TPS Scripting to automate the prostate treatment planning process: does it reduce plan quality?
PO-1900
Abstract
TPS Scripting to automate the prostate treatment planning process: does it reduce plan quality?
Authors: Stefan Hofer1, Martin Maffei2, Paolo Ferrari1, Justyna Waskiewicz3, Markus Haller4
1Südtiroler Sanitätsbetrieb, Dienst für medizinische Strahlenphysik, Bozen, Italy; 2Südtiroler Sanitätsbetrieb, Dienst für onkologische Strahlentherapie, Bozen, Italy; 3Südtiroler Sanitätsbetrieb, Dienst für onkologische Strahlentherapie , Bozen, Italy; 4Südtiroler Sanitätsbetrieb, Dienst für medizinische Strahlenphysik , Bozen, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
In the planning process of prostate
treatments there are a series of steps able to be done by an automatic TPS
scripting tool. The aim of this study is to test the feasibility to use TPS
scripts for prostate treatment planning and to evaluate the resulting plan quality compared
to the quality of manual planned treatments.
Material and Methods
The Raystation (v9.0,
Raysearch Laboratories) treatment planning system uses Iron Python as
scripting language. It was used to implement a planning process for prostate
treatments where several steps have been automized. The prostate plans with two
treatment phases where created with a first Vmat phase and a 3DCRT boost phase.
If the corresponding plan was not able to fulfil the clinical goals1 there was automatically
build a plan with a Vmat boost phase which should further reduce the dose to
the organs at risk. The sequence of the scripted process corresponds more or
less to the maual planning procedure in our institution. The following graph
shows the corresponding workflow:
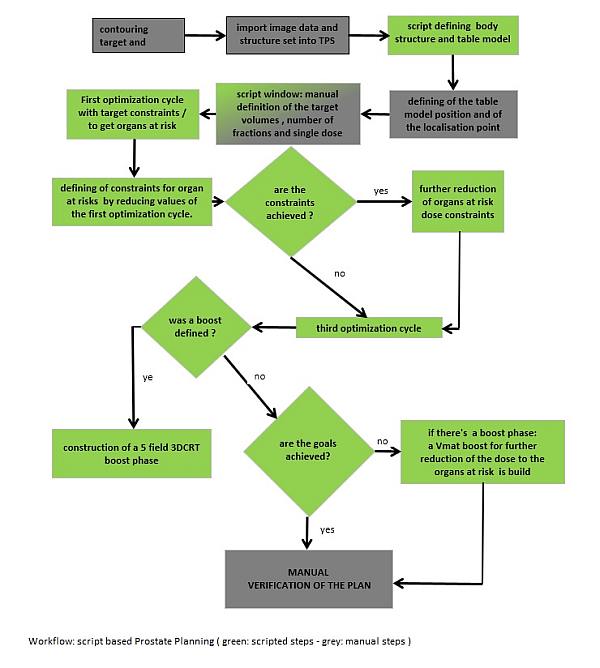
Twelve prostate treatments have been evaluated
retrospectively and the manual created treatment plan has been compared with the
plan created by the scripting tool.
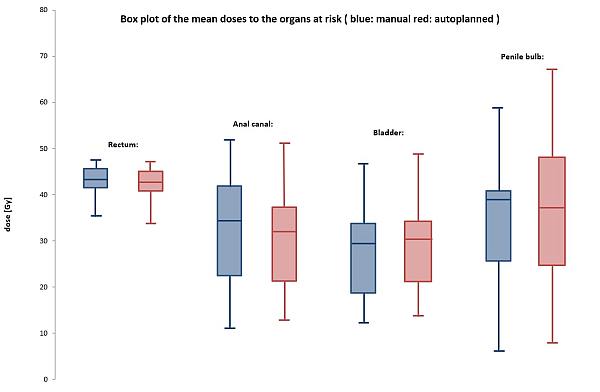
Results
The evaluation showed no significant difference (paired
bilateral T test - p < 0.05) in
target coverage and doses to organs at risk (rectum, bladder, anal canal, penile bulb). Also regarding
the modulation complexity2 there
was no statistical difference between the two plan categories.
Conclusion
The script
used for the automation of prostate planning in our institution is able to
reduce clinical workload and the created plans have similar quality and similar
characteristics as the manual created plans. If the created plan does not
fulfil the desired criteria it is possible to do manual modifications to the
plan at the end of the process.
1 SØREN M. B. et al. , QUANTITATIVE ANALYSES OF NORMAL
TISSUE EFFECTS IN THE CLINIC (QUANTEC): AN INTRODUCTION TO THE SCIENTIFIC
ISSUES, Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 76, No. 3 2010
2 Masi L. et al., Impact of plan parameters on the dosimetric accuracy of
volumetric modulated arc therapy, Med. Phys. 40(7) July 2013