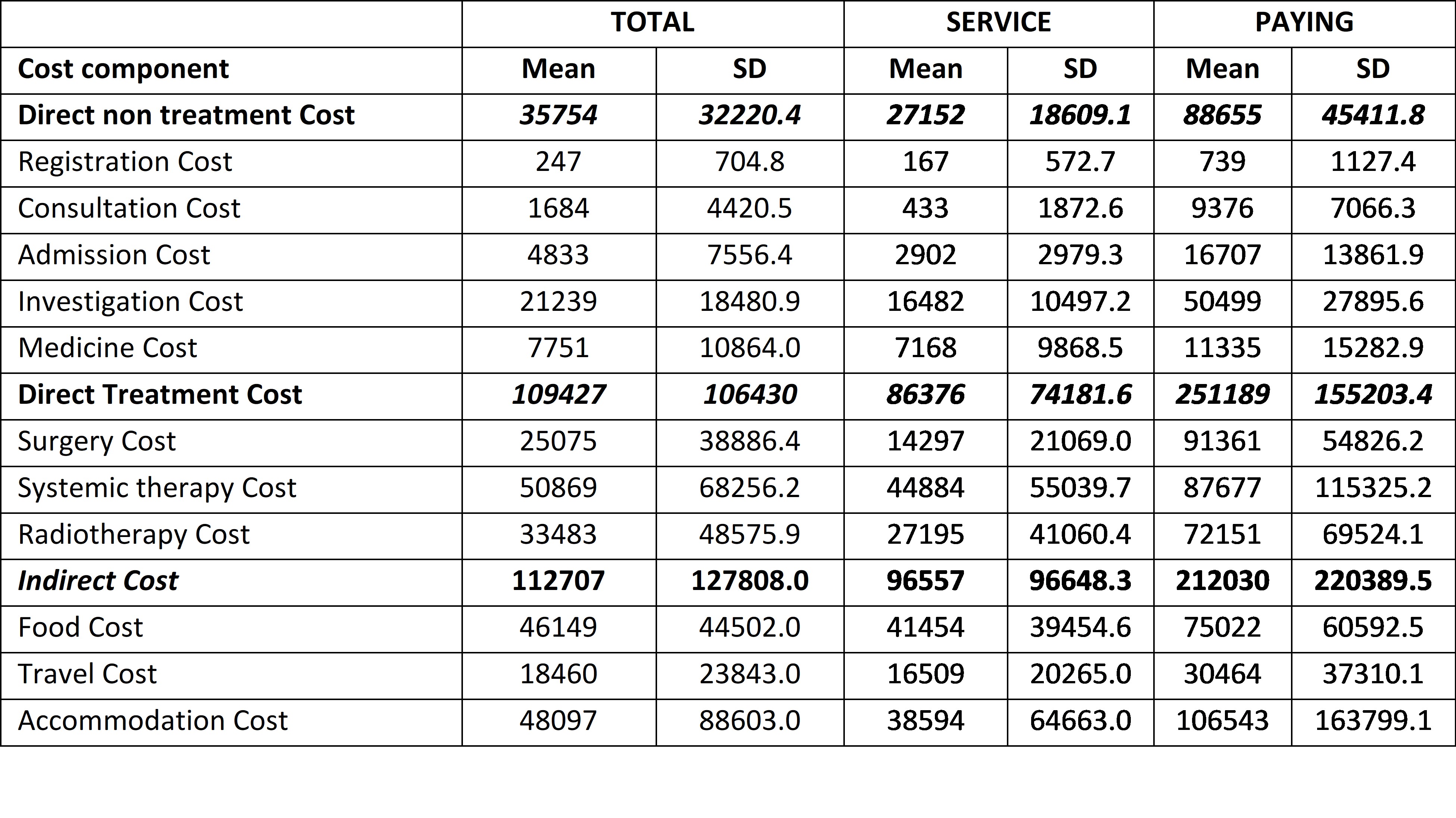
Conclusion
Investigations constitute the major driver of non-treatment direct cost. The least expensive to most expensive treatment modalities were surgery, radiotherapy and systemic therapy. Similarly for the indirect cost, accommodation and food form the most expensive components. The study highlights the need of taking measures to reduce the financial burden of cancer treatment.